With age, many people have problems with the knee joint . Some persons injure the joints when dropped. To identify the condition of the knee, a diagnosis is performed. Today, two types of examinations are used, CT and MRI.
To understand which of these procedures is better, you need to consider the features of each.
It is impossible to say unequivocally which type of diagnosis is better, CT or MRI. These surveys provide a variety of information. Therefore, in some cases, it is advisable to undergo both procedures to identify or exclude any disease.
If cancer pathology is suspected, it is better to choose magnetic resonance imaging. If there are problems with bone tissue, then CT should be preferred. If the body has metal objects (knitting needles, implants), electronic devices, then CT should be done.
CT
This is a radiographic type of study that allows you to get a layered image of the joint in different projections. It reveals any pathological changes in the joints, bones and cartilage at the first stage of their development.
The essence of the procedure is that a person lays on a special table. Then it is placed in the capsule of the tomograph. There the scanning begins. To obtain reliable results, the patient should remain motionless. While in the tomograph, the patient can communicate with the doctor through a microphone. The knee joint is examined for 1-5 minutes.
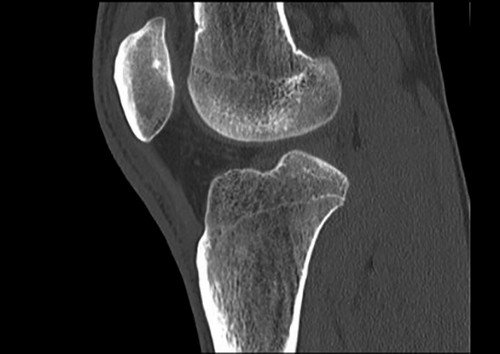
Doctors prescribe a CT scan for suspected diseases such as:
- Neoplasm.
- Arthritis of any type.
- Hematoma.
- Osteoarthrosis.
- Osteoporosis.
- Deposition of calcium and salts.
- Violation of ossification.
This type of diagnosis is carried out with severe injury to the knee.
The doctor may recommend a CT scan if the patient has these complaints:
- Crunch in the joint.
- Knee pain.
- Limitation of mobility.
- Abnormal articulation mobility.
Computed tomography shows the following changes:
- Cartilage thinning.
- Degenerative processes.
- Fractures (comminuted, with displacement).
- Cracks.
- Dislocations.
- Hematomas.
- Foreign bodies.
- Tumors
You must understand that CT is a non-harmless procedure. During the diagnosis, a person is exposed to radiation. Therefore, often computed tomography of the knee is not recommended. You can have a CT scan a maximum of 3 times a year. It is also worth considering the presence of contraindications to this procedure.
The survey is not carried out in such cases:
- The presence of mental problems.
- Pregnancy.
- Age to 14 years.
- The presence of a pacemaker.
- Claustrophobia.
- Obesity (over 200 kg).
- The period of feeding the baby with breast milk.
The procedure can be carried out with and without a contrast agent. The first option is used if it is necessary to identify or exclude vascular pathology.
MRI
It is a radiation diagnostic option. The basis of the survey is the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance. MRI allows you to change the contrast of the image. Due to this, abnormal structures (tumors) are detected. It can be done with and without contrast.
The essence of the procedure is that a person lays on a special table under the tomograph. To obtain reliable data, it is necessary to maintain immobility. An image of the knee joint is displayed on the monitor. The procedure lasts 20-25 minutes.
MRI is contraindicated for people with pins in their teeth, pacemakers, implants, tattoos, knitting needles, splinters. If a person has mental disorders and cannot remain motionless for a long time, then magnetic resonance imaging is not performed or the patient is given a sedative drug.
Doctors refer the patient to such an examination in the following cases:
- Impaired mobility.
- Pain of unclear etiology.
- Severe knee injury.
- Suspicion of rupture of ligaments, tendons, cancer.
Magnetic resonance imaging shows the following:
- Injury of the patella.
- Hernias.
- Necrotic and purulent processes.
- Arthritis.
- Osteoarthrosis.
- Neoplasms.
- Inflammation of the synovial bag.
- Hematomas.
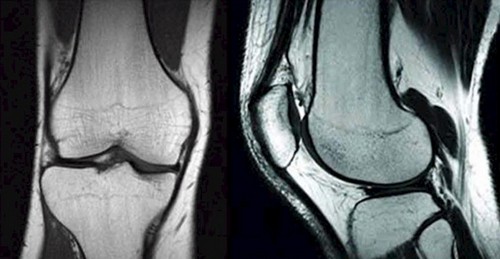
Comparison: Common Features
Considered types of diagnostics have such similar features:
- Show pathology of the knee joint.
- They are informative.
- They are prescribed for knee injury, suspected cancer, hematoma, osteoarthritis.
- They have a number of restrictions for use.
- Not completely safe.
- May be carried out using a contrast agent.
Comparison: Differences
The types of diagnostics considered have the following distinguishing features:
- They are based on various physical phenomena: MRI – on nuclear magnetic resonance, CT – on x-ray radiation, which is absorbed to different degrees by tissues of different densities.
- CT is more suitable for studying the structure of the joint, bone tissue, MRI – for studying the condition of soft tissues, ligaments and tendons.
- An MRI of the knee lasts longer than a CT scan.
- MRI can be performed on children, CT is prohibited until 14 years of age.
- MRI is allowed to be carried out often, CT – no more than 3 times a year.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is considered a harmless procedure.
- Computed tomography is cheaper.



