Adrenal hormones are part of humoral endocrine regulatory systems of the body. Their influence is so diverse that the deviation from normal levels leads to a pathological condition contributes to the manifestation of specific symptoms.
Moreover, the problem of how much and what kind of hormones produced adrenal glands, depends for many acute and chronic diseases.
The adrenal glands – small glands, closely adjacent to the tops of both kidneys. The mass of an adult is only 7-10 g. Protected by thick capsule. The cut is visible over a wide cortical layer and an inner brain.
Place of synthesis
The study of their functional values and the histological structure showed that a substance of adrenal glands, depending on the localization, are produced by the different hormones.
They differ in:
- biochemical structure;
- relations with other endocrine organs and nervous system;
- the source for the synthesis substances.
- effect on the body.
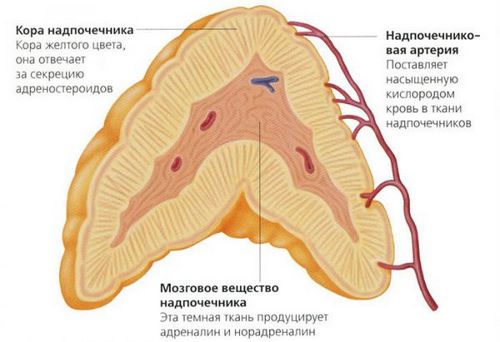
The adrenal cortex produces three major groups of hormonal compounds:
- mineralcorticoid,
- glucocorticoids,
- sex hormones – corticosteroids.
The medulla is responsible for the production of catecholamines. In the process of synthesis of the obtained intermediate substance having a lower activity, but necessary for use in case of an emergency, for example, with a lack of energy reserves, increased spending.
Studies in vitro (in artificial laboratory conditions) allow to study the structure of the parts that make up the hormones, but do not allow to judge about their effect on the body, because they can not fully simulate the human situation.

Hydrocortisone acetate is used as an external remedy in the form of ointment in ophthalmic practice, in diseases of the skin
Significant value is the work on the synthesis of artificial hormones of the adrenal glands. In the practice of medicine is difficult to imagine treatment without Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, Verospiron, Adrenaline and other drugs.
Consider the most important representatives of each group.
Products of the adrenal cortex
Hormones of the adrenal cortex are of aldosterone from the group of mineralcorticoids, cortisol as the most potent glucocorticoid, androgens and estrogens.
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is considered to be matricariae hormone. It affects specific protein, activating its activity. Peptide called ATP-Asa induced by aldosterone. Cellular target is the epithelium of the renal tubules end with calcitonin receptors. After receiving the message, they enhance the synthesis of protein-carrier of sodium.
In the end, the renal epithelium retains sodium ions in the interstitial tissue of the kidneys, from where it returns into the blood. Along with sodium alone does not pass into the urine water molecules.
Simultaneously, there is an increased output of potassium through the urine, salivary gland and sweat. This mechanism contributes to the increase in blood pressure. Especially important during blood loss, increased sweating, profuse vomiting and diarrhea. Aldosterone is involved in the compensation mechanism in the development of a state of shock.
Aldosterone affects sodium reabsorption (back suction)
Production of aldosterone is affected by such factors of regulation:
- renal system renin-angiotensin increases the production;
- adrenocorticotropic hormone of the pituitary gland also enhances the synthesis, but are less intense;
- direct action of sodium and potassium by the tubular epithelium.
Scientists believe that is also the mechanism of action of prostaglandins, kinins.
Identified aldosterone antagonist – atriopeptin or natriuretic hormone, contributing to the increased excretion of sodium in urine. It blocks aldosterone produced at the stage of its synthesis and mechanism of action.
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are produced by beam layer of the adrenal cortex.
The group consists of:
- cortisone,
- cortisol,
- desoxycortisol,
- corticosterone,
- dehydrocorticosterone.
Physiological effect, the most powerful of cortisol. The transfer of hormones in the blood does protein transcortin. It belongs to alpha-2-globulin that binds up to 95% of the produced glucocorticoids. 5% of the hormones is blocked by albumin.
This conversion occurs in the liver with the enzymes α – and β-reductase. Exert important regulating effect on the body.

Maximum production of cortisol accounted for 8 a.m.
Anti-stress:
- provide the individual’s adjustment to stress (increase blood pressure, the sensitivity of the vessels and cells of the myocardium to catecholamines);
- involved in the regulation of the synthesis of red blood cells in the bone marrow;
- organize maximum protection in cases of injuries, shock, blood loss.
Effects on metabolism:
- increase the level of glucose in the blood, synthesizing it in the liver from amino acids (gluconeogenesis);
- at the same time in skeletal muscles and inhibition of protein synthesis with the goal of creating a “depot” of amino acids for gluconeogenesis.
- block the utilization of sugars;
- restore the glycogen stores in the muscles and liver;
- increase fat storage, but contribute to the breakdown of proteins;
- help to detain aldosterone sodium and water.
Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic:
- due to brake, different enzyme systems involved in inflammatory reactions (proteases, lipases, hyaluronidase, kinins, prostaglandins), reducing capillary permeability;
- eliminate the accumulation of leukocytes;
- reduce oxidative processes and the accumulation of free radicals;
- inhibit the growth of scar tissue;
- do not allow the body to produce autoantibodies;
- directly inhibit mast cells, which secrete supporting allergic mediators;
- reduce the sensitivity of the tissues to histamine, serotonin, but raise the adrenaline.
Effect on immunity:
- inhibit the activity of cells of the lymphoid type, directly inhibit the maturation of T – and B – lymphocytes;
- affect the production of antibodies;
- reduce the production of lymph and cytokines in immunocompetent cells;
- inhibit the process of phagocytosis of leukocytes.
Important feature is the dependence of the effects on the immune system from the amount of glucocorticoids that the middle layer of the adrenal glands produces. Proven electoral turnout: at low concentrations in the blood is immune stimulating effect with the dramatically inhibitory effect.
Additional effects:
- increase the secretion of acid and pepsin in gastric contents, therefore, together with vasoconstrictor effects contribute to the appearance of peptic ulcer disease;
- reduce the inhibition of the immune system, radiation and chemotherapy, so it is widely used in the treatment of leukemias and tumors.
In the case of increasing level in the blood causing:
- the loss of bone calcium, osteoporosis;
- the amplified output of calcium in the urine;
- low absorption through the intestinal wall.
Such actions can be seen as antagonism to vitamin D3. One feels muscle weakness.
Shown the influence of glucocorticoids on the activity of the brain:
- build quality processing received from the outside information;
- positive effect on the perception of the receptor apparatus of taste, of smell.
A deviation from the norm causes disorders in the higher nervous centres, famous cases of schizophrenia.
There is evidence of the contrary effect of catecholamines on the synthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone. An example is tuberculous lesions of the adrenal glands. Low blood levels of glucocorticoids makes hard work the anterior pituitary gland. This contributes to the appearance of certain symptoms bronze disease – pigmentation on the skin.
Hormones mesh zone of the adrenal cortex
In reticular layer of cortex under the action of adrenocorticotropic hormone of the pituitary gland synthesizes substances that have sexual significance for a human being because they provide the development of secondary sexual characteristics (type of development of muscles, body hair growth, formation).
These include:
- adrenosterone,
- dehydroepiandrosterone,
- dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate,
- estrogen (in women also produced by the ovaries, and for men only by the adrenal glands),
- pregnenolone,
- testosterone,
- 17-gidroksipropafenon.
More popular names, such as androgens, estrogens, progesterone. Have the highest value in childhood and adolescence, provide the sexual development of the child.
Men are worried about their testosterone, and really ought to be thinking about its earlier forms
Dehydroepiandrosterone is an intermediate product in the production of testosterone, reduces self-destructive effect of cortisol on the immune system.
17-gidroksipropafenon transformirovalsya to Androstenedione then to estradiol and testosterone. Research on this hormone gives information about the participation of adrenal glands in diseases of the ovaries, causes of infertility, confirms adrenogenital symptoms.
A laboratory test is necessarily performed in women with pregnancy disorders, previous nevynashivaniyu.
Importance of testosterone is not only sexual development of boys. At high levels in the fetus proved its effect on future speech function. This is one of the reasons for the late development of spoken language among boys (three years).
Catecholamines – products medulla
Hormones of the medulla of the adrenal glands is called the biochemical composition of the catecholamines. These include norepinephrine and epinephrine.
Histochemical reactions revealed the peculiarity of the secretion:
- chromaffin cells with dark staining synthesize norepinephrine;
- bright – adrenaline.
Researchers believe that norepinephrine affects the feeling of fear and adrenaline on aggressiveness. Under normal conditions the share of adrenaline, accounts for 90% of the total content of catecholamines.
The organs that are influenced by catecholamines in a stressful situation, receive instructions through the blood
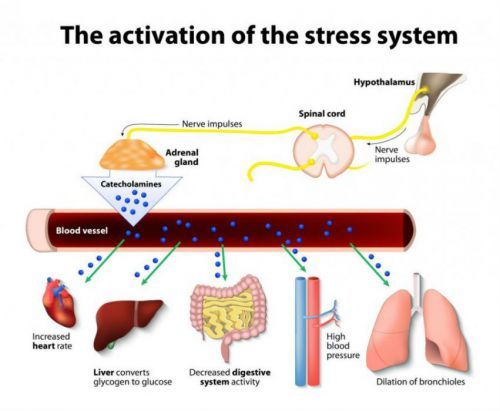
For their formation of essential enzymes:
- the monoamine oxidase (responsible for deamination) is inside the cells of the medulla;
- methyltransferase (adds to the structure of a methyl group) are located in the blood plasma.
Secreted by adrenal catecholamines in the blood are rapidly destroyed, so need the continued support of synthesis.
Physiological effects are manifested in the interaction with α – and β-adrenergic receptors of the cells of the body.
They are related to the sympathetic nervous system:
- palpitations;
- relaxing effect on the muscular system of the bronchi;
- spastic contraction of the arteries;
- increase in blood pressure.
Effects on metabolism in liver cells
Glukoneogenez – “spare” the extra option of splitting glycogen to obtain glucose, which provides energy to cells under stress.
Goes with enzymes:
- adenylate cyclase,
- protein kinase,
- phosphorylase.
Lipolysis – an incremental process of extracting an energy source from fats and fatty acids.
For the sequential splitting enzyme:
- adenylyl cyclase,
- protein kinase,
- triglyceridemia,
- diglycerides,
- monoglycerides.
Catecholamines are involved in the production of heat for the body (thermogenesis). Actively interacting with other hormones. Can inhibit insulin production.
Scientists have discovered another hormone, which is sensitive β-adrenergic receptors. Conventionally, it is called endogenous beta-agonists. I believe that he has a decisive importance on childbearing among pregnant women, reducing uterine activity.
Found that before birth, the fetus begins to vigorously throw into the blood catecholamines. Perhaps it is perceived as a signal of early labor.
The table shows the adrenal hormones at their place of synthesis.
| The place of synthesis in the adrenal glands | The name of the hormones | The main effects on the body |
| Cortical layer:
glomerular area |
aldosterone | a delay of sodium and water; the increased output of potassium;
increase in blood pressure |
| beam area | cortisol,
corticosterone, deoxycorticosterone cortisone, desoxycortisol, |
increase resistance to stressful influences,
the provision of lipolysis and gluconeogenesis to glucose production; the loss of protein; anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic; stimulation or suppression of the immune system. the loss of calcium by bone tissue |
| net area | adrenosterone,
dehydroepiandrosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, estrogen, pregnenolone. testosterone, 17-gidroksipropafenon |
the development of secondary sexual characteristics;
of a pregnancy; muscle building |
| Medulla | norepinephrine,
adrenaline |
prepare organs for stressful situations;
storing and retrieving energy; depression insulinopenia; involved in gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, heat supply; |
The impact of food and diet on the adrenal glands?
The human body constantly needs to replenish energy, including during sleep. We should not forget that hunger and obesity are both considered to be stress and lead to the overexertion of the functioning of the adrenal glands.
In regulation of level of sugar is attended by catecholamines and glucocorticoids. For smooth operation it is necessary that the food received in accordance with the biorhythm of hormone synthesis.
It is recommended:
- early in the morning to make products that increase the rate of synthesis of hormones;
- by evening go for lighter meals and reduce the portions.
The food should be combined with physical activity. The best time physiological state to ensure good endurance of the load is the first half of the day. In the evening you can walk, but not to overwork themselves in physical exercises.
Optimal eating schedule tailored to the physiological drop in the level of glucose in the blood and restore hormones:
- Breakfast before 8 am;
- eating fruit at 9 and 11 hours;
- lunch in 14-15 hours;
- dinner in 17-18 hours.
Before sleep you can eat vegetable salad, fruits, cheese. Not shown refined sugar.
For the maintenance of healthy adrenal glands help the following products:
- fresh fruit, berries, juice;
- lean meat and fish;
- vitamins C, b, E, protect against stress by supporting the necessary level of hormones;
- for the synthesis of energy required magnesium, calcium, trace minerals (zinc, iodine, manganese, and selenium).
Contraindicated:
- alcohol;
- preservatives;
- all culinary products;
- sweets and candies.
Coffee and sugary drinks should be restricted.
Proper operation of the hormonal system of the adrenal gland ensures that the human body prevention from influence of adverse factors preventing many diseases. The use of synthetic substitutes has shown efficacy in the treatment of many diseases.



The medulla is responsible for the production of catecholamines. In the process of synthesis of the obtained intermediate substance having a lower activity, but necessary for use in case of an emergency, for example, with a lack of energy reserves, increased spending.