Functional and moderate bradycardia, which is not accompanied by clinical manifestations, do not require therapy. With organic, extracardiac, toxic forms of bradycardia, the underlying disease is treated. Drug bradycardia requires dosage adjustment or discontinuation of drugs that slow heart rate.
With manifestations of hemodynamic disturbances (weakness, dizziness), prescription drugs of belladonna, ginseng root, extract of Eleutherococcus, isoprenaline, ephedrine, caffeine and others are administered in individually selected doses.
The indications for the active treatment of bradycardia are the development of angina pectoris, hypotension, fainting, heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias.
The occurrence of a Morgagni-Adams-Stokes attack requires consultation with a cardiac surgeon and a decision on the implantation of a pacemaker – an artificial pacemaker who produces electrical impulses with a physiological frequency. Adequate and constant given heart rate helps to restore normal hemodynamics.
Bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia, with a heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute. It occurs as a variant of the norm in trained athletes, but more often accompanies various cardiac pathologies. It is manifested by weakness, fainting and short-term loss of consciousness, cold sweat, pain in the region of the heart, dizziness, instability of blood pressure. In patients with severe bradycardia (heart rate less than 40 beats per minute), leading to the development of heart failure, an operation on implantation of a pacemaker may be required.
Bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia, with a heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute. It occurs as a variant of the norm in trained athletes, but more often accompanies various cardiac pathologies. It is manifested by weakness, fainting and short-term loss of consciousness, cold sweat, pain in the region of the heart, dizziness, instability of blood pressure. In patients with severe bradycardia (heart rate less than 40 beats per minute), leading to the development of heart failure, an operation on implantation of a pacemaker may be required.
Regardless of the cause, bradycardia is based on impaired ability of the sinus node to produce electrical impulses with a frequency above 60 per minute or inadequate propagation through conductive paths. A moderate degree of bradycardia may not cause hemodynamic disorders. Rare heart rate in bradycardia leads to a lack of blood supply and oxygen starvation of organs and tissues, disrupting their full functioning.
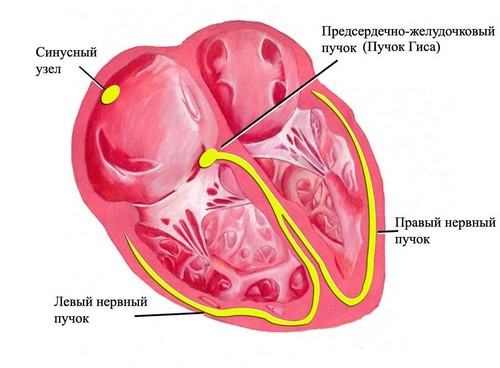
Physically trained people have physiological bradycardia, considered as a variant of the norm: in a quarter of young healthy men, the heart rate is 50-60 per minute; during sleep, under the influence of physiological fluctuations of the vegetative regulation, the heart rate decreases by 30%. However, more often bradycardia develops against the background of existing pathological processes.
Bradycardia classification
According to the localization of the revealed violations, sinus bradycardia is associated with automatism disorders in the sinus node and bradycardia during heart block (sinoatrial or atrioventricular), in which the conduction of impulses between the sinus node and the atria or atria and ventricles is disturbed.
Heart rate may decrease under physiological conditions (in athletes, during sleep, at rest) – this is functional or physiological bradycardia; pathological bradycardia accompanies the course of various diseases.
Pathological bradycardia can occur in an acute form (with myocardial infarction, myocarditis, intoxication, etc.) and disappear after the cure of the disease that caused it, or of a chronic form (with age-related sclerotic heart disease).
For the reasons for the development of sinus bradycardia, the following forms are distinguished: extracardiac (neurogenic), organic (with cardiac lesions), drug, toxic and sinus bradycardia of athletes. Sometimes according to the etiology of bradycardia is divided into toxic, central, degenerative and idiopathic.
Causes of Bradycardia
The extracardiac form of bradycardia can develop with neurocirculatory dystonia, neurosis with vegetative dysfunction, pressure on the carotid sinus (when wearing a tight collar or tie), pressure on the eyeballs (Ashner’s reflex), increased intracranial pressure (with a meningitis, a brain injury, a body, a heart therapy unit, a non-human body, a non-human body, a non-human body, a non-human body, a non-human body, will not work). or brain tumors), gastric ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer. Bradycardia that develops in myxedema is proportional to the severity of hypothyroidism.
The causes of the organic form of bradycardia may be myocardial infarction, myocardial dystrophy, myocarditis, cardiosclerosis. These diseases lead to degenerative and fibrotic changes in the sinus node or conduction disturbances in the myocardium, accompanied by the development of bradycardia.
With organic lesion of the pacemaker, the syndrome of weakness of the sinus node develops, and the frequency of generation of impulses in it dramatically decreases. This condition is accompanied by sinus bradycardia – rhythmic, but very rare contractions of the heart; changing brady and tachycardia or alternating spontaneous pacemakers. The extreme degree of damage to the sinus node is manifested by the failure of the automatism function, as a result of which they no longer produce electrical impulses of the heart.
With the defeat of the myocardial pathways, a blockage of conduction of impulses develops, with the result that part of the signals generated by the sinus node are blocked and cannot reach the ventricles – bradycardia develops. Cardiac glycosides, quinidine, β-adrenoblockers, sympatholytic drugs (for example, reserpine), calcium channel blockers (for example, verapamil, nifedipine), morphine can contribute to the development of the bradycardia dosage form.
The toxic form of bradycardia develops with severe intoxications caused by sepsis, hepatitis, uremia, typhoid fever, organophosphate poisoning, and retarding the processes of automatism and conduction in the heart muscle. This group is also sometimes referred to as bradycardia caused by hypercalcemia or severe hyperkalemia.
The so-called bradycardia of athletes is characterized by a heart rate of up to 35-40 per minute even during the daytime. It is caused by the peculiarities of the vegetative regulation of heart rhythm in people who are professionally involved in sports. Also, natural aging processes in the body can lead to bradycardia; sometimes the causes of bradycardia remain unexplained – in these cases they speak of its idiopathic form.
Bradycardia symptoms
Moderately pronounced bradycardia is usually not accompanied by circulatory disorders and does not lead to the development of clinical symptoms. The occurrence of dizziness, weakness, fainting and fainting is observed in bradycardia with heart rate less than 40 beats per minute, as well as against the background of organic heart damage.
Also, when bradycardia appears fatigue, difficulty breathing, chest pain, fluctuations in blood pressure, impaired concentration and memory, short-term visual disturbances, episodes of confused thinking.
In general, the manifestations of bradycardia correspond to the severity of hemodynamic disorders developing on its background.
The brain first responds to the weakening of the contractile function of the myocardium and slowing blood circulation, experiencing hypoxia. Therefore, bradycardia often leads to bouts of loss of consciousness, seizures (seizures or prodrome of Morgagni-Adems-Stokes), which can last from a few seconds to 1 minute. This is the most dangerous condition in bradycardia, requiring the provision of emergency medical measures, because with a prolonged attack, respiratory activity can stop.
Diagnostic bradycardia
Characteristic of bradycardia symptoms are detected when collecting patient complaints and an objective examination. On examination, a rare pulse is determined, which, with sinus bradycardia, has a regular rhythm, heart tones of normal sonority are heard, and respiratory arrhythmia is often detected. Consultation of a cardiologist is recommended for patients with identified bradycardia.
Electrocardiographic study in bradycardia allows to fix a rare heart rate, the presence of a sinoatrial or atrioventricuclear blockade. If at the time of registration of an electrocardiogram episodes of bradycardia are not detected, resort to conducting daily monitoring of ECG.
With an organic form of bradycardia, an ultrasound of the heart is performed. The method of ultrasound echoCG is used to determine a decrease in the ejection fraction of less than 45%, an increase in the size of the heart, sclerotic and degenerative changes in the myocardium. With the help of the exercise bike ergometry, the heart rate increase is estimated in connection with a given physical load.
When it is impossible to detect transient blockade by ECG and Holter monitoring, a transesophageal electrophysiological study of the cardiac pathways is performed. With the help of CPEFI, it is possible to determine the organic or functional character of bradycardia.
Prognosis and prevention of bradycardia
Adverse effect on the prognosis of the course of bradycardia is the presence of organic lesions of the heart. Significantly aggravates the possible consequences of bradycardia, the occurrence of attacks Morgagni-Adams-Stokes without resolving the issue of electrostimulation.
The combination of bradycardia with heterotopic tachyarrhythmias increases the likelihood of thromboembolic complications. Against the background of a persistent decrease in rhythm, the development of a patient’s disability is possible. With the physiological form of bradycardia or its moderate nature, the prognosis is satisfactory.
Timely elimination of extracardiac causes, organic lesions of the heart, toxic effects on the myocardium, the correct selection of dosages of drugs will prevent the development of bradycardia.




Thanks for this post. I definitely agree with what you are saying.
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I have really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I hope you write again very soon!