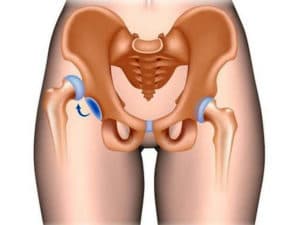
Deforming osteoarthritis of the hip is a progressive, chronic pathology characterized by degenerative changes of the joint and destruction of cartilage. As the progression of the disease in the pathological process involved ligaments, the surrounding muscles, articular capsule, synovial sheath.
Signs of damage – pain and deformity of the affected joint, leading to a gradual decrease of functionality.
Pathology develops slowly, without treatment, ends with a significant reduction in quality of life, loss of mobility and health.
The causes of the disease
The incidence of deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint clearly depends on the age: diagnosis is half the population older than 50 years. There is also a correlation with the floor: pathology more frequently detected in women. This is due to anatomical features of the female body, but also a serious stress on the hip joints during childbirth.
Causes of the disease are:
- mechanical damage;
- developmental abnormalities of the hip joint;
- congenital dislocation of the hip;
- necrotic process in the tissue of the femoral head;
- infectious-inflammatory lesions of the tissues;
- vascular disease can impair blood circulation in the pelvic area;
- degenerative pathology of the spine (osteochondrosis);
- gonarthrosis (degenerative progressive process affecting the knee joint);
- tuberculosis of the bones.
To trigger the development of degenerative process in the hip can impact the following factors:
- the presence of excess body weight;
- lesions of the endocrine system, hormonal disturbances;
- lack of physical activity, lack of exercise;
- excessive stress on the hip joint caused by professional sports, a specific conditions;
- hypothermia on a regular basis;
- diseases of the spine (scoliosis, kyphosis);
- pathology of the feet (flat feet);
- genetic predisposition.
The gene responsible for the development of deforming arthrosis is not, however, inherited characteristics of an organism (e.g. metabolic disorders, weak bone and cartilage). If someone from the family suffers deforming osteoarthritis, the risk of disease increases.
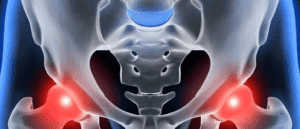
The clinical picture
The disease is manifested by pain and limitation of motion of the affected hip joint. Patients experience difficulties with the diversion of the legs in the area of articulation.

Symptoms are as follows:
- a feeling of stiffness, especially pronounced after a long stay in one position, for example, after a night of rest;
- characteristic crunch when bent, tapping the feet;
- atrophic changes in the muscle tissue adjacent to the affected area.
Progression of disease there is a buildup of bone tissue, the appearance of osteophytes. It is a protective mechanism that is activated in the body to replace the thinning of cartilage. In advanced stages of the disease the osteophytes grow and connect, which leads to a complete disappearance of the movement in the skeletal joint.
In the initial stages of the disease, patients experience unexpressed pain passing alone. The cartilage is worn slightly, the joint space is slightly narrowed.
With the progression of the pathological process observed increase in the intensity of pain syndrome. The discomfort is felt not only after exercise but also at rest. Joint fluid becomes more viscous, which leads to deterioration of sliding of the bones because of the dryness of the cartilage shock absorbing properties deteriorate. At the same time begin to form bony growths, the femoral head is displaced, the bone is slightly deformed.
In advanced stages of the disease, patients experience excruciating pain of a permanent nature, difficult to relief medication drugs. The progression of deforming osteoarthritis leads to the cartilage destruction, the complete disappearance of the joint space. Adjacent muscle atrophy.
Deforming osteoarthritis if not treated may develop ankylosis (fusion of the mating bone, leading to complete immobility of the joint), bursitis, osteoarthritis, arthritis.
Diagnostic measures
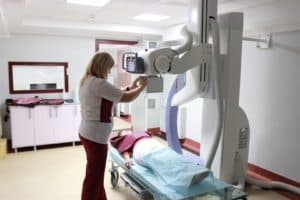
Radiography
When the first symptoms of the disease should go to the orthopedist, traumatologist, surgeon. The diagnosis is based on clinical signs and a number of instrumental studies. The most informative method of x – ray examination. According to the radiographs is possible to establish the degree of spread and stage of the pathological process, its causes, and to assess the condition of the joint.
Additional methods of examination that may be prescribed by a doctor, CT and MRI. Computed tomography data allow us to estimate the degree of change of the joint and bone tissues. Magnetic resonance imaging is necessary if the process involved the adjacent muscles.
Treatments
In the early stages of therapy is conservative. In advanced cases, the changes become irreversible, the patient required surgery.
Therapy includes the following activities:
- receiving medication;
- physiotherapy;
- Exercise;
- massage.
One should strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician to control weight, reduce the load on the affected joint.

For this podiatrists recommend:
- it is not possible to use stairs;
- not to go for a long time;
- not to raise and not to carry heavy loads;
- avoid shoes with heels;
- often change posture, not to stay long in one position;
- during acute to use a cane when walking.
Treatment goals:
- the relief of pain;
- the establishment of blood supply and tissue trophism of the cartilage to restore it;
- improving joint fluid, increasing its volume;
- improving the functioning of the muscle fibers in the surrounding region;
- removing restrictions on the mobility of the affected joint.
For the treatment of terminal degrees of osteoarthrosis developed many radical ways. Resorting to arthroplasty or endoprosthesis.
Drug therapy
The treatment is carried out using the following groups of medicines:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Movalis, Indomethacin);
- chondroprotectors (Artra, Chondroitin, Movex);
- muscle relaxants (Sirdalud, Mydocalm);
- corticosteroid hormone treatment (Celestone, Hydrocortisone).
For a single relief acute attack of pain you can use analgesic. Relief of pain syndrome provide anti-inflammatory drugs, however, the duration of their admission is determined by a physician. Too long use of such drugs inhibits the ability of cartilage to recover. With persistent pain syndrome, not kopiruem NSAIDs, prescribe corticosteroids, injected directly into the body of the joint.
Chondroprotective drugs improve the nutrition of the tissue of the affected cartilage, which contributes to its regeneration. Muscle relaxants are used when the involvement in the pathological process of the surrounding muscles. To restore the blood supply prescribed medicines, which has vasodilating effect.
For the treatment of osteoarthrosis shown the use of drugs local action. They help to alleviate the symptoms of the disease. To improve the trophic and vascularity of the cartilage are used in ointments and creams with a warming effect (Nikofleks, Menovazin). Help relieve intense pain compresses with use of drugs (Dimexide, Bischofite).
Physical therapy
In the early stages of the development of effective physical therapy, has a beneficial effect:
- decreases the intensity of the pain;
- improves metabolism in bone and muscle tissues;
- slow down degenerative processes in cartilage tissues.

Doctors recommend techniques such as:
- phototherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- UHF;
- medicinal electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- electromyostimulation;
- shock wave therapy;
- inductothermy;
- massage;
- manual therapy.
Courses these procedures are for 10-15 sessions. Method and duration of procedures are determined by the doctor according to individual indications of the patient.
Physiotherapy
Special exercises help to restore mobility of the joint, strengthen surrounding muscles, reduce intense pain. In order for the exercises to be effective, experts develop a set of exercises taking into account the indications and nature of disease a particular patient.
Training is conducted only during stable remission, as during acute physical activity painful and may aggravate the disease.
Traditional methods of treatment
In the early stages of folk remedies can ease pain, improve the patient’s condition. Get rid of the disease such methods will not help, they are suitable additional measures. Before using the recipes of alternative medicine should consult your doctor.
In this disease, traditional healers are advised to do rubbing the affected area. For this you can prepare the ointment at home.
- Popular tool of propolis. Bee products are put in a heatproof bowl, pre-raskroshil, pour vegetable oil, keep on a steam bath until the mixture becomes homogeneous. Rubbing propolis ointment do for three months.
- Another effective remedy is the infusion of the flowers of lilac. For its preparation take 0.5-liter jar raw material is filled halfway, pour the alcohol. Mixture infuse for two weeks, the capacity periodically vzbaltyvayut. Ready infusion make rubbing the affected area.
- If the degenerative process is accompanied by inflammation, it will help the compress of cabbage leaf. The washed sheet is smeared on the inner side with honey and applied to the affected joint at night. To do the procedure should be within a month daily.
Preventive measures
The prevention of osteoarthrosis following measures:
- weight control, balanced diet;
- physical exercise (swimming, walking, Jogging);
- exclusion of hypothermia of the body;
- the prevention of mishaps, that may damage the hip joint.
Prevention of diseases of the musculoskeletal system should be those who already have signs of disease, and those who have not encountered it. In cases when the disease has already begun, trying to slow its progression: to wear orthopedic shoes, not to overload the joint, keep your weight.
Predictions when detected at an early stage cases favourable, subject to timely start of treatment, following medical recommendations.



