A particular problem at an early age is a violation of motor function in children, and in the neonatal period and infancy disorders of movement significantly and fundamentally different from those in adulthood and even older children.
Usually problems motor areas associated with lesions of the nervous system – especially the brain or spinal cord that are responsible for motor functions and their coordination. There may also be problems associated with damage to the peripheral parts motor circuits – by nerve fibers by the muscles, as possible while some congenital abnormalities.
Most often in early childhood movement disorders are manifested in the violation of muscle tone or problems with reflexes and movements. Movement disorders can have both lightweight and easily removable only by massage and gymnastics, and a serious progressive disorder, up to such pathologies as cerebral palsy.
Difficulty in defining the problem infants
Nervous tissue has not yet completed its development to the period of birth, and the process of its maturation and development continues. Lesions usually have significant scale and complexity to identify. If during pregnancy or in childbirth has been damaged the nervous system and brain tissue, usually generalized (extensive) damage and is extremely difficult to determine the initial location of damage, the most affected area (for example, where there is a hematoma, a cyst, a region of ischemia). Sometimes neurologists can only speak about the predominant lesion in certain parts of the brain stem, cerebellum, temporal lobe, frontal lobe.

In motor acts involves the pyramidal system and extrapyramidal (this is a special region, where the arc motor reflexes). At an early age, even experienced physicians are sometimes difficult to distinguish pyramidal damage from others, and it is important for further tactics and prognosis.
The main criteria and characteristics that operate in the diagnosis of problems with the nervous system and motor field kids are:
- Muscle tone
- Reflex acts.
To evaluate the muscle tone correct can only a doctor familiar with the physiology of the age of children, as in the first year of the change of tone is quite substantial, as well as the reflexes of the baby.
It is particularly important to correctly assess muscle tone in children at birth and then in periods up to three months and from three to six months – they have a special feature – physiological hypertension of the muscles, passing in certain periods.
Disorders of motor functions in SDN (the syndrome of motor disorders) can manifest as:
- Dystonia muscular areas of the body
- Hypertension muscle elements (local or diffuse)
- Hypotonia of the muscles (local or widespread).
The change in muscle tone is not a disease, it’s just pathological syndrome, caused by certain changes in the nervous system (trauma, ischemia, and other injuries).
Muscular hypotonia: causes of development and symptoms
The syndrome of hypotonia of the muscles in children there is reduced resistance to passive movements, will also typically increase the volume, if the doctor or parents make the move handles, legs.
That is, flexion of the arms and legs of crumbs not meet resistance, in difficult situations, children can be like “rag dolls”. In severe hypotension muscle elements may substantially be limited to random motor activity or suffering spontaneous (chaotic movements of newborns), which is due to reflexes associated with normal tendon reflexes, or pathological (abnormal their increase or decrease). Sometimes some of the reflexes can even be omitted (dropped out), it depends on the specifics of the damage to the nervous system.
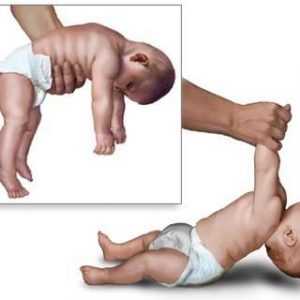
The syndrome of muscular hypotonia neurologists very often detected in children during the neonatal period and in infancy, it can be molded from birth or develops and is transformed into increasingly difficult with the growth of the baby.
Congenital hypotonia of muscles typical for:
- Severe hypoxia, intrauterine transferred Il in childbirth, asphyxia of a child
- The congenital forms of neuromuscular diseases
- Injuries to the head or spine in childbirth, with the involvement of the brain or spinal cord
- Defeat in childbirth of peripheral nerves (ulnar or brachial, femoral, facial)
- Hereditary metabolic disorders, leading to changes in nutrition of the nervous tissue
- Chromosomal syndromes and genetic anomalies
- In the presence of pathologies from congenital dementia, or situations where it is acquired at an early age.
Also you should know that the hypotonia of the muscles can first manifest themselves or become more serious and difficult in any stage of growing up, sometimes its manifestation is formed in a few months after birth, and its course steadily progresses to severe States. When it comes to a fairly common and severe hypotension, which captures a large amount of muscles leads to a decline in the health of the child.
Hypotension, which manifests itself in early childhood, can fade in normal muscle tone or dystonic status, hypertension, muscles, or else it remains one of the leading symptoms of SDN in children throughout the first year of life.
The severity of such abnormal muscular hypotonia among toddlers can vary from a mild and insignificant decrease (weakly there is reduced resistance to passive actions and movements) until the complete shutdown of active movements and the almost complete atony or immobility.
What is the danger of hypotension, what is its impact on the development of infants
Naturally, violated the tone of the muscle fibers may significantly affect the child’s health and violate its full development, especially if we are talking about hypotension.
If decreased muscle tone is detected in a mild form and not its combination with any other neurological pathologies, such as either does not affect the growth and physiological development of the crumbs, or leads to an inhibition and delay in terms of psycho – motor development of the child, usually starting from the second half of the year, at this time, particularly active should be formed motor acts and critical skills.
And typically that underdevelopment is uneven, can be inhibited sufficiently complex motor acts and functions which may require for its implementation of simultaneous coordinated interaction of various muscular groups. An example may be the fact that the child is approximately nine months with the presence of muscular hypotonia, if you go the doctor or the parents can sit, and here alone he could sit down, coordinating his body can not.
There are options of muscle hypotonia:
- a localized region of one limb occurs as a traumatic exposure (paresis of hands or legs). In such cases, the delay in the formation of skills will be limited to the affected area and its impact on the rest of the body of the child.
- common distinct presence of severe muscular hypotonia. This fact may have a severe and significant impact on motor development of kids. For example, the development of motor acts in such diseases as spinal muscular atrophy (syndrome Hoffmann-werdnig) have a ten month old child corresponds to the three-month level.
Delays in development of motor functions, of course, become the cause and characteristics in the formation of the mental functions of the child. It is important to understand when there is no possibility of grasping handles of objects, this leads to the formation of a defective hand-eye coordination and manipulation with objects and toys.
Often formation of muscle hypotonia combined with various other neurological disorders in the form of paresis of the cranial nerves, development of hydrocephalus, or convulsions, all this combined with aggravating circumstances affects the delay of normal development and is determined not only by reduced muscle tone, but also all the other influences.
In parallel, it is worth noting that the localization and the severity of reduced muscle tone, its effect on the inhibition of physical and mental development will largely depend on the disease that has led to such phenomena. In the presence of seizures on the background of congenital dementia (or early acquired forms) not only hypotension, but also delay in mental development leads to pronounced the gaps and learn the required movements.
Dystonic syndrome in children
The concept of SDN in babies in the first year after birth may also be included, such as as dystonia of the muscles is the alternation in the muscle groups of the limbs (usually the feet or hands, less body) as reduced muscle tone, and increasedor change in the tone of muscular elements on the basis of specific effects on the nervous system.

So, at rest in these babies with only passive motor acts to be expressed explicitly muscular hypotonia, generic. But when trying to execute their specific movements or on the background of positive emotions or negative starts the growth of muscle tone, occurs the formation of pronounced pathological reflexes, with predominantly tonic in nature. This phenomenon is called the attacks of dystonic attacks.
Especially often such a phenomenon dystonic disorders see those kids who suffered at birth hemolytic disease, born during gestation rhesus-conflict, or an incompatible blood group pregnancy.
With a pronounced syndrome of dystonia of the muscles is formed by the complexity of developing a full-fledged toddler straightening reflexes in the torso area, plus suffers from the development of balancing reactions. This is due to continually changing muscle tone. When this syndrome is lightweight and transient dystonia of the muscles, it will not have a pronounced negative effect in the process of growth and development of the baby as you age. Gradually, as the maturation of brain centers, all aligned.
Muscle hypertension in children
Syndrome hypertension individual items or entire muscle groups will be characterized by the opposite phenomena, rather than hypotension. This increased resistance to passive movements, in addition, restriction of the power of this arbitrary or spontaneous motor activity of infants.

Also typically increase the reflexes of the tendons with the expansion of the zone of origin, the pathological settings of the knobs and feet (inverted, clamped). Usually increased muscle tone may prevail in the area of the flexor muscle groups, as well as holding a pose can be greatly modified muscles in the hips and shoulders, resulting in the adoption of a child of a certain typical poses. But only on the basis of the posture diagnosis do not put, and hypertension of the muscles is not determined is an additional criteria and relative pathologies.
Additional criteria will be the alteration of innate reflexes and particular symptoms of Gordon’s reflex Babinski or Oppenheim. Under normal circumstances, they are mild, have an irregular appearance and as soon as the child develops, to weaken and fade away. Against the background of high muscle tone, they are constantly observed, and not have the dynamics of extinction.
In the severity of the syndrome of hypertension muscles may have options from a slight increase and enhanced resistance to passive movements of the baby being unable to move and Comanesti (this is called decerebration rigidity is a complete non-random and other movements, so toned muscles).

In such serious cases, even the use of medication that has properties of muscle relaxant (relaxes the muscles) can cause muscle relaxation, and the more impossible the implementation of passive movements of the hands of parents or doctor.
If the syndrome of hypertension has mild, not compatible with the presence of pathological (aka tonic) reflexes or not complicated by other neurological disorders, it will affect the development is not much. Usually this manifests itself in the inhibition of development of motor abilities in children in the first months (to years old) – they later turned, the thief start to crawl, etc. on the Basis of localization, in which the muscle groups more elevated tone, inhibited is the development of certain skills and motor acts.
For example, if excess muscle tone in the handles, there could be a delay in the development of directional movement of the handles with respect to the facilities, difficulties with the capture of the toy or manipulate objects. Especially can suffer grasping the skill in his hands. In parallel with the fact that the children later begin to grab my things and toys for manipulation, they have for a long time will burn to stay specific (ulnar) capture – they take all items with a brush. But pincete the gripper fingers can be formed slowly, in some cases requiring special training and additional incentives. Can inhibited the development of the formation of the protective functions of the hands in these situations will be respectively inhibited and reaction of balance lying on his stomach, when learning the sitting and standing and when walking.
If you suffer muscle tone of the legs, can not rotate, the support reactions from the feet and the skills of independent sitting down, then these children are hard and reluctant to stand up on his feet, giving preference to a crawl, with the support of the support stand on tiptoe.
Cerebellar disorders: a role in motor disorders of children
The cerebellum is an important brain centers, he is responsible for the coordination of movements and statics, as well as the smoothness and combination of motor acts, posture maintaining. Lesions of cerebellar nature kids early childhood may be the result of his prenatal underdevelopment (agenesis of cerebellar hypoplasia, hypoplasia – decrease in volume), and it can also be affected as a result of birth trauma or acute asphyxia at birth. Sometimes a special variant can be hereditary problems of its development or early degeneration, tissue death soon after birth.
Such problems are brought to the decrease in muscle tone, problems with coordination in hands, as well as disorders of balance, when the children gradually master the skills in age – learning to sit and stand, then walk. In addition, cerebellar syndromes typically the appearance shaking in the hands and feet, problems with coordination and unsteady gait, you can define them after the kids possess arbitrary and active movements.
First time parents can start to suspect problems in coordination, if you watch children and how they are drawn to the toys, they can grab the handles and pull to your mouth, as well as how they stand or sit, then go.
Children in infants who have problems of the cerebellum and coordination, grasping and holding toys can do a lot of unnecessary movements, such especially pronounced when the babies are in a sitting position. An independent seat is formed with a pronounced delay of about 10-12 months, often in this age children hardly hold the balance, to immediately fall if necessary, turn to the side or, if necessary, to take things. The child is afraid to fall, and therefore he does not play with objects with two hands, only one, holding myself and keeping a foothold due to the second hand. To walk children start closer to two years of life, they often fall, and some of the toddlers due to this I prefer crawling in the period when it is high time to walk properly.
In some cases, on the background of cerebellar disorders in the first year of life can be observed in floating eye movement and speech disorders, the first symptoms of dysarthria of cerebellar origin. If the lesions associated with damage to cranial nerves, may have specific delays in development – late fixations on objects, tracking them, and then problems with the motor-visual coordination and disturbance of orientation in space, the growth of significant problems with the development of speech and especially active.
The formation of cerebral palsy as extreme disorders
The most severe and extreme form of syndrome of motor disorders in toddlers first months will be the development of cerebral palsy (phenomenon of cerebral palsy). Set of clinical manifestations (symptoms) in children with cerebral palsy will depend on the presence of disorders of muscle tone and their severity, but increased tone typical for all forms of pathology, the severity of different disorders. So, some children are born with high muscle tone, progressive as they get older, others initially, it is reduced or has severe dystonia, turning then to hypertonicity.
This category of children at birth looks dull and poverty of spontaneous activity, they inhibited unconditioned reflexes, the second month of life, if a child is put on a stomach or vertically to hold that he did attempt to hold the head, there are signs of dystonia. The kid can periods of worry, muscle tone increases sharply, grips well and wrapped inside of the shoulders and forearms, hands, fingers are compressed in fists. While the legs straighten and the cross, are inside. These seizures last for several seconds, repeating for days, and can be triggered by various stimuli from outside – shouts, loud sounds.
The occurrence of movement disorders in the formation of cerebral palsy will be due to the fact that the lesion of cerebral structures, which is still very immature, can disrupt the proper sequence in the maturation of the brain. Due to this higher cortical centers that are responsible for the coherence and coordination of all movements and skills, can’t say no inhibitory effect against congenital primitive stem reflexes. Therefore, inhibited the disappearance of unconditional reflex activity, not blocked pathological reflexes, changes in muscle tone that becomes an obstacle for the formation of the rectification of the body and its balance, the development is inhibited and disturbed, the body does not obey the proper impulses of the brain, which seriously damaged.
Treatments kids
In many ways, the difficulty with treatment is determined by the fact how early identification of problems and how they are complex and heavy, is there any organic lesion of the brain is irreversible. Today, neuroscientists are many effective methods that can resolve motor dysfunction in the early period and quite quickly and efficiently. After a full medical and adjunctive treatment of functional disorders go unnoticed, and with organic disorders in non-running phases can significantly improve the situation.
Naturally, all recommendations are individual, but in General the principles of treatment consists of:
- Courses therapeutic massage conducted only by a specialist with experience in the regulation of muscle tone in infants
- Physical therapy and special motor mode, regular classes with the child
- The use of physiotherapy with various types of effects
- The use of groups of drugs that improve the transmission of nerve impulses and the perception of its muscle fibers
- Drugs which normalize the response of muscles on the incoming impulses from the nervous system
- Vitamins neurotrophic row (group)
- Rehabilitation activities, lessons at home with parents according to special methods.
In the presence of light options SDN Bhd the children are quickly correctable, however, serious organic pathology can be corrected is not completely necessary ongoing monitoring and rehabilitation throughout life.




?? confused??