The signs of stomatitis in children again depend on the type of disease and the degree of its spread. But the overall picture is that the child has a white coating on the tongue and gums in his mouth, painful sores may appear, which brings the baby and his parents anxiety.
Each type of stomatitis is caused by certain reasons and, depending on the age of the child, differs in its developmental features.
Therefore, before you are interested in what stomatitis looks like in children, you need to know what its varieties are.
It is worth noting that not all varieties of the disease are listed below, there are a lot of them and it is simply impossible to list everything, so we will consider the most common types of childhood stomatitis.
Herpetic
This kind of ailment does not appear immediately, but some time after the virus enters the children’s body. Children from six months to three years of age are exposed to it. Prevention of the disease is impossible, but parents should still look closely at the environment of their child, exclude possible contacts with sick people.
Herpes stomatitis in children appears when infected with the herpes simplex virus. The source of infection is children and adults who have cold sores on their lips and nose. The virus is transmitted immediately to the mucous membrane of the child’s mouth, which is vulnerable to any ailment, especially.
It is worth noting that the virus can be picked up not only by airborne droplets, but also through household items. An ordinary dummy can become a source of infection.
The disease develops very quickly, the incubation period is up to five days. The disease is mild, moderate and very severe. A mild form of herpes stomatitis in children is treated at home, the doctor prescribes special drugs based on the results of the tests. A severe form of the disease is treated exclusively in a hospital.
Aphthous
This form of herpes is considered the most common and its name is due to the way in which the disease manifests itself. In the oral cavity of the child, many aphthae are formed, which externally represent a lesion of the erosive shell. It is a rounded or irregularly shaped formation in the mouth of a gray, yellowish or white color. Aphthae themselves are surrounded by a reddish area.
Doctors do not exactly know the exact reasons why aphthous stomatitis appears in children, but many are inclined to believe that the autoimmune nature of the disease affects the occurrence of aphthae. Autoimmunity is an immunity that is directed against itself, during such a pathological condition, the protective mechanisms of a child’s body begin to recognize cells and tissues in their body as foreign. Recognition of normal cells as infection leads to the fact that antibodies begin to defend themselves from their own cells, which leads to the appearance of this form of stomatitis.
By the nature of the course of aphthous stomatitis in children, one can distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- acute form. The disease progresses very quickly, the peak of the disease falls on the third or fourth day, and then it all passes away just as quickly;
- chronic form. It develops after an acute form with improper treatment or even in its absence. The disease manifests itself, then fades, and so lasts a very long time;
- recurrent form. Relapses of the disease are characteristic of children who have suffered a chronic form of the disease.
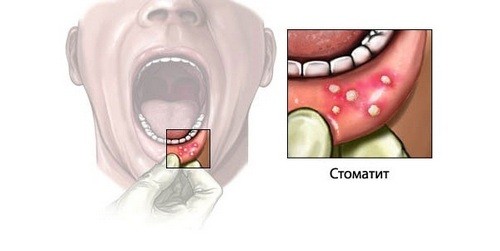
It looks like stomatitis: white plaque and painful sores
Candidiasis
Candidiasis stomatitis in children is considered quite common. The causative agent is a yeast fungus of the genus Candida. In the normal state, this fungus is in the microflora of the mucous membrane of the mouth, intestines and vagina, but if there is a lot of it, then excessive reproduction of the fungus can disrupt the internal ecosystem of the body and cause great discomfort to the patient.
If this particular stomatitis appeared in children, its symptoms can not be confused with anything. The fungus begins to grow in the oral cavity of the child on the tongue, palate and other areas of the mucosa a white film appears like cottage cheese.
Very often, this type of ailment is passed on to the child by the mother at the time of his birth, if she had an urogenital thrush.
Other causes of candidal stomatitis in children are:
- objects that the child drags into his mouth. In the smallest, this is a dummy, older children can infect through different toys;
- artificial feeding, especially mixtures with sugar content;
- if the child took antibiotics, cytostatics and many other drugs;
- malignant tumors;
- prolonged illness of the child, during which his immunity weakens;
- if the child wears braces or dentition.
Allergic
A variety of allergens cause this kind of disease. They can be plant pollen or household dust, animal hair, and more. The appearance of symptoms of stomatitis in children in this case is affected by the intake of various food allergens and drugs. Very often, before the appearance of stomatitis, the child suffered a diathesis.
It is worth noting that this form of the disease stops only after the elimination of the allergen. For example, if the baby is no longer fed with a mixture or the cat is removed from the apartment.
Bacterial
If you are interested in how stomatitis of this variety is treated in children, then, first of all, you need to find out why it appeared. The cause of the appearance is considered to be the ingress of various bacteria into the wounds and cracks of the oral cavity. Most often, the mucous membrane of the mouth is affected by staphylococci and streptococci. Their newborn can pick up even in the hospital during its birth, because they are present everywhere.
The above bacteria constantly live in a weakened children’s body, especially with diseases of the nasopharynx and throat. But if the integrity of the mucous membrane is not violated, there is no need to fear stomatitis, but the smallest injury can lead to its appearance.
Sometimes bacteria pass into the wound from the outside. Inflammation can begin at the corners of the mouth, gradually it passes into the oral cavity. This occurs when in contact with the patient, when eating unwashed vegetables and fruits, or during dental treatment in a child’s office. But bacterial stomatitis is not completed on these bacteria; spirochetes, spindle-shaped bacteria, diplococci, and many others can be its causes.
Symptoms of the manifestation of various types of stomatitis
Consider in more detail the signs of each type of stomatitis:
- herpes pediatric stomatitis. In the first hours of the disease, herpetic stomatitis in children is manifested by an increase in lymph nodes, fever and bleeding gums. The baby becomes irritable and restless, refuses to eat, his skin can turn pale. Rashes in the mouth are in the form of small sores or blisters with diameters of up to three millimeters, inside of which there is fluid. Bubbles burst over time, ulcers form. You can’t touch the sores, they are painful and the baby is crying. The mild form of herpetic stomatitis in children does not cause severe pain, the vesicles in the mouth are very small and after five days they disappear. But in the presence of moderate and severe forms of the disease, the number of vesicles increases, and the disease lasts longer – up to two weeks;
- children’s aphthous stomatitis. Diagnosis of this kind of ailment in older children usually does not cause difficulties. The child complains of discomfort in the mouth and education in the oral cavity. He also says that he cannot eat normally, especially acidic or salty foods, as well as very hot foods. Therefore, if aphthous stomatitis is diagnosed in children, treatment based on the complaints of an older child is carried out quickly and effectively. After a quick examination, the doctor will immediately detect aphthae that are located on the tongue, palate, inner surface of the cheeks and lips. Sometimes they can be on the gums. But with babies everything is more complicated. After all, they still cannot tell about their feelings, although they are all naughty and crying all the time. Therefore, the diagnosis and treatment of aphthous stomatitis in infants is more difficult. The unpleasant moment is that even a mild form of the disease causes a general malaise in infants – drowsiness, crying, refusal to eat, fever. Therefore, many mothers write off such symptoms on SARS, while they begin to stuff the baby with medicines. But in any case, you need to show the baby to the doctor, and even better – if the parents will examine the baby’s oral cavity every day;
- candidal stomatitis in children. At the initial stage of the disease, symptoms in children of stomatitis of this species may be completely absent. But as the fungus grows in the oral cavity, a curdled white film appears in the tongue. It can be in the sky or other places. Many parents remove this film and notice that problem areas begin to bleed. It hurts the child. The mucous membranes in the mouth are swollen and red, and if treatment does not take place, the corners near the mouth may crack, older children complain that the food is tasteless, and this happens with a loss of taste. If food is swallowed, pain and discomfort may occur;
- allergic childhood stomatitis. Symptoms of this kind of ailment include burning, dryness, and itching in the mouth. Older children complain of difficult swallowing of food, and taste sensations change again. When examining the oral cavity, swelling, redness, rashes in the form of erosion are noted. The language has a peculiar “varnished” look. Allergies can go to the lips, mucous membranes of the mouth and cheeks, tongue. Children may have a depressed mood and fever;
- bacterial pediatric stomatitis. You probably want to know how stomatitis of this variety looks in children. It is worth noting that the disease begins with a painful meal. It is especially difficult for a child to eat acidic foods and drinks, fruits, spicy foods and various marinades. In the future, redness and swelling of the mucous membrane in the mouth begins. There are ulcers, cracks, salivation intensifies, an unpleasant and pungent odor comes from the mouth.
If you look at the gums of a child, then they are loose and swollen, when you touch, bleeding begins. The whole child’s body begins to react painfully to the manifestation of the ailment – the temperature rises, there is weakness, the child has a headache and joints. If the infection falls on the tonsils – a sore throat appears.
Treatment of childhood stomatitis
It is clear that the question of how to cure stomatitis in a child is very worrying for all parents. First of all, you should contact a specialist. He will make an accurate diagnosis, determining the nature of the occurrence of the disease, and only then appropriate treatment is prescribed. The task of any parent is to strictly follow all the instructions of the doctor, because children, especially small ones, will not be treated.
It is worth noting that the process of treating stomatitis in children is not the same as in adults.
The first principle of therapeutic measures is to anesthetize, otherwise the child will refuse food and stop sleeping well, will become tearful and moody. The second principle of treatment is based on the treatment of the oral mucosa with drugs that the doctor prescribed. If necessary, medications are prescribed that can accelerate epithelization.
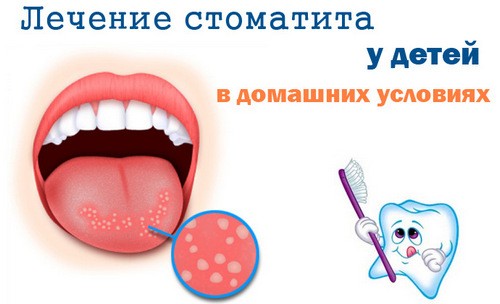
Remember that treating childhood stomatitis is different than treating an adult.
Medications
If stomatitis is diagnosed in children, a dentist appoints the treatment of this pathology. The treatment process itself depends on the cause that caused the disease. If a fungal form is diagnosed, then parents should regularly treat the child’s mouth with a bandage moistened with soda solution at the rate of 1 tsp. soda in a glass of boiled water.
Herpetic form of the disease is treated with antiviral drugs. It can be rectal suppository “Interferon” or “Viferon”. In addition, doctors prescribe medications that can relieve swelling – “Demidex” and the like. Dead cells on the oral mucosa need to be removed and this can be done with the help of chicken egg protein, it is bred in water and rinsed in the mouth.
If you are interested in how stomatitis of allergic origin is treated in children, then the first thing they will prescribe is anti-allergic medicine, then immunostimulating drugs are prescribed.
Some parents begin to smear their child’s mouth with green, but this can’t be done, because green can cause mucous burns. Hydrogen peroxide is also not suitable for this. It is best to use a five percent ointment “Acyclovir”.
To increase immunity, Imudon and Interferon tablets are prescribed. The Holisas gel is also quite effective, which has antibacterial, antiviral, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
General events
From the medical treatment of stomatitis in children there will be no use if the parents do not monitor the child’s hygiene and nutrition.
Therefore, you should adhere to such simple rules:
- the baby should wash his hands before eating, after going to the toilet and the like;
- all sweets and products containing sugar should be excluded from the child’s diet, because microbes love to develop in sugar;
- after eating dairy products, you need to rinse the baby’s mouth or pat it with a cotton swab with a soda solution;
- Boil a dummy more often or pour boiling water over it;
- if the baby is breastfed, the woman should wash her nipples before each feeding;
- make sure that the baby does not take dirty objects into his mouth;
- all family members who have herpes should urgently treat it to prevent infection of the baby.
Alternative method of treating stomatitis
Many parents are interested in how to cure stomatitis in a child with folk remedies and whether it can be done at all. Many folk recipes cope well with the disease, because it is not for nothing that our grandmothers used them for their children.
Healing ointments
We offer recipes for therapeutic ointments for pediatric stomatitis:
- take three cloves of garlic. Rub them on a fine grater and add the dessert spoon of yogurt to the garlic mass, after which mix everything well. Apply the resulting treatment mixture to problem areas in your mouth three times a day. But such a procedure is not suitable for very young children, for them it will be painful;
- take a leaf of aloe. Cut it and slice it on the sores in the mouth of your child. Older children can chew a leaf, especially if a large area in the mouth is affected by stomatitis;
- take a teaspoon of these components : natural honey, unrefined sunflower oil, one egg white and one ampoule of five percent novocaine. Combine all the ingredients, mix well and lubricate the affected areas with ointment.
Treatment of stomatitis in infants
Everything is much more difficult with these kids, but you can try these recipes:
- soda. In a glass of boiled water, dissolve a tablespoon of baking soda. Dip a gauze swab in a soda solution and begin to wipe the baby’s mouth, while carefully trying to clean the white coating;
- infusion of chamomile or calendula. A tablespoon of any flowers should be brewed in a glass of boiling water and insisted for one hour, then the infusion is filtered. Use the infusion in the same way as soda;
- the use of herbal preparations. They will help to heal wounds in the mouth faster. For this, rosehip oil or sea buckthorn, flax or peach oil is used. Kalanchoe juice is also good. Carefully treat the baby’s mouth with these drugs.
We hope that all of the above information has helped you, and now you know how to treat stomatitis in children. The most important thing – do not panic if you notice the first symptoms of this ailment, it does not pose a great danger, but this does not mean that treatment should not be given due attention. Follow all instructions of your pediatric doctor clearly and the disease will go away very quickly without any complications.
This material is for informational purposes only, before using the information provided it is necessary to consult with a specialist.



