Rheumatoid arthritis can be attributed to diseases, a characteristic feature of which is damage and destruction of connective tissue in the joints of the legs and fingers. Untimely diagnosis and treatment contribute to its transition to a chronic form, which causes severe pain and the appearance of functional disability in an adult or child.
Diseases of the articular joints are considered quite common. But the most dangerous form of this An ailment for an adult and a child is rheumatoid arthritis of the legs. The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that it sneaks up unnoticed, and the emerging symptoms are often disguised as other diseases.
Therefore, the true causes of pain can not be established immediately and the treatment may not be as effective as we would like.
The focus of inflammation in the joint joints of the legs and fingers most often occurs in the synovial bag and is accompanied by increased production of intraarticular fluid. Its accumulation in the synovial cavity contributes to venous and lymphatic congestion, which only aggravates the patient’s condition. With the further progression of the disease, the following processes are destructive: the head of the bone, cartilage, articular bag, tendons and ligaments.
As treatment practice shows, both men and women, whose age exceeded 30 years, are exposed to rheumatic pathology. But a feature is the fact that rheumatoid arthritis is three times more often diagnosed in the female half. However, the disease occurs not only in an adult, it can also be detected in a child. This form is called juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
Factors and causes of rheumatoid arthritis of the legs
A variety of reasons can provoke rheumatoid arthritis. But the main one is the rejection by the immune system of cartilage in the joint. Also, experts are inclined to believe that an increased amount of uric acid in the blood contributes to the onset of inflammation in the joints of the fingers and toes.
When identifying the cause of the pathology, one cannot ignore the hereditary factor. For people who have a predisposition to this disease, the occurrence of a certain combination of pathological processes and related factors is sufficient for rheumatoid pathology to occur.
In general, we can single out the main reasons that contribute to the development of the pathological process in the joint joints of the fingers and toes:
- virus attack;
- malfunctioning in the immune system;
- age-related changes;
- external factor;
- injuries and microtraumas;
- too much stress on the joint and base of the toes.
Rheumatologists have noticed the seasonal nature of the onset and exacerbation of this type of arthritis. With the beginning of lowering the air temperature, the number of complaints with complaints of joint pain increases several times. Experts tend to associate this feature not so much with weather conditions as with increased stress on the immune system.
Features of the development of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis of the legs
Despite the fact that the percentage of morbidity in childhood is quite low (no more than 1%), pathology can lead to irreversible consequences up to the child’s disability. Rheumatoid arthritis in children is caused by various circumstances, but the main reasons lie in the disruption of the immune system.
An inadequate response of the child’s immune system can occur against the background of such pathological processes as contact with a viral infection, severe and frequent hypothermia, untimely preventive vaccinations, and trauma to the joints of the legs and base of the fingers.
Symptoms in a child may manifest as an allergic rash, prolonged high fever, lymphadenopathy, myocarditis, and anemia.
Symptoms that accompany this disease in the initial stages of a child are almost the same as adults. But with further progression, children’s rheumatoid arthritis can go into the articular or articular-visceral form.
Signs of rheumatoid arthritis
initial stage
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are overwhelmingly manifested already at the initial stage. However, their prevalence can easily be misleading. The first bells warning about the development of pathology are discomfort in the legs and fingers, slight swelling and morning stiffness without any pain. Closer to the middle of the day, all the initial symptoms disappear, the stiffness in the movements disappears and good health returns to the patient.

Symptoms that occur in the initial stages of the disease:
- a slight increase in body temperature not exceeding 37-38˚С;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- fast fatiguability.
It should be immediately noted that, as such, pain at this stage of the disease is absent. Therefore, the patient does not pay special attention to the symptoms that appear. This is where the insidious arthritis lies.
Second stage
Further progression of the disease begins to make itself felt in the form of pain. Symptoms of the pathology also manifest as severe swelling of the joints at the base of the toes. In this case, swelling is symmetrical.
As for pains, they mostly increase until noon, and towards the evening they disappear altogether or become barely noticeable. At this time, the patient feels a slight relief.
However, closer to the morning, the pain syndrome returns again, the intensity of which can be compared with toothache.
The main symptoms characteristic of the second stage:
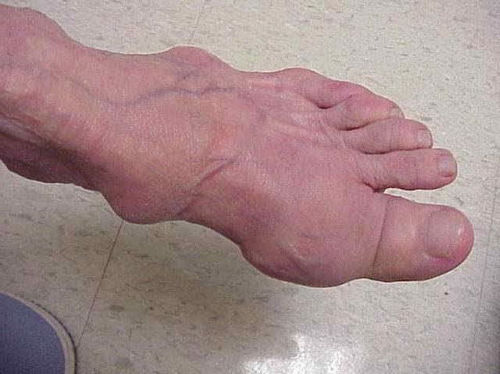
- joint deformities in the lower extremities and at the base of the toes ;
- severe swelling in the affected joints;
- severe pain;
- rheumatoid nodules on the joint, visible through the skin;
- damage to muscle tissue;
- limited movement.
Diagnosis of a disease of rheumatoid arthritis of the legs
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in an adult or child is largely dependent on correctly conducted diagnostic studies. The diagnosis of this disease is complicated by the fact that the early symptoms are non-specific.
In most cases, from the moment of inflammation in the joints to the establishment of an accurate diagnosis, at least 9-12 months pass. And typical clinical signs can be seen after 1.5-2 years.
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is established by the following studies:
- blood test (general);
- synovial fluid examination;
- radiological changes;
- bone scintigraphy.
- MRT.
Therapeutic therapy
Treatment of pathology should be systemic and comprehensive. Only in this case, rheumatoid arthritis can be forced to retreat. It is possible to effectively relieve symptoms, control the course and prevent the re-emergence of the disease using both medical treatment and physiotherapy, as well as correction of nutrition and lifestyle.
Basic therapy
Treatment of rheumatic pathology with the use of medications is aimed at reducing pain and inflammation in the joints of the legs and fingers, as well as restoring lost functions. Choosing therapy, the doctor takes into account the age, general condition of the patient, the degree of activity of the process and the location of the foci of inflammation.
Basic treatment involves the appointment of three main types of drugs:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They can be aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, etc., help reduce the inflammatory process in the joint tissues, reduce swelling and pain. In order to reduce their harmful effects on the gastrointestinal tract and on the whole body, they must be taken with food or with antacids and inhibitors;
- corticosteroids. Drugs of this type are prescribed in the form of tablets or injections into the joint cavity. The need for them arises with the transition of the disease to an acute form or in the case of ineffectiveness of non-steroidal drugs. Usually prescribed in short courses. Taking medications may be accompanied by side effects such as cataracts, weight gain, atrophy of muscle tissue, and thinning of the skin and bones.
Non-medicinal cure
A good effect on rheumatoid arthritis is provided by physiotherapy, the choice of procedures for which depends on the stage and form of the disease.
During exacerbation, the use of non-aggressive dry methods is recommended:
- magnetic therapy;
- UV radiation;
- laser and cryotherapy.
For rheumatoid arthritis that does not have an acute phase, the following are suitable:
- massage sessions;
- treatment of the affected area with infrared heat;
- mud applications;
- therapeutic baths.
The final phase will be treatment at balneological resorts, which is allowed to be carried out no earlier than two months after basic therapy. Balneotherapy includes the appointment of mud applications, radon and salt baths. Procedures do not contribute to improving blood circulation in the affected joint and restoration of joint tissues.
Prevention of foot rheumatoid arthritis disease
The effectiveness of the treatment depends on the age of the patient and the general condition of the body. However, a huge role in maintaining the result will be a person’s lifestyle. Therefore, good nutrition, containing a large number of fresh vegetables and fruits, physiotherapy exercises, as well as the elimination of all bad habits should be the basis that will help to exclude the return of this insidious disease.
In addition to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, I would like to advise readers to be sensitive to their own feelings.
The human body is a hypersensitive biological machine capable of self-regulation. Therefore, timely response to signals and respect for its resources will help to avoid serious failures in the system.