FGDS – a procedure during which the upper digestive canal is examined . Allows you to identify various pathologies. There are two methods of conducting: through the nose and through the mouth. The publication considers the advantages and disadvantages of each method, describes for what purposes they are suitable.
Many agree that the transnasal diagnostic method is more convenient for humans. It is important to understand that only the doctor can prescribe the optimal study option.
Today, more comfortable methods that can turn a visit to a doctor into a pleasant walk are beginning to develop more and more actively.
FGDS through the mouth
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) is the most informative method for examining the surfaces of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum.
Advantages of the procedure:
- Getting a lot of information on the problem under study.
- Security.
- Relatively easy tolerance by patients.

Important recommendations before the study:
- The last meal is 12 hours before the procedure.
- Do not smoke 3 hours before the examination.
- Do not take medication in capsules.
- Tell your doctor about your allergies.
- Do not drink water immediately before the procedure.
- Do not chew chewing gum.
- Set yourself in a positive mood.
- Follow all doctor’s advice.
FGDS allows you to identify a number of diseases: gastritis, gastric ulcer, cancer, the presence of an inflammatory process, duodenitis and polyps.
FGDS through the nose
The development of a new direction in endoscopy was dictated by the stressful state in patients. Many people experience a classic fear of being strangled during a classic mouth test. This is due to negative experience during previous procedures.
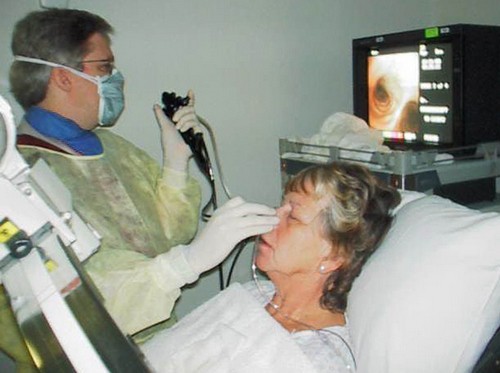
The essence of transnasal endoscopy: the introduction of the camera through the nasal passages. Main advantage: no need to swallow the probe. A variant of local anesthesia is used with a 10 percent solution of Lidocaine.
Indications for the procedure:
- The presence of complaints (nausea, heartburn, pain in the upper abdomen).
- Gastritis.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Monitoring the dynamics of existing diseases.
- The inefficiency of the therapy.
- Inability to carry out FGDS through the mouth (there is a strong gag reflex, fear of suffocation).
The disadvantages of the method:
- There is a risk of damage to the nasal mucosa.
- The risk of bleeding increases.
The study is performed with an empty stomach. The patient should not eat food 10 hours before the procedure. List of allowed drinks: water without gas, tea without sugar.
Algorithm for conducting FGDS through the nose:
- Treatment of the nasal passages with a gel that contains foam suppressants.
- A person is helped to take the correct position (on the side).
- The introduction of a gastroscope on the threshold of the nose.
- Assessing the width of the strokes.
- The introduction of the device into the upper parts of the nasopharynx.
- Lowering the gastroscope to the esophageal sphincter and below.
- A study of the gastrointestinal tract.
After the procedure, bloating may be observed, it passes without a trace.
Similarities
FGDS through the nose and through the mouth allows you to assess the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, endoscopic studies make it possible to conduct a biopsy, polypectomy and stop bleeding.
Visual methods allow the doctor to identify erosion, ulcerative changes, tumor processes, as well as evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Thus, a specialist can get a complete picture of the ongoing changes in the gastrointestinal tract.
What are the differences
The differences in the procedures are presented in the table.
| Criterion | FGDS through the nose | FGDS through the mouth |
| Gastroscope contact with sensitive areas | Not available | Is available |
| The presence of a gag reflex | Is absent | There is a urge to swallow an instrument |
| The need to take sedatives | No need, the patient has a stable emotional state | Sedatives should be used |
| The presence of pain | Are absent | The patient is in pain |
| Ability to talk during the procedure | A person can talk with a doctor | Is absent |
| Duration of the procedure | Shorter procedure compared with endogastroduodenoscopy by mouth | 10 minutes |
| The ability to eat immediately after the study | You can eat right away | Do not eat right away |
| Treatment costs | Less costly method | A large number of medications are used, this increases the cost of treating the patient |
| Endoscope size | Small | Larger equipment |
For what purposes are better suited
Nasal gastroscopy is best used in the following cases:
- There is a need for additional examination of the nasopharynx and larynx.
- There is a urge to vomit.
- The patient is required to report a condition in any part of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Only local anesthesia (based on lidocaine) can be used.
- Children’s age (babies are usually in an excited state, it is difficult for them to do the classic procedure).
- Complete intolerance to pain.
- Swallowing reflex is difficult.
Phagogastroduodenoscopy is performed in a number of cases:
- A person experiences discomfort when a foreign body is introduced into the nasopharynx.
- Bleeding from the nose.
- There is a need to introduce additional equipment.
- Curved septum of the nose.



