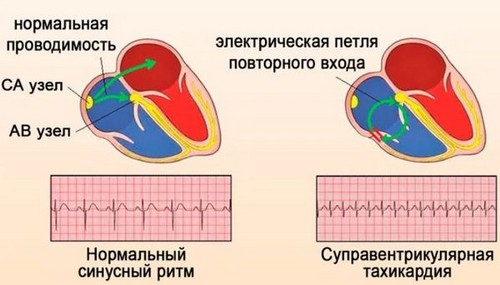
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is a condition characterized by sudden attack of palpitations and the same sudden termination, at the same time heart rhythm disturbances.
This type of tachycardia is generally caused by increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system, but may be a consequence of the disruption of electro conductivity of the heart.
The types and code in ICD 10
Usually the attack occurs on the background of stable General condition, the duration of the attack varies from several seconds to several days, and there are:
- unstable version (in which the electrocardiogram is recorded from three cuts in 30 seconds);
- stable version (lasting more than half a minute).
According to ICD-10 release:
- atrial supraventricular tachycardia;
- atrioventricular (nodal).
Supraventricular tachycardia in ICD 10 has the following code – I47.1.
The symptoms paroxysms
Different types of supraventricular tachycardia give slightly differing from each other in the clinical picture:
- Attacks of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia are usually held for a person malozamechennyj because of its short duration and limited to a dozen excitations of the myocardium, a typical option is the duration of the paroxysm of the order of several seconds, the most sustained attack for about a few minutes. Accordingly, the subjective symptoms of supraventricular tachycardia may be absent. The attacks can happen again, the influence of the autonomic nervous system, which leads to their rapid completion. The most common complaint usually is a sudden sensation of palpitations, low-intensity attack of vertigo.
- Atrioventricular paroxysmal tachycardia more policemen, palpitations occur abruptly, and can have a duration from several seconds to days. Less than half of patients palpitations notes not on the forefront of an attack of pain in the heart area and dyspnea present even at rest. Vegetative reactions such as sweating, feeling short of breath, weakness, changes in blood pressure are less common here as the body’s response can be attributed to the increase in the volume of urine output.
Paroxysm of supraventricular tachycardia in the presence of chronic heart disease may provoke States that are close to the clinic to fainting, which is associated with short-term disruption of the power supply to the brain due to the low intensity heart rate rapid and occur because of this oxygen deficiency.
Supraventricular tachycardia on ECG has a number of special features:Signs on ECG
- Atrial tachycardia:
- the presence before each ventricular complex readjustment of P wave, or even negative, which indicates that preservation of the sinus rhythm in this type of tachycardia;
- no changes in the ventricular complexes, neither the size nor the form, which indicates their lack of interest when a paroxysm of atrial fibrillation;
- it may be a lengthening of the PQ interval greater than 0.2 sec. It should be borne in mind that in atrial tachycardia the heart rate is usually not more than 135. In addition, if the ECG-signs with a higher number in this indicator indicates atrial tachycardia should be regarded as multifocal.
- Atrioventricular tachycardia:
- ECG-signs of supraventricular tachycardia are characterized by the fact that the prong R is negative, it is merging with the ventricular complex, or atrial prongs did go for him, or superimposed on the ST segment;
- ventricular complexes intact, which indicates that their size and amplitude in the normal range;
- the paroxysm of atrioventricular supraventricular tachycardia precedes extrasistole with the so-called critical coupling interval, and after the reflected paroxysms of supraventricular tachycardia occurs in compensation pause;
- usually the heart rate during supraventricular tachycardia is atrioventricular about 150-170 beats per minute, however, can reach 200-210 beats.
Treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
Largely with supraventricular tachycardia treatment depends on hemodynamic variables. If the stability of hemodynamic parameters, it is often the doctors or even the patient himself, if he is properly trained, resort to the use of vagal samples.

One of the most simple, and often effective, especially if we are talking about paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, called the Valsalva test:
- The patient is instructed to hold the breath for 20-30 seconds, while he seemed to nutriiveda.
- The ineffectiveness of acceptance from the first attempt, it is recommended to repeat up to 5 times, until the normalization of condition, disappearance of the ECG characteristics of supraventricular tachycardia or subjective symptoms of the person as palpitations, anginal pain, dizziness, severe weakness.
The easiest to perform, especially in the presence of a health worker or relative is a sample Aschner is a soft, but tangible enough to achieve the effect of pressure on the eyeball of the patient with the fingers of a stranger, the duration is short, about 3-5 seconds, but should be used with caution to avoid damage to the anatomical structures of the human eye.
In satisfactory physical condition, no problems, the patient with the knee and hip joints, use a test with a squat squat, squat deep, and repeat a few times.
At home has the right to life reception through lower face in a bowl of cold water, is hold your breath for 15-20 seconds if possible, this sample requires a satisfactory General condition and required monitoring of the patient, as in supraventricular tachycardia there is a tendency to syncope States.
Health workers most commonly used the sample with the use of carotid sinus massage. For this patient the tuck, head turn to one side and to exercise a soft massage movements in the projection of the carotid sinus to achieve the effect and decrease heart rate.

The simplicity and accessibility, as well as a fairly high efficiency vagal samples makes them indispensable as a first stage of assistance with supraventricular tachycardia, but there are a number of contraindications, in which their use is not recommended:
- syndrome sick sinus;
- cerebral infarction in anamnesis;
- pronounced symptoms of heart failure;
- glaucoma;
- versions of heart disease in which there are violations of the pulse at the cardiac conducting system;
- encephalopathy of any Genesis, etc.
If the above techniques do not give effect to either of the implementation is difficult or contraindicated, for further assistance use of medications:
- 10 ml of a 10% solution of procainamide intravenously in physiological solution, the introduction is carried out under the strict control of heart rate and blood pressure,
- if no effect is used with pre-cardioversion sedation diazepam.
In unstable hemodynamic performance of any non-pharmacological methods are excluded, as the patient’s condition becomes heavier and it takes you to complete vagal sampling time can be not only inefficient, but also dangerous for the patient. Immediately injected intravenously 5cc of 0.5% solution of diazepam and standards 100-200-300-360 is cardioversion.
Forecast
Supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia in itself is one of the most favorable types of tachycardia, as the attacks are intermittent and usually a little painful for the patient, and thus the saving rate, which significantly improves the prognosis of the disease.
The symptoms and treatment of supraventricular tachycardia is strictly individual. However, patients with this diagnosis should be seen by a cardiologist on a residence, regularly monitor the pulse, systematically take ECG, constantly take prescribed drugs cardiologic to treat concomitant pathology, to avoid complications and transition of this state is more dangerous.
Other types of tachycardia
Cause of human heart rate can not only be of supraventricular origin. Other options are the following:
Ventricular
Symptoms of this type of tachycardia is nonspecific, but at worst case the heart rate more than 210, develops severe hypotension, stenokardicheskie pain in the heart area, attacks of loss of consciousness, etc. ECG-signs mostly consist of obvious changes of the ventricular complex, it expands, can change its polarity in the ECG is often reminiscent of a blockade feet beam gissa, disturbed coordination between the Atria and ventricles.
Sinus neparoxizmale
Option to increase your heart rate more than 90 beats per minute while maintaining normal sinus rhythm. Usually do not endanger human health and often situational due to physical exertion, stressful situations. On ECG no specific changes, except for the heart rate.
Conclusion
- Supraventricular tachycardia is the condition that is usually well-relieved non-pharmacological methods of treatment, namely, vagal samples.
- The effectiveness of their use in this type of tachycardia is 80%.
- This allows you to quickly provide help anywhere, including to perform some of the samples themselves and thereby reduce the risk of life-threatening conditions.