When a doctor prescribes EGD of the stomach, for many patients, this becomes bad news. Fear of this kind of research is very common but in spite of all the disadvantages of the method, it remains one of the most effective manipulations for the diagnosis and prevention of diseases of the stomach.
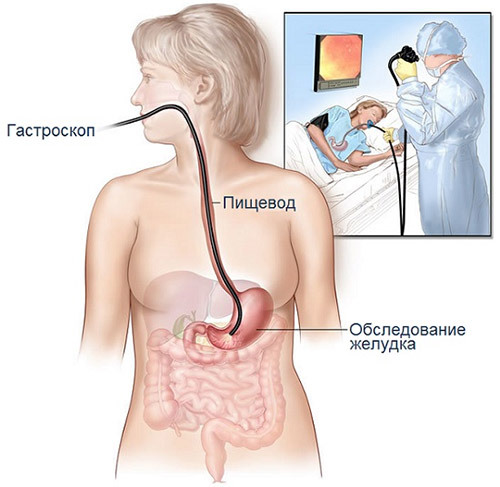
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy – the survey-overview the endoscopic equipment. Gastroscopy is used to visualize internal organs. The screen image transmitted from the camera located at the tip of a thin tube – probe, equipped with a fiber optic system.
It is inserted through the patient’s mouth, gently held in the esophagus, and through the eyepiece or a monitor that shows the stomach and the surface of the alimentary canal, the doctor examines the body. The result of the research is the conclusion about the presence and stage of the disease. Decoding the received data produces only a specialist.
Most often, EGD is used to find undeveloped much of the disease of the gastrointestinal tract, promptly proceed to their treatment or removal, if we are talking about tumors.
What the survey shows?
On the monitor screen during the EGD shows the surface of the stomach and esophagus. Gastroenterologist can be assessed by various changes of the mucosa, on the basis of the result of the findings of cross bodies. If inside are bleeding, with the help of FGS, you can determine its exact location and completely eliminate the problem.
Using the gastroscope, the doctor can see:
- If the stomach and esophagus any dangerous growths.
- Where are localized scars, polyps, wounds, normally if the cavity.
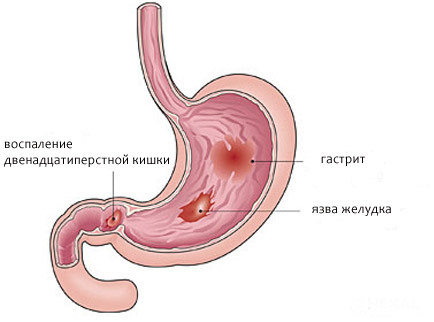
- Is there a dangerous bacterium Helicobacter pylori, causing gastritis, peptic ulcer disease and complicating their disease.
- Existing ulcers and the threat of perforation.
The patient receives a certificate, a conclusion about the condition of his internal organs.
How to prepare?
To ensure that the survey went without complications and unpleasant noise, the patient must comply with the following guidelines:
1. Study on an empty stomach. The last time before the procedure the patient need to eat 7-8 hours before the appointment.
2. That day, when will be the examination of the FGD, prior to the examination should not drink even water.
3. A week before the reception stop eating irritating foods, drink alcohol, to smoke, to try to lead the normal lifestyle for the establishment of safe acidity.
4. Some pharmaceuticals have a negative impact on the gastrointestinal tract and distort the results of the study. To avoid this, the patient should discuss beforehand with the doctor the appropriateness of suspending such drugs.
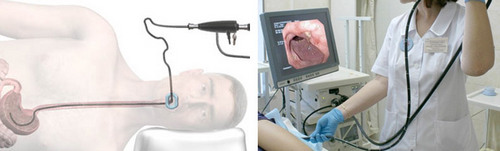
Testimony
Gastroenterologists appoint an EGD in a few cases:
- 1. If a patient is diagnosed inflammation of the walls of the esophagus – esophagitis.
- 2. Age – more than 40 years. When you reach that age, the annual survey is a necessary measure to prevent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- 3. Acute or chronic gastritis.
- 4. The varicose veins.
- 5. Chemical and thermal burns.
- 6. Gastro-esophago-reflux disease (emission of hydrochloric acid from the stomach into the esophagus with subsequent injury to its walls. Normal this should not happen).
- 7. The occurrence of various non – malignant and malignant tumors.
- 8. Ulcer perforation, bleeding.
- 9. Pyloric stenosis – a sharp reduction in the output Department because of the appearance of the scar.
Contraindications
This survey method is very accurate, but there are limitations, as with any physiotherapy. Only a medical specialist decides whether the research method EGD, and can give a negative response if the patient has:
- 1. A strong narrowing of the esophagus.
- 2. Pregnancy (depending on the time, position of the fetus, the General condition of the mother and the embryo).
- 3. Aggravation of inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
- 4. The acute phase of myocardial infarction or stroke.
- 5. Violation of cerebral circulation.
- 6. Mental illness.
- 7. Infectious inflammatory diseases of upper and lower respiratory tract (sore throat, tonsillitis).
- 8. Aneurysms of the aorta.
- 9. Hemophilia.
- 10. The aggravation of bronchial asthma.
- 11. Strong stomach bleeding.
- 12. General weakness, malaise, the deterioration of the patient.
- 13. Deviations from medical standards of weight: obesity or, on the contrary, anorexia.
- 14. Pulmonary failure.
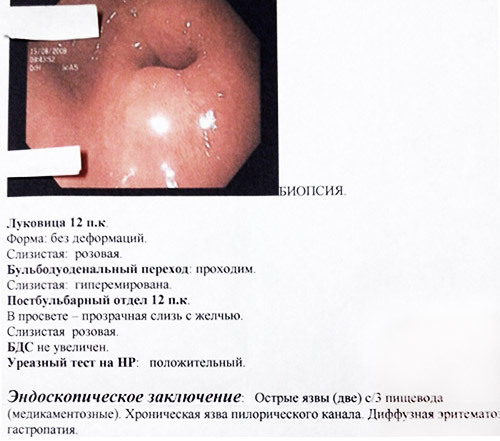
Evaluation and interpretation of results
A transcript of the survey and put yourself properly diagnosis the patient can not. You need to remember that the meaning of some indicators, especially if there is a serious threat to health and life.
On the resulting certificate will contain the following results:
1. Evaluation of the esophagus: is determined by the colour inside, slimy coating, the degree of permeability. The doctor identifies the presence of lesions, adhesions and other changes, which the norm cannot be a healthy person;
2. Seen the place of transition of the esophagus into the stomach (kardiya). Assesses the degree of its closure. The status “hiatus” cardia decoding is simple – not closing. This is the first symptom of reflux disease.
3. Stomach. Estimated color of mucosa, presence of tumors, ulcers, pramodini, folds on the surface of the body. If EGD of the stomach shows that was discovered bleeding and ulcers, necessarily determined by their size and degree of hazard.
4. The inner contents. In the norm it should be transparent, with a small admixture of mucus. Unacceptable color change, accumulation of fluid, dark brown or red blotches.
5. Estimated pylorus – pyloric Department. It needs to be anatomically not changed and easily passable. The appearance of scars and deformations is determined by their degree of deviation from the norm and nature of origin.