Depending on the objectives pursued esophagoscopy is therapeutic (removal of small tumors, coagulation of bleeding ulcers and erosions, foreign body removal) and diagnostic (determining the cause of pain, dysphagia, bleeding, structural changes of the esophagus), emergency and planned.
Esophagoscopes study is carried out by endoscopists with greater caution, since the parts of the digestive tract is located in close proximity to many vital organs.
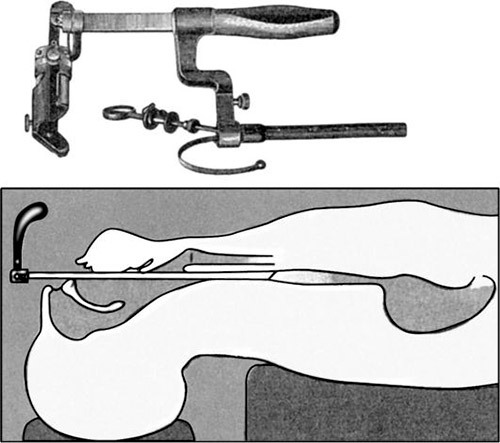
This term is necessary to understand the method of endoscopic examination of the esophagus, performed using a special optical instrument – esophagoscope. This device usually consists of a halogen illuminator, handle, set of tubes of various diameters and lengths, and additional devices (e.g. batteries, forceps, hook, nozzles for suctioning mucus). Design esophagoscope usually flexible, that is its Central element is an elastic fiber core, but also hard the device, the base of which is a hollow metal tube.
Methods of examination of patients with pathology of the esophagus, not very different from the models used in the examination of other internal organs. Patients are also interviewed for the presence of complaints of certain symptoms, examines the history of disease and life (General medical history) and, of course, is an objective study which plays an important role esophagostomiasis method.
During the procedure, esophagoscopy specialists pay attention to the following aspects:
- peristalsis and the diameter of the esophagus;
- the color of its mucous surface;
- folding;
- vascular pattern;
- the presence of tumors.
It is worth noting that different age groups have their normal values. So, for example, in young patients during the inspection must be clearly visible longitudinal folds. The elderly owing to atrophic processes, on the contrary, are not visible, but the greater severity of becoming a venous plexus and is not considered a deviation from the norm.
How is ezofagoskopia diagnosis?
Since this method is largely similar to the gastroscopic (difference from esophagoscopy gastroscopy only in the fact that in the first case, the study is subject only to the esophagus, and the second – the whole upper gastrointestinal tract, i.e. the esophagus + stomach + duodenum), the preparation directly to him and his conduct is also similar.
Thus, if inspection of a hollow muscular tube is scheduled for the morning, it is produced on an empty stomach. In the case of passing esophagoscopy after dinner, a light Breakfast is allowed 6 hours before the procedure. As for anesthesia, quality and technology directly influenced the success of the survey, because any touching of the pharynx, soft palate, arches causes discomfort and reflex retching. To mitigate such a painful condition endoscopists use one of the options for anesthesia: local or General.
Local anesthesia of the pharynx with esophagoscopy usually is such anesthetics as Xylocaine and Lidocaine. The desired effect is reached when a person is non-responsive cough, gag movement to the lubrication of the lower part of the pharynx and the entrance into the esophagus. After anesthesia the doctor asks the examinee to open his mouth and stick out his tongue to enter esophagoscopy in the upper part of the digestive canal. If the purpose of the procedure diagnosis of the pathological state, esophagoscopy is carried out using a flexible fiber optics device, and the patient between the teeth additionally inserted the mouthpiece (mouthpiece). In the case of the extraction of the esophageal foreign body, or biopsy specialists use hard esophagoscopy made of steel tubes.
We should also mention the position of the patient during examination under local anesthesia. Usually it takes posture lying on left side or back. Esophagoscopy is less often sitting on a special chair – the chair of Brunings. In this embodiment, endoscopists require additional assistant, who is behind the patient to hold his shoulders and head in the right position.
General anesthesia is used by doctors in exceptional cases, for example, under such aggravating factors as:
- inflammation or injury of the wall of the hollow organ;
- bleeding;
- fixing large object in the throat or the cervical, thoracic, abdominal (ventral) division;
- muscle spasm;
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular system;
- mental disorders;
- deaf-mutism.
Technique esophagoscopy with several distinctive. First, the examination is always held in the horizontal position on the back. Second, the specialist opens the patient’s mouth with the fingers of the left hand and pushes through the corner to the entrance of the esophagus the tube esophagoscope.
Training
In addition, the study should be done on an empty stomach to reduce the gag reflex, the patient needs to adhere to several other rules of training:
- 1. to pass the examination of the cardiovascular system;
- 2. to donate blood and urine for laboratory tests;
- 3. an x-ray of all the organs;
- 4. observe careful hygiene of all parts of the body;
- 5. be removed before the session esophagoscopy dentures (if any);
- 6. shortly before the procedure to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution.
Training from the specialist involves the following steps:
- forceps, tubes, probes and other fixtures esophagoscope (except handle with lighting device that are processed with alcohol) are subject to mandatory disinfection by boiling;
- disinfected instruments are arranged so that a desired were located closer to the doctor-endoscopist or surgical nurse;
- room, which is esophagoscopy should be moderately dark, that is, the health worker performing the role of an assistant, sees a seamless and delivers the needed equipment and daylight it does not interfere with the passage of the session.
Indications and contraindications
Esophagoscopy was performed in all cases, when the patient is showing signs of diseases of the esophagus: dysphagia, pain, and bleeding from the upper part of the alimentary canal, dyspepsia (heartburn, esophageal vomiting, belching). In addition to diagnosis, the procedure may pursue the therapeutic purpose, so it is used for emptying of the diverticulum, filled with the food mass, pulling foreign bodies, excision of small tumours, begerovaya and dissection of the cicatricial structures.

Contraindications for esophagoscopy are:
- 1. cirrhosis of the liver on the background of the dilatation of the lower segment of the esophagus;
- 2. aortic aneurysm;
- 3. a sharp narrowing of the tubular body, which made impossible the passage of esophagoscope;
- 4. States that require absolute rest (for example, decompensated heart disease, acute period of stroke, myocardial infarction).
Endoscopists can also refuse to perform the procedure, if the patient does not fit the conditions of preparation.
The price of the survey with the help of esophagoscope, of course, every region is different, but the average across Russia cost of services is as follows: diagnostic esophagoscopy – 1400 roubles, the medical-diagnostic – 2500.



Agreed- people have an obligation not to take this for granted issue any longer. And?
I really prize your piece of work, Great post.
I appreciate the nuance in this article, however I would like to read more info from you soon.
Would you expand on this?
I will immediately grab your rss as I can not find your email subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
I enjoy what you guys are up too. This sort of clever work and exposure! Keep up the fantastic works guys I’ve you guys to blogroll.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I
appreciate you penning this post plus the rest of the website is very good.