In the maintenance of self-regulation processes of the human body, namely, the ability to maintain constant internal state of the vital systems of the kidney play a leading role.
Contained in urine complex molecular compounds can keep low-soluble substances in the dissolved condition and in the minimum concentration.
During the day, the kidneys of a healthy person excrete up to 0.4 grams of neutral fat and to 0.24 grams of phospholipids. The presence in the urine of significant quantities of fatty acids, which creates on the surface of urine visible fat film called Liberia.
Their functional activity is:
- in allocation of end products of metabolism;
- maintaining acid-base and water-electrolyte balance;
- involvement in hormone secretion;
- the regulation of blood pressure.
In our article we want to tell at what pathological and physiological conditions appears fat in the urine, the causes of this phenomenon and ways of its treatment.

What is the fats, their biological role in the human body
Organic substances that are present in the structure of tissues are called fats.
They include the following fat – like compounds- lipids:
- triglycerides (neutral fat) is represented by fatty acid esters of glycerol;
- biologically active substances – sterols, various vitamins, phosphatides.
In the human body the largest amount of data of organic compounds contains subcutaneous adipose tissue and adipose tissue are:
- in a fold of visceral peritoneum – omentum;
- one of the ligaments of the abdominal cavity, the mesentery;
- retroperitoneal (retroperitoneal) area.

Muscle tissue, liver, bone marrow also contain a significant amount of fat.
Their biological role is that they are constituent elements of the cellular structure and necessary:
- for plastic functions (build new structure);
- the implementation of the processes of human life;
- provide mechanical protection and insulation of organs.
The fat included in the tissues of the human body, is a “reservoir” of nutrients and is actively involved in metabolic processes and energy supply of the body
Lipid metabolic disorders are the main cause of lipuria
Lipid metabolism begins in the digestive tract from the process of breakdown of fats under the influence of lipases (water soluble enzyme). The first phase emulsification, an important role in the crushing of the fat to the smallest particles designated the bile acids and their salts. Further, the process of dissolution of organic compounds occurs in the epithelial layer of the small intestine – there is a continuous fat synthesis of triglycerides, which are absorbed from the intestine.
The presence of a person of small bowel diseases, colitis, dysentery, violates the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and fatty acids.
Lipid metabolism disorders can occur when the disorder of processes of digestion and absorption of food is observed:
- with the development of pathological processes in the pancreas;
- insufficient flow of bile into the intestine which can be caused by various reasons;
- diseases, which are accompanied by acceleration of passage of food through the digestive tract;
- functional and organic lesion of the mucous membranes of the intestine.
Disorders of digestion and absorption of fatty compounds can be caused by a group of diseases of unknown etiology such as:
- celiac disease in child – poisoning the child’s body by the products of undigested proteins;
- spontaneous fatty diarrhea.
The release of fat is through sebaceous and sweat glands and intestines. In feces and urine a negligible number of organic compounds.

When excess sebum by the sebaceous glands (seborrhoea) have vitamin deficiency and diseases of the skin – eczema, acne
In violation of fat metabolism in the stool may contain large amounts of fatty acids – this phenomenon is called “steatorrhea”. Lipuria manifested by the appearance on the surface of urine stains.
This phenomenon most often occurs when:
- the consumption of food containing large amounts of fat;
- lipoid nephrotic syndrome (a fatty degeneration of the renal tissue);
- injury to a large area of adipose tissue;
- fractures of the limbs.
In disorders of fat absorption complete exclusion from the diet food is unacceptable – with the human body receives the vital elements and vitamins. Although fat-like substance easy responsible for the generation of the intermediate metabolic products of carbohydrates, inadequate intake of fatty substances from food provokes the development of human deficiencies.
The composition of fats of natural origin always contain the highest essential omega-6 fatty acids – monoprotic linoleic acid with double bonds C18H32O2, and C18H30O2. Insufficient intake of food triggers the development of chronic skin pathologies that occur in the necrotic lesions of tissues. It is believed that the complete absence of unsaturated fatty acids may also cause disorders of fat metabolism.
The fat content in human blood
Circulating blood through the vessels contain sterols, free neutral fats, phosphatides. Their number depends on the food load, age of the person and his physiological state. Normal total concentration of fat in the blood ranges from 390 to 590 mg. However, diagnostic importance level of content of individual fractions of organic compounds and the relationships between them.
High concentration of neutral fat is a sign of violation of processes using fatty acids that enter the body with food. This phenomenon testifies to the increased synthesis of cholesterol is necessary for vital activity of organism, excessive amounts of which contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
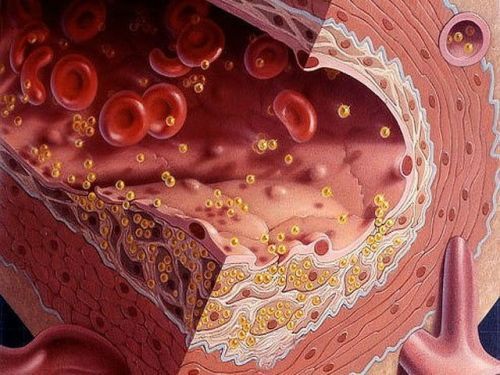
High concentration of cholesterol in the blood forms in the blood vessels ‘ walls cholesterol plaques, the dangerous lesions of the arteries of the heart muscle
Increasing the amount of fat in the blood – hyperlipemia – accompanied by prolonged starvation and certain pathological processes, such as:
- nephrosis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- exudative diathesis;
- acute hepatitis.
Increasing the concentration of lipids in the blood also occur if the intoxication of the organism and lack of adrenal function, thyroid and sex glands. When hyperlipemia, the cause of which was abundant intake of fat from food (most often after the use of castor or almond oil, fish oil, the reception is prescribed to children), characterized by the appearance of alimentary lipuria.
A pathological condition appears when:
- phosphorus poisoning;
- alcohol intoxication;
- urolithiasis;
- severe form of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Reducing the level of fat in the blood – hypolipemic characteristic of hypothyroidism and malnutrition.
Causes of lipuria
Urine from a healthy person contains only about two milligrams in one liter of fat – due to the content of organic compounds in the epithelial cells of the urinary tract. People suffering from severe form of diabetes, the kidneys secrete a slightly larger number of lipids. This condition is due to the fact that the digestion and absorption of triglycerides is directly connected with the processes of carbohydrate metabolism.
The composition of the human body contains up to 20% of various fats, but in some cases the number reaches more than 45%. The most common cause of this phenomenon – alimentary obesity due to consumption of high-calorie food with minimal energy costs. Excess carbohydrate in foods are easily digested and converted into fat.
Morbid obesity is the result of violations of neurohumoral regulation of fat and carbohydrate metabolism is observed in disorders of functional activity of endocrine organs:
- deficiency of hormones of adenohypophysis, thyroid, sex and adrenal glands;
- excess secretion of biologically active substances of islet of the pancreas.
Excessive accumulation of fats in various tissue cells contributes to their destruction and dystrophic changes
Disorders of lipid metabolism are the cause of development in the human body of various pathological processes. Violation of the mechanisms of intracellular (interstitial) metabolism of carbohydrates and fats leads to the development in humans of serious complications.
Drops of fat floating on the surface of urine may indicate pathological conditions such as:
- severe pulmonary tuberculosis;
- the crushing of the subcutaneous fat;
- kidney stones;
- inflammatory and malignant processes in the urinary organs;
- fat embolism of the capillaries of the kidneys;
- diabetes mellitus;
- cardiovascular disease;
- complicated fractures of tubular bones.
Lipuria recognized macroscopically by the presence on the surface of urine as if”fat” film, microscopically – on grease in the urinary sediment. Carrying out such medical procedures as probing (method of diagnosis and treatment) of the urinary system answers the question of why is the “fatty urine”.
During mechanical expansion of the cavity of the urethra, or urinary pozravlyat special metal fixture – the bougie, it is lubricated with sterile glycerin to reduce injury to the body.
Remediation of disorders of fat metabolism
With physiological obesity to struggle not so difficult, one of the methods is the preparation of a full diet with restriction of consumption of carbohydrates but sufficient amount of organic acids, vitamins, fats and proteins.

In disorders of fat metabolism due to a variety of pathological conditions used medicines containing lepidosirenidae funds
The mechanism of action of these drugs (statins) is inhibition of the enzyme activity, which is involved in the conversion of fats.
Currently the most effective lipid-lowering means are:
- Simvastatin is indicated for elevated concentrations of total cholesterol, increases the risk of atherosclerosis and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system. Appoint 20 mg 1 times a day.
- Pravastatin reduces the risk of developing diseases of the heart and vascular systems, does not require conversion in the liver. The recommended dose is 20 to 40 mg per day.
- Fluvastatin prevents development of unstable angina, myocardial infarction and other cardiovascular complications. The drug sparing effect on the hepatocytes (liver cells), it is possible to use a special form of 80 mg per day.
- Atorvastatin dosage 80 mg a day is used for the rapid reduction of lipid levels. Reception of 20 mg per day will help normalize the concentration of total cholesterol in patients with cardiac ischemia (reduced blood supply). Doses of 10 mg / day is sufficient to adjust lipids with a moderate increase in blood pressure and mild diabetes.
- Rosuvastin is the most effective statin to reduce lipid levels enough dose 5 -10 mg per day. The maximum dose (40 mg daily) is used when the patient has a pathological condition with a very high risk of cardiovascular complications.
In conclusion, I want to note that the appearance on the surface of urine droplets or film of fat is a serious reason for concern. Lipuria directly related to the presence of a large number of unsplit lipids in the blood. To find out the causes of this phenomenon it is necessary to seek the advice of a qualified medical specialist and pass a comprehensive examination, including laboratory and instrumental methods.



Thanks for sharing useful information!
I found your web site from Google as well as I have to state it was a terrific discover.
Many thanks!
I ‘m fairly certain that you are acting preachy in this argument solely to attract attention.
Hey there, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog in Ie, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, terrific blog!
I couldn’t disagree more- except I couldx :p
Your common sense should be accepted as the standard when it comes to this topic.
Toller Artikel. Vielen Dank.