Urinalysis is a laboratory diagnostic method used to detect inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system and other pathological processes in the body of the subject.
Normal human urine is transparent, it has a light yellow or straw color, so any change in color should give the doctor the idea of beginning of a disease. The urinary sediment contains elements such as leukocytes, erythrocytes, epithelial cells and other components in small quantities.
When the concentration of leukocytes in urine exceed the maximum permissible figures, this means that the patient will be determined by the pus in the urine.
In medicine there is a term pyuria, which means the appearance of pus in the urine. It is also widely used the concept of leukocyturia, which is a synonyms of the same process.
Where in the urinary sediment appears pus?
In order to understand the main causes of “purulent” urine, you need to understand the issues about what is pus, and how it is formed.
The mechanism of the inflammatory response is quite complex, it includes the simultaneous launch of the biochemical processes and the activation of different components of the immune response
When the organs of the urinary system penetrates the infectious agent, the patient’s body starts mechanisms to combat the pathogen and its complete elimination. In place of introduction of the pathogen are sent to the leukocytes (neutrophils), macrophages and other immunoactive cells (cytokines, tumor necrosis factor, etc.). They secrete substances that are able to destroy and inactivate. The appearance of pus is nothing but dead cells as “defenders” of the body and infectious agents.
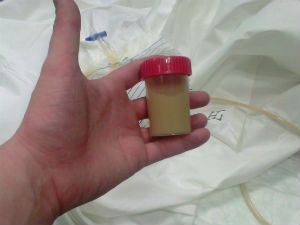
Therefore, the pus in the urine is a direct indication that the urinary tract has an inflammation of various localization.
The main causes of pyuria
Pyuria occurs in men and women of all ages, due to the large list of factors that can cause this to happen.
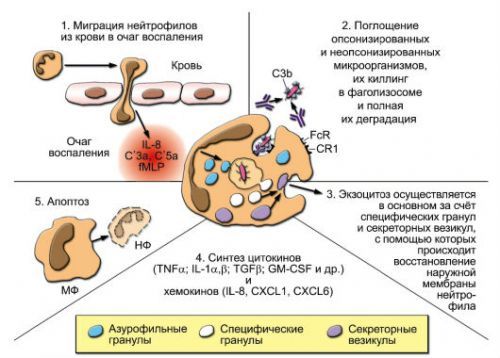
Among the main reasons for the pathological symptom is to provide the following:
- Inflammation of the kidneys (acute and chronic pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis, tuberculosis, abscess, etc.). Marvel at maybe one or both kidneys, the penetration of the pathogen most often occurs from the lower divisions of the urinary tract (bladder or urethra), as well as from other infectious foci distant localization. During pregnancy, the possible emergence of a disease such as gestational pyelonephritis.
- Inflammatory processes in tissues of the bladder (acute or chronic cystitis). Most often disease is recorded in women, while pyuria is characteristic and pathognomonic symptom of the disease.
- The inflammatory process in the tissues of the urethra (acute or chronic urethritis). The disease has very unpleasant symptoms and, as a rule, it is connected with infections of venereal origin (STIs).
- The inflammatory process in the tissues of the prostate (acute or chronic prostatitis). The disease is the lot of men, when the disease occurs in approximately every second man older than 40 years.
- Inflammation in the tissues of the penis and the foreskin (acute and chronic balanoposthitis). Most often, this diagnosis is exposed to a child who has a congenital narrowing of the foreskin, which leads to a constant accumulation there of pathogenic micro-organisms.
- Urolithiasis. If the background of ICD there is pyuria, it is a direct indication that the patient has complications such as inflammation in the lower urinary tract (ureters, bladder or urethra).
- The appearance of purulent discharge in women may be due to diseases such as candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, oophoritis, vulvovaginitis and other processes that allow the ingress of leukocytes into the urine.
- Lack of personal hygiene before collecting the urine sample. Insufficient treatment of the genital organs, or its absence, improper cleaning woman (from the anus toward the vagina), etc. Exactly the wrong preparation for examination often causes about leukocyturia, as the sexual organs and the lumen of the vagina contain pathogenic microorganisms and leukocyte cells that can get into the urine.
- Knowingly using non-sterile container, the walls of which may be infectious agents (we are talking about containers of their food products or containers for a long time in contact with the air). It is therefore important to collect your urine in a special container purchased in any pharmacy.
Bacterial vaginosis – one of the causes of pyuria
The symptoms that you need to pay attention

Pyuria may be asymptomatic, or it is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms such as:
- pain in the lumbar region on one or both sides which may radiate into the perineum, rectum or thighs;
- the emergence of dysuric disorders (pains or cramps when urinating, unpleasant or uncomfortable feelings, etc.);
- frequent urge to urinate, including at night time period, scanty urine, etc.;
- the temperature increase and body, appearance of General weakness, malaise, etc.;
- change the color or shade of your urine (it looks muddy, it appears different inclusions, traces of pus or blood).
Diagnostic methods

Laboratory and instrumental examination of the patient involves the following procedures:
- General analysis of blood and urine (estimated severity of the inflammatory process);
- urine analysis according to Nechyporenko (gives the most information about the number of white blood cells in the urinary sediment, as well as the concentration of red blood cells and cylinders);
- a urine culture on nutrient media, and determination of antibiotic sensitivity of the infectious agent;
- method trehstakannoy samples, the essence of which is simultaneous urine collection in three containers;
- x-ray diagnostics (panoramic image and excretory urography);
- Ultrasound of the urinary system;
- CT and MRI (as indicated).
Trehstakannoy analysis allows for a primary diagnosis determine the localization of the inflammatory focus at different levels of the urinary system:
- if pus is allocated only in the first portion of the urine, it indicates the presence of inflammation in the urethra (the urethra);
- if pyuria is observed only in the third portion, it is necessary to exclude the patient prostatitis;
- if pyuria is observed in all three portions, it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis between pyelonephritis and cystitis.
Trehstakannoy method of diagnosis of the urine is essential at the stage of primary diagnostics of infectious processes in organs of the urinary tract
Care to patients with pus in urine
Therapy the patient begins only after it is finally established the cause of the appearance of pus in the urine, this treatment is called etiological. If pyuria is diagnosed accidentally, the patient’s General condition remains satisfactory, and no complaints, it is necessary to make repeated examination of urine.
This will help to avoid false diagnosis and unnecessary costs to the survey.
The main role in the therapy of inflammatory processes of any localization (in the kidney, bladder or urethra) belongs to antibacterial drugs. The treatment is widely used penicillins (including protected), the latest generation of cephalosporins, macrolides and others.

In the complex treatment uses funds from different pharmacological groups:
- painkillers and antispasmodic medications;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diuretics and others.
In the treatment of inflammatory diseases of urological profile widely used herbal medicine due to proven efficacy
If the urine has changed their natural color, become cloudy or there is any impurity visible to the naked eye, you should immediately contact a specialist, even if your health remains satisfactory. It is important to diagnose the disease and to conduct appropriate treatment, in order to avoid serious complications, as well as the transition process in the chronic form.




This makes better sense than most…