“Glycosuria” or the detection of glucose in urine is a serious symptom of disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, kidney damage, always requires examination and clarification of the duration, due to the heredity.
Can cause physiological factors. In the diagnosis it is necessary to determine the effect of violation of renal excretory function. In any case, the loss of glucose with urine is harmful to the body because this substance is necessary for the formation of cellular energy.
Renal glycosuria manifests with normal blood sugar.
The purpose of medical research:
- promptly recognize the mechanism of the transition of glucose in the urine;
- to clarify the role of endocrine glands and kidneys in this situation;
- to make a differential diagnosis.

Only then can be developed the correct treatment approaches.
The role of the kidney in glucose metabolism
The level of glucose in the blood under normal conditions is controlled by:
- the pituitary gland;
- pancreas;
- adrenal glands;
- thyroid.
The state of the vessels of the kidneys depends, whether there will be glucose in the urine
The endocrine gland associated with the nervous system. About her role says, for example, the stress response. Fear, excitement, hard work cause excitation of certain centers of the brain. To overcome it, the body needs additional energy. “Instructions” do endocrine glands, they produce elevated levels of epinephrine, norepinephrine, which in turn contribute to increased levels of glucose in the blood (hyperglycemia).
In blood vessels sugar goes into muscle cells, heart, lungs. As a result, the body is able to perform additional work and to protect themselves from the negative effects. Blood glucose is sent to the kidneys.
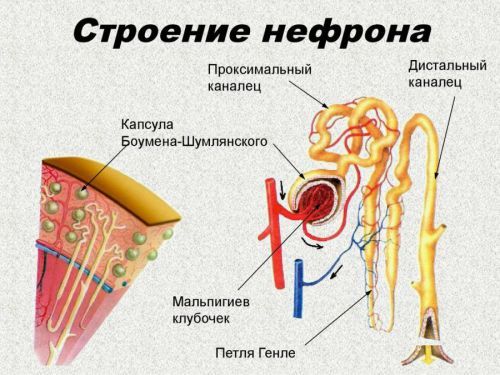
This body is constantly working millions of structural units – the nephrons. They constitute the glomeruli of the finest capillaries surrounded by a capsule (Shumlyansky-Bowman). Under pressure from the capillaries, the liquid and part of the substances dissolved in it, passes the (filtered) through the membrane wall and is collected in the tubules of the medulla.
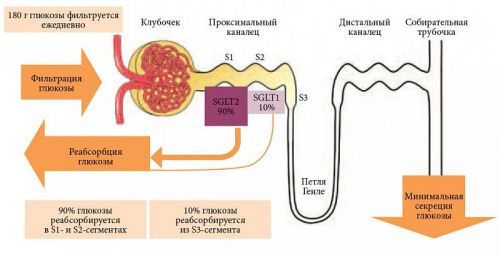
In addition to glucose, this fall, nitrogenous substances, electrolytes (sodium, chloride, potassium), amino acids. The membrane do not pass large molecules, e.g., protein.
Further, from the tubules are selected and are absorbed back (reabsorbed) into the blood necessary connections. Breakdown products and waste products of metabolism stay in the urine.
The role of individual segments of the tubular system in the reverse absorption of glucose
Found that “return” glucose answer epithelial cells. They contain special carriers that ensure the transport of glucose molecules with sodium ions. Potassium-sodium pump in the basal membrane creates the necessary differential concentration of sodium ions to this movement. It turns out that the active transport of sodium facilitates passive transport of glucose.
Returned to the blood glucose goes into cells, and the excess is converted into liver glycogen and provide the necessary energy supply.
What happens when the glycosuria?
The mechanism of participation of the kidneys in the glycosuria is in some problems:
- transport function sodium is terminated as soon as there is complete saturation of the cells;
- tubules are not able to absorb glucose in the blood glucose levels in the capillaries of 8.9-10 mmol/L.
This figure is called the “renal threshold.” For children and pregnant women, it is slightly lower (about 7 mmol/l).
As a result, the reabsorption is terminated, all residual glucose get into urine and excreted through the bladder together with unnecessary waste products. Work healthy kidneys with the growth of glucose in the blood.
For renal glycosuria important threshold for hyperglycemia, but the basis is the pathology of membranes or tubules that violate the inverse process of absorption. To elucidate the role of altered filtration and reabsorption of the kidneys a time-consuming process. It will require numerous studies of daily urine, inspection of internal organs and the urinary system.
Causes and types of glycosuria is very diverse. Each should be considered separately.
Physiological glycosuria
The title says that this species has been observed temporarily in perfectly healthy people.

The definition of sugar in the urine is possible:
- when “too much” coffee, soft drinks, starchy foods (cakes, sweets, chocolate) – this type of glycosuria is called a food, it is associated with excessive flow of sugar from food, caffeine – stimulant hyperglycemia;
- after hard work the night shift, worries, previous stressful situations, so the physiological glucosuria is also called a “functional”;
- during pregnancy;
- on the background application in the treatment course, glucocorticoid hormones, they are usually prescribed for the purpose of anti-inflammatory effects in various diseases.
Allocate alternative temporary hyperglycemia and glucosuria in newborns. It is believed that it is due to toxemia of the mother, family stress or intracranial injury. Unrelated to the changes of the pancreas.
To the “provocateurs” of glycosuria include the participation of young people energy juice.
Therefore, in order to ensure the proper functioning of the kidneys, the patient is instructed to retake analyze, collect urine per day. Choose a period when you perform the instructions in nutrition, remain quiet.
Pathological renal glucosuria
Causes of glycosuria for different diseases can be:
- associated with kidneys (this type is called kidney or renal);
- to be of extrarenal origin.
It should be noted that the number of diseases is accompanied by end-stage renal disease, therefore renal glucosuria is divided into:
- primary – occurs because of the immediate initial of renal system due to defects of the structure;
- secondary – violation of filtration and reabsorption are caused by the development of nephritis, renal failure, consequences of polycystic disease and hydronephrosis.
True renal glycosuria is not accompanied by a rise in blood sugar. Extrarenal – type always occurs with hyperglycemia.
Some authors use the terms to characterize the pathology:
- diurnal – refers to physiological reasons;
- real – in endocrine pathology;
- kidney in case of kidney disease.
The names of obsolete, confusing classification.
Pathological extrarenal origin of the glycosuria
The rise in blood sugar and the urine is found under different pathological conditions. Diabetic origin, we will consider separately.

In the clinic are the following types:
- Central or reflex – occurs in cases of traumatic injuries of the brain and centers the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism (contusions, concussions, head injuries), when tumors in the brain inflammation shells (meningitis), ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, infectious encephalitis;
- pancreatic – called necrosis of cells synthesizing the hormone insulin in acute pancreatitis;
- toxic – affects the cells of kidney tissue under the influence of nephrotoxic poisonous substances and medicines in case of poisoning (morphine, salts of phosphorus, chloroform, during the anaesthetic, strychninum compounds, methylated spirits of alcohol);
- endocrine – sugar in the urine is one sign of hyperthyroidism, syndrome Cushing’s, pheochromocytoma, acromegaly;
- hyperthermic – accompanies febrile diseases amid high temperatures, possible overheating of the children in the heat, in the bath.
Anesthesia using Chloroform at the present time on the territory of the Russian Federation is not carried out
Glucosuria is observed in the patient’s condition at:
- sepsis;
- shock of any origin;
- alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver.
Why do I get sugar in urine in diabetes?
Glucosuria in diabetes has its own mechanisms of development. The most significant cause is a lack of the hormone insulin produced by the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.
To return the glucose from the primary urine in the blood is needed for the process of phosphorylation. And it is only with the participation of the enzyme hexokinase. Insulin is an activator of this enzyme. Therefore, its deficiency violated the biochemical processes of glucose uptake. This diabetes called insulin dependent. It is characterized by glucosuria, even with a relatively low level of glucose in the blood.
In some cases, the disappearance of sugar in urine may indicate a secondary lesion of the kidney – diabetic nephropathy. The body gradually loses the ability to filter urine.
The development of diabetes associated with the additional influence of increased synthesis of hormones:
- adrenaline;
- glucagon;
- cortisol;
- growth hormone.
These substances block the flow of the glucose into the cells, so it accumulates in the blood and the thresholds passes into the urine. For the disease characterized by polyuria (increased urine volume), in response to dehydration develops thirst (polydipsia).
What symptoms are indicative of sugar in urine?
The main symptoms of glycosuria does not depend on causes. They are caused by the effects of dehydration and energy starvation.
You should pay attention to:
- a constant complaint of a man in thirst;
- the use of a large volume of liquid;
- frequent urination, especially at night;
- unmotivated weight loss;
- blurred vision;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- raising sweat;
- itching of the skin, external genitalia.
In children the primary renal glucosuria is accompanied by delayed physical development. Kids fall behind in weight gain.
All ambiguous, especially in people with existing genetic cases of diabetes, endocrine pathology are subject to immediate inspection to identify the cause and prevention of kidney damage and other organs.
What is used to treat?
The elimination of glycosuria is no easy task. First of all, the doctor should investigate the cause of the symptom. Usually given at 2-3 weeks, the diet with restriction of sweet and easily digestible carbohydrates (pasta, pasta, grapes, sweet fruits) and fats. Then re-check blood and urine glucose.
If diet managed to bring the body to normal, the doctor will recommend a constant diet, which plays a key role in preventing possible pathological deviations. Under physiological type of glycosuria should not be complacent. Women during pregnancy and after childbirth should be observed by a doctor to check the tests.
For the treatment of pathological conditions, endocrinologist appoints:
- antihyperglycemic tablet means;
- preparations on the basis of insulin replacement action;
- vitamins;
- tools that improve the function of liver and pancreas.
Renal glycosuria requires treatment of diseases associated with lesions of the functions of filtration and reabsorption.

Apply:
- antibiotics if necessary;
- corticosteroids;
- preparations of cytotoxic drugs;
- means, improves blood circulation in the nephrons.
With the development of toxic shock and renal failure shows plasmapheresis, hemodialysis. Perhaps, irreversible change will require surgery organ transplantation.
Hemodialysis allows you to maintain body functions, replaces the work of the renal filter
Endocrine pathology associated with dysfunction of the endocrine glands, is treated with special hormones, rapid elimination of tumor growth (at tumor in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands).
The Central type of glycosuria must use computer tomography to ascertain the area of damaged brain. The patient was observed and treated neurosurgeons, oncologists.
Glucosuria is an important symptom of many diseases. So definitely treat it is impossible. There are times when the original symptom is regarded as physiological, and further manifested the true reason. Because illnesses can long proceed in secret and not to cause any deterioration of health.