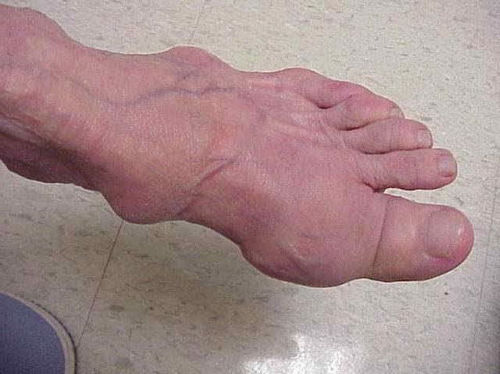
In children, the disease begins with severe pain. It can be episodic or regular and aching. Therefore, timely consultation with a specialist to diagnose arthritis and determine its causes is very important.
When proceeding in childhood, the disease has a number of features characteristic of a certain period of a child’s life.
With this form of the disease, one joint can be affected or symmetrically. They begin to hurt and swell. At this point, redness of the skin due to excessive blood supply to the vessels (hyperemia) is observed. Pathology usually covers large joints. Not only the knee, but also the ankle joints can be affected.
Types of Arthritis:
- rheumatoid juvenile;
- sistemsko-visceralny;
- juvenile ankylosing spondylitis;
- reactive;
- infectious;
- viral;
- tuberculous.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Concomitant complications are also possible, such as:
- lymphadenopathy;
- an increase in the size of the spleen and liver;
- polymorphic skin rash;
- inflammation of the choroid (uveitis).
The disease is manifested by stiffness in the morning. Gait may change due to pain in the knees. Some children two years of age and younger may stop walking altogether. Against the background of the acute form of the disease, body temperature can rise to 39 ° C.
Systemic-visceral type
With this form of the disease, the following pathologies are characteristic:
- lymphadenopathy;
- arthralgia;
- polymorphic skin rash;
- persistent fever;
- myocarditis;
- anemia;
- polyseritis (pleurisy, pericarditis).
The progression of the disease leads to joint deformation. Every fourth child may become disabled due to the development of amyloidosis of the heart, liver, kidneys and intestines. Movements in children become limited, partially or completely.
Juvenile ankylosing spondylitis
This type of disease affects the joints asymmetrically. Symptoms of the disease are common manifestations of arthritis. It is expressed as oligo or monoarthritis.
In most cases, these joints of the legs are affected:
- knee
- metatarsophalangeal joints of the big toes;
- joints of the tubular bones of the foot (metatarsus).
At an older age, ankylosis of the intervertebral joints and affected hip can cause disability.
Also during the pathological process develop:
- inflammation of the Achilles tendon;
- rigidity of the spine;
- inflammation of the sacroiliac joint;
- inflammation of the choroid of the eye;
- nephropathy;
- secondary renal amyloidosis;
- aortic insufficiency.
Reactive arthritis
In a child, this type can occur as a complication after a genitourinary or intestinal infection.
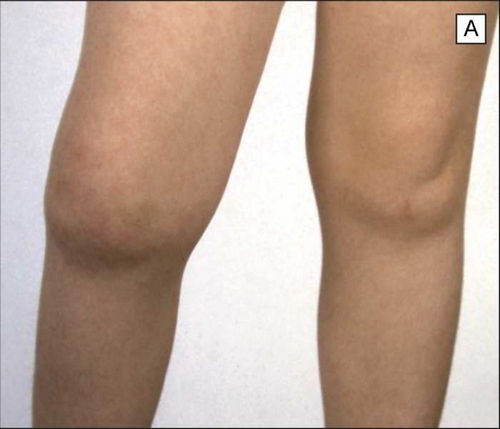
It appears after about three weeks with the following symptoms:
- swollen joints
- soreness in the joint, especially when moving;
- the development of tenosynovitis, enthesopathy, bursitis;
- redness or blueness of the skin over the affected area.
To diagnose the disease, it is necessary to donate blood, feces and urine to laboratory tests. Traces of transferred infectious diseases in the test results substantiate the diagnosis of reactive arthritis. Damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, eyes (conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis), and the heart (myocarditis, pericarditis) can join all of these symptoms. Skin changes manifest as erythema nodosum. Against the background of reactive arthritis, body temperature rises. Anemia, muscle hypotrophy, lymphadenopathy occur.
This disease in childhood is reversible. But if the disease lasts for a long time or becomes chronic, then it is possible that glomerulonephritis, polyneuritis, amyloidosis are attached. Treatment aims to eliminate the infection that causes the disease.
Therapy can range from two weeks to several months. It all depends on the stage of the disease and its severity. Also, the child needs physical rest. During an exacerbation, you can not play sports.
Infectious Arthritis in Children
This type occurs under the influence of a bacterial infection on the body. It proceeds in an acute form. The general condition of the child as in colds. There is weakness, loss of appetite, fever (fever), headache. At the site of the lesion, the joint swells and increases in volume, the skin turns red over it. Pain is present even at rest and intensifies with movement. The child has to take a certain position of the body to reduce discomfort and pain.
Viral Arthritis in Children
The course of this form of the disease develops very quickly. It is one to two weeks. The baby can completely get rid of this ailment, since the disease is reversible.
Tuberculous arthritis
With it, one joint is affected, which is called monoarthritis. It occurs against the background of intoxication and subfebrile fever. The skin is pale, but fistula formation occurs with the release of caseous masses of white color. This type is also called a pale tumor.
Diagnosis
It is more difficult for a child to make a diagnosis and determine the form of arthritis than an adult. Kids still do not understand and cannot accurately describe the localization of pain and the manifestation of other discomfort. They become irritable, often cry and act up. Basically, it is on these grounds that one may suspect that the child has health problems. There is also a decrease in appetite. Often, instead of playing games, children try to lie down or sit without sudden movements. Arthritis is stronger in the morning after rest.

Swelling over the joint is also not always visible to the eye. The ones most likely to notice signs of knee arthritis are those around the child’s family. It will create the impression that the baby is avoiding stress, being too lazy to do physical exercises, or just playing actively. In fact, movement can give him discomfort. Pain in the knee will interfere with the normal lifestyle of the child. If the baby will be forced to move, he will react with crying and whims. Children’s age does not allow him to informatively complain of malaise and describe the localization of pain. Also, the baby may begin to limp.
For the correct diagnosis, the child needs the advice of several doctors. Children’s arthritis is accompanied by a fuzzy manifestation clinic. Symptoms may not appear for a long time. To determine the diagnosis, MRI or ultrasound of the joint, blood biochemistry are needed. An increased ESR indicator will show the inflammatory process in the body. A clearer picture of the disease appears after several attacks. Especially often confusing is the fact that a child can lead a habitual active lifestyle in the evenings, and in the morning complain of pain and weakness, in connection with an exacerbation of the disease.
Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a full examination with the following children’s specialists:
- rheumatologist;
- pediatrician;
- dermatologist;
- ophthalmologist;
- cardiologist;
- neurologist.
The diagnosis can be clarified by a rheumatologist. General symptoms may apply to various other diseases.
To prescribe treatment, it is advisable for the child to conduct a full examination. This will help establish the causes and type of arthritis. The treatment of children is long-term comprehensive, aimed at restoring normal functioning of the body. It can be stationary and dispensary.
Manifestations of the disease
Arthritis of the knee begins with pain in the leg. At first the pain is unexpressed. When resting and resting the legs, the soreness becomes dull, but for a while. Every day the patient’s condition will worsen. Gradually, the tissue around the knee begins to swell. The inactivity of the joint is noted. In the acute period of the disease, a fever appears. An intoxication of the body occurs, which is characterized by muscle pain, lethargy and general weakness.
The smallest age group of children is characterized by reactive arthritis. Usually this is a consequence of the transferred ARI. At the very beginning, the disease manifests itself in a morning attack. It hurts the child to straighten his leg and he begins to cry and be capricious. Lameness may occur. In this case, anti-inflammatory treatment should be performed to eliminate the pathology. Careful observations of relatives living with the baby will help the specialist to understand the diagnosis. Also, the first symptoms may be similar to the onset of other bone diseases.
At the age of three to eight years, the child is actively growing. During this period, he may be bothered by “pains of growth”. Their symptoms are manifested in periodic attacks, most often during sleep. The pains are bilaterally localized and are interconnected with growth hormones. They do not affect the functional ability of the joints. As a child grows, his body needs more calcium to form bones. And if it is not enough, then osteoporosis can develop.
The main causes of the disease:
- hypothermia of the child and complications of colds;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- injuries
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- diseases of the immune system;
- metabolic disease;
- previous infectious diseases of a sluggish nature.
At the age of 15 years, rheumatoid arthritis is predominantly manifested. He is characterized by fever, severe pain in the knees and aches in the bones. The skin above the joint acquires a crimson color and has an elevated temperature at the site of inflammation. The joint enlarges and its swelling is noticeable on the eye, and touching the knee is very painful.
Prevention and Therapy
The cause of arthritis of the knee joint is its vulnerability due to its large size. In this case, the disease has more noticeable symptoms. The positive thing is that the joint is easily accessible for diagnosis, therapy and physiotherapy procedures.
Therefore, with the timely determination of arthritis, good results in treatment can be achieved. Nonsteroidal drugs are used for arthritis to relieve the inflammatory process in the body. They are taken after meals so as not to harm the stomach.
To get rid of the illness of the child, it is necessary to put on a diet and reduce physical activity. It is useful when the baby is engaged in special physical therapy.
For the prevention of knee arthritis, it is necessary to temper children and increase their immune system. Since the body’s good ability to resist infections will not allow an existing disease to go into a more severe or chronic form.
Arthritis of the knee in children is a disease associated with inflammation of the cartilage in the knee. Pathology can occur due to erasure of the cartilage or its infection. The disease is difficult to diagnose, although it can develop from the first days of life. If arthritis is not treated, it will manifest itself in adulthood, but in a more severe form. With timely therapy, a positive effect of treatment is possible, and the absence of the disease in the future.