People of different ages are susceptible to this disease, and especially after 40 years. In the initial stages, coxarthrosis of the hip joints can be cured without surgery.
For this, it is important to make the correct diagnosis in time and establish the reasons by contacting a doctor.
If you do not take the fight against the disease, then it will progress, causing pain.
The causes of coxarthrosis can be the following factors:
- injuries, fractures, dislocations;
- violation of the blood supply to the joint. Poor metabolism affects the nutrition of tissues, which leads to the destruction of cartilage;
- changes in cartilage, hormonal dysfunction, impaired metabolic processes;
- infection and inflammatory processes in the joint;
- pathological spinal deformities;
- flat feet;
- excess loads that lead to joint overload. This applies to athletes who play sports professionally. It is also a risk factor for overweight people;
- joint dysplasia;
- hip dislocation in newborns, which leads to dysplastic coxarthrosis;
- inactive lifestyle;
- heredity in the form of a weakness of the skeleton;
Types of pathology
Doctors define the disease in two types, primary and secondary coxarthrosis. In the primary form, the causes of its occurrence are not clear. Often there is a lesion of the spine, as well as the knee joint. In the second case, it is a consequence of other diseases and is indirect in nature.
With such a degenerative disease, both one and both joints can be affected. Therefore, bilateral coxarthrosis is a fairly common pathology.
The structure of the hip joint
Two bones, called the femoral and iliac, are articulated to form a hip joint. Its mobility is ensured by the articulation of the femoral head, rotating in the iliac groove.
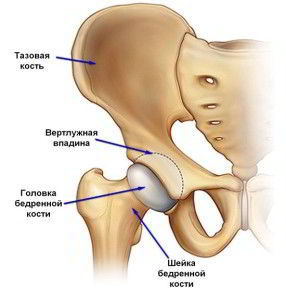
Thanks to this joint, a person can perform various movements, walk and squat. When the joint is healthy, the bones that form it are covered with an elastic strong cartilaginous tissue, in the place of contact with each other.
The articular cartilage in this system works as a shock absorber, distributing evenly the load when walking. When there is a load on the joint, the cartilage moisturizes the surface of the articulating bones with grease. When the load stops, this joint fluid is absorbed by the cartilage. The release of lubricant is proportional to the applied load. It lubricates and nourishes cartilage.
Joint to muscle relationship
For the joint to function properly, it should be surrounded by well-developed gluteal and femoral muscles. With underdeveloped muscles, the functioning of the joint is impaired. Muscles take on part of the distributed load when walking, running and jumping. Therefore, they are so vulnerable.
Femoral and gluteal muscles reduce the risk of joint injuries. During muscle work, they perform the function of a pump pumping a large amount of blood through their vessels. With sufficient blood supply, the joint receives all the nutrients it needs. Therefore, the dependence is monitored that the better the muscles work, the healthier the joints will be.
Pathological changes with the development of arthrosis
The first sign of joint changes is a thickening of the joint fluid. This viscosity causes cartilage to dry out. Its surface becomes rough and covered with cracks. Over time, the cartilage becomes thinner and ceases to fulfill its moisturizing and nourishing function. Since the cartilage of the joint is thinning, the distance between the bones narrows and their deformation occurs.
Therefore, the disease is called deforming arthrosis or coxarthrosis of the hip joint. The properties of the joint fluid change, in this place the blood supply is disturbed and the metabolism worsens. With the progression of pathology, muscle atrophy gradually occurs.
During the period of the disease, there are exacerbations that are accompanied by joint pain, and are called the reactive period. This is the reason for seeking medical help.
The mechanism of pathology
Symptoms of dysplastic coxarthrosis mainly depend on the stage of the disease. Also, depending on this, the doctor will prescribe treatment.

Coxarthrosis of the hip joint has common symptoms with other diseases:
- pain in the joints;
- the appearance of pain in the groin and thigh;
- lameness;
- shortening of one leg (patient);
- loss of functionality of the femoral muscles;
- limited movement.
Stages of the disease
There are three degrees of coxarthrosis, depending on the severity of the disease. The first degree is characterized by periodic pain that occurs against a background of physical activity and load on the joint. Rest helps to cope with pain in the hip area. Movement in the first degree of the disease is not limited, muscle strength is not lost, and there is no disturbance of gait.
An x-ray during this period shows slight growths on the bones. They are located mainly around the swivel of the joint, on the inner or outer edge. The femoral head and neck are not changed at this degree. There is a slight narrowing of the joint space. The main thing is to start treating the affected joint in time.
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the second degree is characterized by increased pain of a more intense nature. In addition to the localization of pain in the joint itself, it manifests itself and gives to the inguinal region and thigh. Discomfort is felt even at rest. A prolonged load on the leg causes lameness in the patient. The normal functioning of the joint is impaired. There are restrictions on the movements of the hip to the side or circular movements of the thigh. The hip extension muscles lose their strength.
In the second degree of the disease, the patient has more and more bone growths, which are clearly visible on the x-ray. Deformation of the femoral head occurs. In the place of the swivel, the formation of cysts is possible, since the maximum load falls on that place. The femoral neck in this period of the disease expands and thickens. The head of the hip begins to shift upward.
The third degree of coxarthrosis is characterized by persistent severe pain. This is the main symptom of the disease. They appear even at night. The patient can move with a cane. Movement is limited, muscles atrophy. More noticeably, one leg is shorter than the other. The patient has to step on his toes in order to reach the floor with his foot while walking. On the x-ray, bone growths are noticeable, which occupy a vast area on the femoral head. It is already very difficult to treat this stage.
Diagnosis and treatment
Due to various symptoms that do not indicate a specific disease, the disease is diagnosed at a later date when surgery is already required. Usually, a person seeks medical help when he is constantly tormented by pain and muscle atrophy is detected on the sore side of the leg. With the progression of the pathology, discomfort extends from the gluteus and inguinal region to the knee joint, which can hurt more than the hip, which is misleading when making a diagnosis. If coxarthrosis of the hip joint is started, surgery may be required.
Treatment of pathology depends on the stage of the disease. With the most neglected third degree, the operation is almost mandatory. It is performed with joint replacement. To clarify the diagnosis, a radiograph is usually prescribed. The method of treatment and the course of physiotherapy exercises that are prescribed to the patient depend on the correct diagnosis.
Dysplastic coxarthrosis of the hip joint treatment has a comprehensive, medication. It is advisable to start it in the initial stages of the disease. These are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that are taken for a long time. Such drugs include ibuprofen, indomethacin and others. These pharmacy products help block the inflammatory process and reduce pain. As well as painkillers, aspirin, analgin can be used. But they will not block the pain for long. All these drugs will not cure the disease. Only stop the symptoms. Therefore, additional measures to combat pathology are needed. Treatment is prescribed by the doctor individually in each case. In the advanced stage of the disease, surgery is indicated.
To improve the blood supply to the damaged area, the doctor may prescribe vasodilators. In combination with anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve swelling, the best effect of treatment can be observed.
Muscle relaxants are also used. They relax the muscles, relieve muscle cramps, because of which a person feels pain. If none of the treatments helped then surgery is prescribed. Chondroprotectors also have a good therapeutic effect. They are drunk to restore cartilage, which is destroyed by dysplastic coxarthrosis.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are also used to improve blood flow and tissue nutrition. But any treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since many drugs have side effects and accumulate in the body.