Botulism is an acute food poisoning, which is emerging as result of entering into the human body is botulinum toxin. Infection occurs through the alimentary, most often by eating food containing spores of the botulism canned food.
Botulism is characterized by damage to the nervous system as a result of botulinum toxin blocking acetylcholine receptors of nerve fibers, manifested in the form of muscle paralysis and paresis.
The main danger of botulism is in the development of complications such as acute respiratory failure and heart rhythm disorders. Diagnosis of botulism is based mainly on data of the anamnesis of disease and results of the neurological examination.
Botulism
Botulism is an acute food poisoning, which is emerging as result of entering into the human body is botulinum toxin. Botulism is characterized by damage to the nervous system as a result of botulinum toxin blocking acetylcholine receptors of nerve fibers, manifested in the form of muscle paralysis and paresis.
Characterization of the pathogen
Botulinum toxin secreting bacterium Clostridium botulinum – spore-forming gram-positive Bacillus, obligate anaerobe. Adverse conditions in the external environment is going through in the form of spores. Spores of clostridia can persist in dried state for many years and decades, developing into vegetative forms when ingested in optimal living conditions: temperature 35 C, the absence of oxygen.
Boiling kills vegetative forms of the pathogen in five minutes, temperature to 80 With bacteria was incubated for half an hour. Spores can survive in boiling water more than half an hour and inactivated only in the autoclave. Botulinum toxin is easily destroyed during boiling, but is able to be well preserved in brine, and canned foodstuffs, the rich variety of spices. The presence of a botulinum toxin does not alter taste of foods. Botulinum toxin is among the most strong toxic biological substances.

Reservoir and source of Clostridium botulinum is soil, but also wild and some domesticated (pigs, horses) animals, birds (mostly water birds), rodents. Animals-carriers of Clostridium usually are not harmful, abjection occurs in the feces, the bacteria are released into the soil and water, animal feed. Contamination of environmental objects by the Clostridium is also possible by decomposition of the corpses of patients with botulism in animals and birds.
The disease is transmitted by the fecal-oral mechanism of food through. The most common cause of botulism is getting use of canned in the home contaminated with spores of the pathogen products: vegetables, mushrooms, meat products and salted fish. A prerequisite for the multiplication of clostridia in foods and accumulation of botulinum toxin is the lack of access of air (tightly sealed tins). In some cases, probably spore contamination of wounds and ulcers, contributes to the development of wound botulism. Botulinum toxin can be absorbed into the blood from the digestive system and mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, eyes.
In humans, there is a high susceptibility to botulism, even small doses of the toxin contribute to the deployment of the clinical picture, but often the concentration is insufficient for the formation of antitoxic immune responses. In cases of poisoning by botulinum toxin from canned foods, frequent cases of family destruction. Currently, the cases become more frequent due to the spread of home canning. Most often botulism sick persons from the age group 20-25 years.
The symptoms of botulism
The incubation period of botulism is rarely more than a day, often amounting to several hours (4-6). However, sometimes it may take up to a week or 10 days. Therefore, monitoring of all people who ate the same food with the patient, continues up to 10 days. In the initial period of the disease may be nonspecific prodromal symptoms. Depending on predominant syndrome distinguish between gastrointestinal, ocular, and also clinical form of acute respiratory failure.
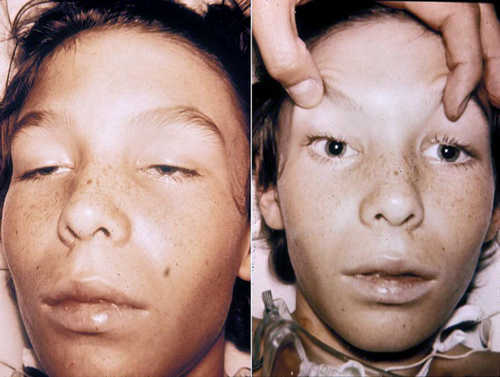
Gastrointestinal variant is the most common and is the type of foodborne illness, with pain in the epigastrium, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea. The severity of enteric symptoms is moderate, however, there is inadequate total fluid loss dryness of skin and often patients complain of disorder of swallowing food (“lump in throat”).
The initial period of botulism occurring in the ocular variant, is characterized by disorders of vision: blurred, flickering “flies”, the loss of clarity and reduction of visual acuity. Sometimes there is a sharp farsightedness. The most dangerous option for the initial period of botulism is an acute respiratory failure (suddenly growing and progressive shortness of breath, spreading cyanosis, cardiac arrhythmias). It develops extremely quickly and facing lethal outcome after 3-4 hours.
The clinical picture of botulism in the midst of the disease is quite specific and is characterized by the development of paresis and paralysis of various muscle groups. In patients with marked symmetrical ophthalmoplegia (pupil steadily expanded, there is a strabismus, usually convergent, vertical nystagmus, drooping of the eyelid). Dysphagia (swallowing disorder) is associated with progressive paresis of the muscles of the pharynx. Initially, patients experience discomfort and difficulty swallowing solid food, with the development of the disease it becomes impossible to swallow the liquid.
Speech disorders developing, passing successively four stages. First change the tone of voice, there is osiplosti as a result of insufficient humidity of mucous on the vocal cords. In the future, due to paresis of the muscles of the tongue appears dysarthria (“porridge in the mouth”), the voice becomes nasal (palatal paresis of the muscles of the curtain) and disappears completely after the development of paresis of the vocal cords. In the result of disorders of innervation of the muscles of the larynx, the cough impulse is lost. Patients can suffocate when hit in the respiratory tract of mucus and fluid.
Botulinum toxin contributes to paralysis and paresis of mimic muscles, causing asymmetry of the face, domeniu. Overall there is weakness, unsteady gait. Due to paresis of the intestinal muscles develop constipation. Fever for botulism are not typical, in rare cases, possible low-grade fever. The condition of the heart activity is characterized by increased heart rate, some increase in peripheral blood pressure. Disorders of sensation, loss of consciousness is not typical.
Complications of botulism
The most dangerous complications of botulism is the development of acute respiratory failure, respiratory arrest due to paralysis of the respiratory muscles or apnea airway. Such complications may lead to death. Due to the development of stagnant phenomena in lungs, botulism can provoke secondary pneumonia. Currently, there is evidence of likelihood of complications of infection myocarditis.
Diagnosis of botulism
In connection with the development of neurological symptoms the patient with botulism in need of examination by a neurologist. Specific laboratory diagnosis of botulism in the early stages of infection is not developed. The basis for diagnosis is the clinical picture and epidemiological history. The toxin is isolated and identificeret with a biological sample in laboratory animals. In the midst of the disease is possible to determine the presence of toxin in the blood with the help of HGUF the antibody with the antigen.
The antigens of pathogens are detected by immunofluorescence analysis (IFA), and – RIA and PCR. Isolation of the pathogen by plating of fecal matter does not bear significant diagnostic information, as may be the development from spores vegetative forms of clostridia in the intestine of a healthy person.
Treatment of botulism
If you suspect that botulism is made compulsory hospitalization to the Department with the ability to connect the ventilator with the purpose of prevention and timely assistance in the case of life-threatening complications. The first treatment produced in the first days of the disease is gastric lavage with a thick probe.
Botulinum toxin circulating in the blood of patients, is neutralized by using a single polyvalent introduction protivobotulinicheskoy serum by the method Besredka (after the implementation of the desensitization of the body). In the case that a single administration of serum was not effective enough and after 12-24 hours the patient is the progression of neurological symptoms, serum infusion, repeat.
Quite effectively introduction protivobotulinicheskoy human plasma, however, this drug is quite rare due to the small duration (no more than 4-6 months). Currently, the treatment of botulism is used protivobotulinicheskoy immunoglobulin. The complex of measures causal treatment includes antibiotics prescribed to suppress the probable development of the vegetative forms of the pathogen, as well as thiamin pyrophosphate and ATP. The positive effect of hyperbaric oxygenation.
Otherwise, treatment is prescribed based on the severity and symptoms. In the case of the formation of acute respiratory failure patients transferred to artificial lung ventilation. Feeding patients in the case of the formation of persistent dysphagia produce liquid food through a thin probe, or transferred to parenteral nutrition. In the recovery period good effect in terms of early recovery functions of the muscular system has the physical therapy.
The prognosis of botulism
Forecast at a high dose of toxin received, and the absence of timely medical care can be extremely unfavorable, the lethality of these cases reaches 30-60%. The use of etiotropic treatment and methods of intensive therapy in the development of serious complications and significantly reduce the risk of death (up to 3-4%). In the case of timely treatment, the disease ends in recovery with full restoration of function after a few months.
Prevention of botulism
Preventive measures against botulism imply strict adherence to sanitary and hygienic norms in the manufacture of canned food, sterilization of utensils for storing products long-term storage. Fish and meat products must be preserved exclusively in fresh and carefully cleaned from soil particles. Conservation overripe fruit unacceptable. Canning in the home must be in strict accordance with the formulation in a sufficient concentration of salt and acid in an oxygen container.

In the case of timely treatment, the disease ends in recovery with full restoration of function after a few months.
Contamination of environmental objects by the Clostridium is also possible by decomposition of the corpses of patients with botulism in animals and birds.
Hi. I have checked your osvilt.com and i see you’ve got some duplicate content so probably it is the reason that you don’t rank hi in google. But you can fix this issue fast. There is a tool that generates articles like human, just search in google:
miftolo’s tools
I kinda got into this website. I found it to be interesting and loaded with unique points of interest.
I real delighted to find this site on bing, just what I was looking for : D also bookmarked .