Steroidit is one of the severe forms of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses and its symptoms do not cause a person to lose their working ability, and treatment requires antibiotics. Among groups of sinusitis (inflammation of the sinuses) steroidit occurs in approximately 12 % of the total number of clinical cases.
Pathognomonic pattern is very scarce, the symptoms can manifest themselves only during special tests. Are often detected at random when the survey radiography of the facial bones of the skull.
Acute sphenoidal almost diagnosed mainly establishes a chronic inflammatory process, which can be translated with successful treatment in the phase of long-term remission. Completely cure this disease is impossible.
Affects the main or the sphenoid paranasal sinus. Inside it is the mucous membrane secreting a specific secret, moisturizing the air passing through the nasal passages. Slight signs enable people to be treated at home, but under constant supervision by the attending physician.
The pathogenesis of the disease and the development of inflammation
The location of the sinuses
The pathogenesis of the disease is based on the penetration of pathogens into the cavity of the primary or sphenoid paranasal sinuses. The development of the inflammatory process with swelling of the mucous membrane that may be a feeling of pressure in the area below the eye sockets. Severe swelling interferes with the capillary blood supply. This worsens the outflow of blood from selected toxins and poisons. Accumulating in the sphenoid sinus, they quickly lead to scarring and narrowing of the anastomoses of the outlets. Thus impeding the outflow of mucous secretion.

Sphenoid sinus is located inside the front of the skull on both sides of the nasal septum. It is adjacent to the carotid artery, skull base and ocular nerves. All of them may suffer from what is happening inside the main sinuses of pathological processes that affects the clinical picture of the disease. Look at the photo below it looks like and where is the sphenoid sinus, a cavity which may develop acute and chronic sphenoidal:
Infections can cause all forms of coccal microflora. This Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, pneumococ and meningococcus. Less often in crops are determined by Moraxella catarrhalis and Haemophilus wand. Approximately 5% of cases the primary cause of the inflammatory reaction are respiratory viruses and fungal microflora.
It is established that in case of any infectious disease in the nasal passages and nasopharynx in a cavity of the sphenoid sinus occurs a hidden inflammatory process. However, in the absence of obstacles to the outflow of mucous secretion steroidit not formed. The immune system quickly enough neutralize all the microorganisms and mucous membranes are purified independently.
There are risk factors, the presence of which the probability of development of acute and chronic sphenoiditis increases dramatically:
- chronic rhinitis bacterial etiology;
- high degree of sensitization of the body with reflex manifestations of allergic rhinitis;
- the narrow exits from the sphenoid sinus and the anatomical change of anastomoses;
- foreign bodies in the paranasal sinuses, including cystic changes;
- a deviated septum in the upper part, paired with latticed bone;
- congenital deformation of the sphenoid sinus or improper development during infancy.
Acute sphenoidal takes place not longer than 14 days. If during this period, the restoration of the mucous membrane does not occur, it begins to thicken. Formed chronic sphenoidal, the treatment of which will require extensive restorative therapy.
Clinical picture: symptoms and signs of sphenoiditis (with photo)
The clinical picture in acute conditions is erased due to the overlap of symptoms of acute respiratory disease, which is the leading cause of infection. Typical symptoms of sphenoiditis can manifest as nasal congestion, sensation of pressure around the nose, rise in body temperature. Secondary symptoms in a chronic state based on the difficulty of outflow of mucous secretion.
Then come to the fore:
- headache concentrated in the temporal and occipital part of the skull;
- the purulent secret with unpleasant putrid odor from the nose;
- frequent sneezing with discharge of mucus and irritation of the mucous membranes of the upper parts of the nose;
- change of smell, inability to recognize certain groups of smells.
- increased intracranial pressure;
- the sensation of pressure on eyes;
- reduction of resistance of immunity to various infections, transmitted by airborne droplets;
- chronic fatigue, muscle pain, malaise, periodic rise of body temperature to subfebrile digits in the evening hours.
Steroidit can be unilateral (more common in congenital and acquired deformities of the sphenoid sinus) and bilateral. Secondary symptoms may include blurred vision, constant migraine headaches, allocation from the nose purulent mucus, Ozen (smelly runny nose). Approximately 10% of patients there is a risk of meningitis, especially when seeding meningococcal disease.
In chronic sphenoiditis symptoms can only be a constant headache unspecified origin. Patients can years to treat cervical degenerative disc disease, vertebral artery syndrome, and other neurological conditions and not to a positive effect.
To diagnose used x-ray panoramic image. Sometimes the use of contrast agents for the assessment of the internal cavity of the sphenoid sinus. The most reliable, but inaccessible method clinical diagnostics is computer tomography.
Already in primary rhinoscopy doctor will be able to see the swelling of the nasal mucosa in the place where out a fistula of the sphenoid sinus. When pressed, could stand a small portion of purulent or Muco concentrated secret that talks about stagnation.
The principles of treatment of sphenoiditis at home
The principles of modern therapies offer the patient only conservative influence. Under its influence you can bring a chronic inflammatory process in the phase of long sustained remission.

As a rule, the treatment of sphenoiditis at home includes the following aspects:
- conduct bacterial culture to detect pathogenic microflora and its sensitivity to different groups of antibacterial and antimicrobial agents;
- antibiotic, antiviral or antifungal etiotropic therapy;
- the use of antihistamine drugs to relieve swelling of the mucous membranes;
- hormone drops with vasoconstrictor effect and mucolytics help rid the sphenoid sinus from accumulation of fluid there.
Among the most effective antibiotics in the clinical practice of audiologist is possible to allocate “Augmentin”, “Amoxiclav”, “Cefodox”, “flemoksin” Solutab”, “Zinnat”, etc. in Addition, prescribers of stimulating the immune system and protecting against viral infection. This “Lavomax”, “Amiksin”, “Ingavirin”, “Kagocel”, “Arbidol”, “Rimantadine”, etc. all provide increased production of interferons. This speeds up the process of reorganization of the cavity of the sphenoid cavity. Good results are obtained by sensing the main sinus and its washing with disinfectant solutions with antibiotics. This procedure can conduct an otolaryngologist in the outpatient setting outpatient appointment.
For improvement of outflow of mucous secret is used burying his nose in the solution of epinephrine or vasoconstrictor drops based on Xylometazoline (the”Naphazoline”,”.”, “Naphazoline”). In severe cases, shows the use of nose drops with hormone component (“Nazoneks”).
In addition, you must improve the immune defense of the human body. Patients with chronic sphenoiditis shown courses of treatment “Wobenzyme” in spring and autumn. You can also take 2 times per year “Polyoxidonium” and “Extract Echinacea”.
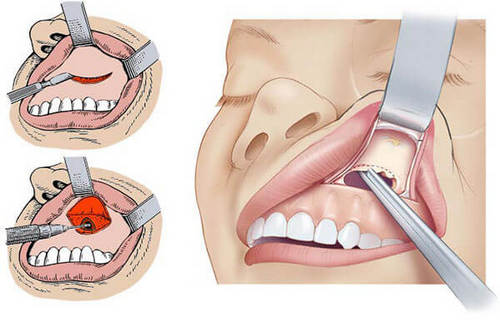
Surgical methods for the treatment of chronic sphenoiditis apply only in cases where conservative therapy does not give positive result within 2-3 months. Often during the operation, carried out the reorganization of the internal cavity of the sphenoid sinus and stenting (extension) of the duct through which of it is the outflow of mucous secretion. Duration of surgical intervention is 20 – 30 minutes and is performed using local anesthesia. The recovery period is 7-10 days.


Hello, i think that i saw you visited my site thus i came to return the choose?.I am attempting to to find issues to improve my site!I guess its good enough to make use of a few of your ideas!!