Hemolytic disease of the newborn is a dangerous pathology, the development of which leads to the breakdown of red blood cells (red blood cells).
Pathology occurs due to the fact that the antibodies of a mother with a negative Rh factor penetrate the placental barrier to a Rh-positive child. As a result, there is a fixation of antibodies on the outer shell of red blood cells with their subsequent destruction.
Sometimes a hemolysing E. coli is found in infants, which can lead to serious intoxication, poisoning, the development of dysbiosis, cystitis, pyelonephritis and a number of other complications.
Classification
Given the type of immunological incompatibility, pathology is classified as follows:
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn by blood type.
- The development of pathology as a result of a conflict of Rh factors.
- In rare cases, conflicts with other antigens are observed.
Depending on the clinical manifestations, the disease is classified as follows :
- Anemic form of hemolytic disease of the newborn. It is rare. In this case, the child is pale, mother’s milk is bad, he may experience tachycardia, systolic murmurs and muffled heart sounds. Even during pregnancy, you can identify the characteristic signs of violations. One of them is an increase in the volume of the placenta due to the occurrence of edema. The most serious consequence of this form is spontaneous miscarriage already in the initial stages of pregnancy. Women who have suffered such a Rhesus conflict are subsequently susceptible to toxicosis during pregnancy, liver dysfunction, and anemia.
- An icteric form of the disease is the most common. During the examination, an increase in the liver and spleen can be detected. At birth, the area around the navel and amniotic fluid are colored yellow. Jaundice can develop during the first days after birth.
- The edematous form of hemolytic disease of the newborn is one of the most severe, accompanied by pallor of the skin, as well as edema. These signs can be supplemented by DIC, cardiovascular dysfunction, hypoxia. During the examination, the doctor may find that the borders of the heart are widened, and the tones are muffled. With this type of hemolytic disease of the newborn, the symptoms in the baby can manifest as respiratory failure immediately after birth.
The form of the disease can be mild, moderate and severe. With a mild form, moderate manifestations of pathology are revealed. With moderate – bilirubin rises, jaundice may develop. In severe cases, respiratory disorders and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system are observed.

Causes
The cause of the hemolytic disease of the newborn is the penetration through the placental barrier of specific antibodies from the mother’s body to the child. As a result, there is the appearance of foci of extramedullary hematopoiesis, under the influence of which indirect bilirubin increases, which has a toxic effect on the fetus.
The disease can develop under the influence of a number of factors:
- Due to a violation of the barrier function of the placenta.
- With a decrease in the level of albumin, which can be triggered by the use of antibiotics, sulfonamides, salicylates and steroid hormones.
- Exposure to Rh conflict (Rh negative mother and Rh positive child).
- The impact of an immune conflict, which can develop if the mother has 1 blood group, and the child has 2 or 3.
- A child can be born with hemolytic disease if the mother has sensitization (hypersensitivity to environmental factors, including childbirth).
- Due to the development of cholestasis – stagnation of bile, which occurs as a result of a violation of the secretion of bile into the intestinal region.
- The causes of hemolytic disease of the newborn are also often associated with the development of anemia.

Manifestations, the clinical picture
In pregnant women, any specific signs do not appear. In some cases, the development of symptoms similar to late toxicosis is possible. In severe hemolytic disease, fetal death may occur in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Such a serious complication can be triggered by edematous, icteric or anemic forms.
Rh factor hemolytic disease of the newborn has a number of characteristic symptoms that require immediate medical attention. The clinical picture is formed depending on the form of pathology.
For the edematous form, such manifestations are characteristic :
- The child’s face is painted in a pale color, has a rounded shape. A decrease in muscle tone and inhibition of reflexes is observed.
- The doctor notes the increase and barrel-shaped structure of the abdomen. The spleen and liver are significantly enlarged.
- The skin and tissues are edematous, effusions are formed – accumulations of fluid that comes out of the vessels. The danger is that the formation of effusions is observed in the pericardial region, as well as in the region of the lungs. A similar reaction is provoked by a violation of the permeability of capillaries, as well as a decrease in protein concentration.
With an anemic form, the formation of manifestations occurs during the first few days :
- There is a rapid progression of anemia.
- The liver and spleen are enlarged.
- There is a deterioration in the overall well-being of the child.
The following symptoms are characteristic of the icteric form :
- Coloring of the baby’s skin in intense yellow-orange color due to excess bilirubin, as well as its metabolic and decay products. The mucous membranes and sclera can turn yellow.
- Hemoglobin may decrease.
- The spleen and liver are enlarged.
- The earlier jaundice appears, the more severe the course of the pathology will be.

With the progression of this form of the disease, symptoms manifest in the form of motor anxiety, increased muscle tone, cramps, which are accompanied by a sharp arching of the back of the child back. The child can throw his head back, stretch his arms and legs, bend his fingers and hands. The occurrence of the so-called “setting sun” symptom is also characteristic, in which the eyeballs move down and the irises of the eyes cover the lower eyelids.
If you do not take appropriate measures, after 7 days due to the intensive breakdown of blood cells, the development of a thickening of bile syndrome and the occurrence of symptoms of cholestasis can be observed: the skin becomes green-brown, feces become discolored, and urine becomes dark. Clinical studies can detect an increase in the level of bilirubin, which passed through the liver and became harmless.
Diagnostics
There is a specific protocol for hemolytic disease of the newborn: HP-028, according to which the diagnosis and treatment of the disease is prescribed. Diagnosis should be carried out before delivery for the timely determination of the conflict of the immune systems of the mother and child.
Necessary activities:
- First of all, a gynecological examination and an oral questioning of the mother regarding past abortions, miscarriages, and the birth of dead children is required. Also, a woman will be asked about blood transfusions without taking into account the Rh factor.
- It is necessary to establish the Rhesus factors of the parents of the child. If a man has a positive Rhesus, and a woman has a negative Rhesus, then the child is at risk. Women with the first blood group also constitute a risk group.
- Since the cause of hemolytic disease in newborns is the development of incompatibility of the Rh factors of the blood of the mother and the child, repeated determination of the titer of antitussive antibodies is required throughout pregnancy.
- If a woman is at risk, then at the end of pregnancy, a special procedure is required, during which the fetal bladder is pierced in order to analyze the amniotic fluid. There is a study of the level of bilirubin and antibodies.
- Throughout pregnancy, a woman should undergo regular ultrasound examination. If hemolytic pathology develops, then an ultrasound scan will show compaction of the walls of the placenta, the occurrence of edema. The abdomen of the fetus may be increased in size.
After the birth of the child, additional diagnostics are carried out :
- Possible clinical manifestations of jaundice, anemia, enlargement of the spleen and liver, and the symptom of the setting sun are determined.
- Laboratory parameters will be studied: hemoglobin level, red blood cells, urine composition.
- Particular attention is paid to the Coombs test to determine incomplete anti-erythrocyte antibodies.
If any violations are identified in the future, a pediatric hematologist may be required.
Therapy
The main objective of the treatment is the removal of toxic elements from the body of the child: indirect bilirubin, antibodies. It is also required to normalize the functional state of the affected organs.
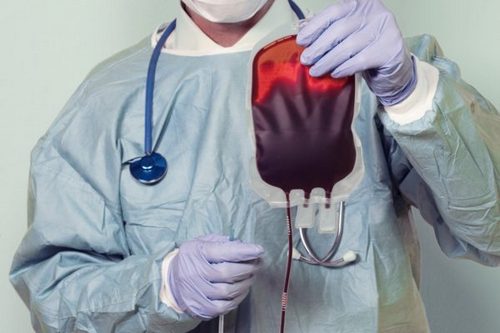
If a severe form of hemolytic disease of the newborn is diagnosed, treatment involves the following procedures:
- Bloodletting followed by blood transfusion from a suitable donor.
- Blood can be passed through a special system in which absorbing substances (activated carbon) are found. After the procedure, all toxic elements are eliminated.
- Plasmapheresis, during which the liquid part is removed from the blood – the plasma in which toxic components accumulate.
- With a replacement blood transfusion, indirect bilirubin, which is characterized by increased toxicity and does not pass through the liver, can be eliminated. As a substitute, it is advisable to use bilirubin from maternal antibodies, as well as supplementation with red blood cells.
- In severe cases of pathology, the child is immediately prescribed the introduction of corticosteroid drugs for 7 days.
Due to the fact that today there is an increased risk of contracting hepatitis and HIV infection, it is not whole blood that is used for transfusion, but erythrocyte masses in combination with frozen plasma. If the causes of hemolytic disease of the newborn are associated with group incompatibility, then erythrocyte mass of the 1st group can be used, and plasma – 4 groups.
If pulmonary edema and severe respiratory failure are observed, the use of artificial lung ventilation is required – a method in which the patient’s respiratory function is supported using a special device. When ascites is detected, laparocentesis is performed using ultrasound.
Conservative treatment
After transfusions, conservative methods of therapy may be involved:
- Protein preparations and glucose for intravenous administration.
- Vitamin complexes, which include ascorbic acid and B vitamins, as well as cocarboxylase, which helps to restore the functioning of the liver and metabolic processes.
- When thickening bile, it is advisable to use choleretic drugs.
- If hemolytic E. coli is detected in infants, treatment involves the use of drugs from the group of probiotics (Linex, Hilak forte, Bifidumbacterin).
With delayed treatment of this pathology, the risk of death is increased.
In addition to the conservative treatment of hemolytic disease of the newborn, phototherapy may be recommended. During the procedure, the baby is irradiated with special lamps with blue or white color. After this procedure, bilirubin is oxidized and excreted along with excrement.
Treatment of the hemolytic disease of the newborn should begin as soon as possible, under the supervision and in strict accordance with the instructions of a competent, qualified doctor.
Complications, Possible Consequences
If a hemolytic disease of the newborn is detected, the consequences can be the most severe and irreversible.
Among them:
- The development of congenital disability.
- Delay in psychomotor development.
- The occurrence of reactive hepatitis, which is accompanied by inflammatory processes in the liver and stagnation of bile.
- With hemolytic disease of newborns in the blood group, the consequences can be associated with the development of cerebral palsy – a whole complex of symptoms, accompanied by both motor disorders and changes in muscle tone.
- The child may not distinguish sounds (development of hearing loss).
- Visual impairment, up to complete blindness.
- The development of a psycho-vegetative syndrome, which is accompanied by mental disorders.
- With a severe form of hemolytic disease of the newborn, the consequences can be associated with the development of anxiety, depressive disorders, sleep and eating disorders.
Prevention
Specific measures to prevent the development of this dangerous condition include the use of immunoglobulin during the first two days after the birth of the baby. Such prevention of hemolytic disease in newborns will help if the mother has a negative Rhesus and the baby is positive.
In severe illness, the prognosis is poor. During pregnancy, prophylaxis of blood through adsorbing substances or intrauterine replacement blood transfusion may be recommended as a preventive measure. A similar procedure can be performed at 27 weeks of gestation. Washed red blood cells of Rh-negative blood can be used. In severe cases, stimulation of preterm labor may be required.



