Fluoroscopy of the stomach is widespread in medical practice, research method, based on the study of the structure, morphological and functional changes of the digestive system by x-ray radiation.
It can be carried out in 2 ways: radiography and fluoroscopy. In the first case abnormalities are detected according to the x-ray shadow of the picture obtained on the photosensitive film.
The second option fixed the optical image is displayed on the monitor screen with the possibility of increasing its size and recording on electronic media. Thus, fluoroscopy has several advantages over x-rays of the stomach and, in contrast, allows you to see how the body in real time, and even trace if necessary for the operation.
But despite such a big difference, both methods are inseparable from each other and are carried out by one specialist anthologia, which in addition will advise the patient on the results of the survey.
How it’s performed, and what shows?
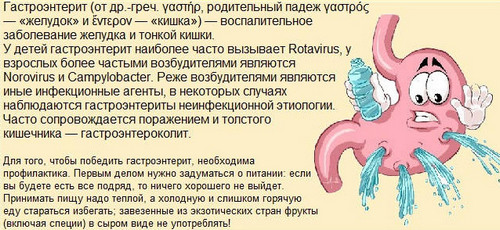
To visualize the internal organs of the digestive system were highest in the stomach, the doctors introduce a special contrast agent is barium sulfate. This white powder, without taste and smell, certainly before preparing the study, mixing with warm water in the ratio 2:1 or 4:1. If fluoroscopy is done to the child, the other ratio taken is 1:2. The mixture is thoroughly homogenized due to the long-term (at least 4-5 minutes) stirring. The dosage is also determined according to the age of the patient. So, for example, an adult paste of barium is inserted through the mouth or probe in a volume of 250-300 ml, the child the amount used of the mixture 3 times reduced.
The passage of barium sulfate in the esophagus is carried out instantly. Settling in the stomach, after 30 minutes of some portion of the contrast agent leaves him, and after another hour is displayed completely. As for the intestine, then after half a minute after the tool was made, beginning to fill with barium its first segment is the duodenum.
Other regions of the small intestine reaches the drug over 15-60 minutes, getting into the colon occurs even later (depending on the body position of the subject, the hydrostatic pressure of tissue fluid and blood in the body, the viscosity of the suspension). The result of the passage of barium sulfate on the gastrointestinal tract of the studied organs are distinctive from adjacent tissues, allowing you to review them on the screen, and later on film.
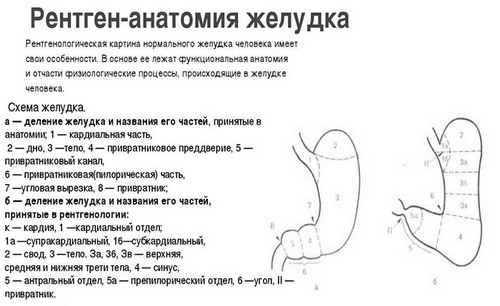
Thus, an x-ray of the stomach may show:
- the location of the bodies (normal or shifted), their size and shape;
- the structure and elasticity of the walls;
- folding of the mucous layer;
- the level of motor-evacuation function of the intestine;
- changes (contraction/expansion) of the lumen of the esophagus, stomach and intestine.
Often the initial phase of screening is carried out without the use of contrast. It is necessary for professionals to detect free air in the abdominal cavity that occurs on the background of destruction of walls and the presence of defects of filling.
Indications and contraindications
The appointment of a fluoroscopy of the stomach and x-rays required with a hereditary predisposition to tumors, and when there are symptoms of diseases of the digestive system, namely:
1. frequent vomiting and nausea (women with the exception of pregnancy);
2. pain in the epigastric area and in the chest, associated with food intake;
3. difficult swallowing (dysphagia);
4. disorder of defecation (constipation, persistent diarrhea);
5. belching, heartburn, halitosis (putrid, acidic);
6. blood in the stool, vomit;
7. rapid weight loss;
8. tympanitis (so strong bloating that when you hit it with your palm turns out a loud sound similar to the sound when playing the drum).

Thanks to fluoroscopy of the gastrointestinal tract that is able to show the dynamics of current pathology, it becomes possible to diagnose diseases such as achalasia of the esophagus (inability of the lower sphincter to relax with swallowing), swelling of various etiologies, pyloric stenosis (narrowing of the passage connecting the stomach and the first section of the duodenum), ulcer, erosion, polyps (overgrowth of polyps on the mucous walls). With the aid of fluoroscopy is also possible to obtain data on the effectiveness of the therapy and the outcome of surgical treatment.
Is contraindicated this method of examination of the stomach in the following cases:
- when the patient is in a critical condition;
- when there is continued internal bleeding;
- during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester.
In addition, the procedure fluoroscopy the doctors can opt-out if you have not complied with the conditions of preparation.
What to do before the procedure?
Preparation before x-ray of the stomach and intestines, which at the time of the survey should be empty is diet and cleansing sessions. Moreover, regardless of what time was the scheduled procedure, the patient for 7 hours prior to the event prohibits any meal, including drinking and Smoking, taking drugs and even chewing gum.
To obtain the most objective data, the patient should be 2-3 days before the screening of a hollow organ, the duodenum and other parts of the small and large intestines to adhere to a special 3-day diet, which requires:
- exclude from the diet foods and dishes from them that encourage the development of bloating (e.g., beans, cheese, cabbage, onions, soda, milk, apples, brown bread, green pepper, broccoli);
- give preference to fresh cereals, low-fat boiled fish and meat, white stale bread, weak tea.
In the case of being in the stomach of a patient to excessive amounts of fluid (due to narrowing of the lumen or increased secretion) shown him for several days, the wash procedure. And constipation the day before the barium swallow should be cosmotherapy.
As a means for cleansing the intestines from toxins and pollution can be applied pharmaceuticals. According to the reviews, a review of the best of them is as follows:
1. Fortrans is a laxative and thinning of the intestinal contents, thereby facilitating defecation.

2. Espumizan – effective cure for flatulence; his method prevents the occurrence of image defects caused by gas bubbles when x-rays of the stomach and duodenum.
3. Activated carbon is a tablet of natural origin adsorbent action.
For fluoroscopy and radiography of the esophagus, the preparation is the same as in the examination of this part of the alimentary canal there is often a need of examination of the stomach, for example, in connection with the presence of tumor, ulceration, stenosis in the region of the inlet into the hollow body. Directly in front of a fluoroscopy of the stomach is necessary to remove objects, which have a negative impact on image quality. It dentures, jewelry, watches, belts, clothing.
Only with the right preparation, x-ray of the stomach, intestines and other organs may show reliable results. The patient should not be afraid of irradiation: x-ray beams do not carry any harmful effects on human health.