Rectal (or rectal) bleeding is a discharge of blood and/or blood clots from the anus.
Pathology occurs because of the violation of the integrity of the rectal vessels, which, in turn, can be observed in a number of diseases of the rectum or due to trauma of the vascular wall.
Rectal bleeding is the most common manifestation of bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract: the structure 20-25% of all cases falls on the release of blood due to irregularities in the rectal blood vessels.
General data
Mostly rectal bleeding aged 63-77 years.
It is on the age factor, you should pay attention: the probability of occurrence of rectal bleeding in 80 years to 200 times higher than the age of 30.
These patients are treated proctologists and/or gastroenterologists (small clinics).

Causes of rectal bleeding
Rectal bleeding is not a separate disease. It may be due to the development of a number of inflammatory, infectious, oncologic, traumatic and other pathologies, which are diagnosed from the rectum. The rectum is supplied very good and stuffed with small vessels, a wall which is pretty quickly undergoes destruction during a particular pathological process.
The immediate causes of rectal bleeding very much, so it is convenient to divided into large groups:
- ekoobrazovanie;
- abnormal proliferation of the rectal mucosa nonneoplastic nature;
- inflammatory disease of the rectum;
- its a non-inflammatory disease;
- congenital abnormalities of the rectum;
- her infection;
- violation of local circulation;
- complicated diseases of other organs and systems;
- trauma;
- radioactive impact.
The occurrence of rectal bleeding could trigger virtually any neoplasm of the rectum.
But in most cases it develops in malignant tumors are:
- become overgrown in the surrounding tissue with germination and/or erosion of the walls of the blood vessels;
- are in the process of disintegration, in this process also disintegrate tissue and vascular walls.
Of rectal tumors to rectal bleeding is often cancer of the rectum. Of benign tumors your bleeding “famous” for rectal polyps (especially villous) and genital warts.
Abnormal proliferation of the rectal mucosa is the formation of nonneoplastic in nature. One of the most illustrative examples of this pathology is pseudopolyps rectum. In this case of rectal mucosa-covered speakers or more raised above the surface a kind plaques, which are regarded as pseudopolyps. Pseudopolyps accompanies some rectal rectum diseases – such as chronic ulcerative colitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large intestine, accompanied by the formation of its defects) with the location of the pathological process in the rectum.
Of inflammatory diseases of the rectum the most frequent cause of rectal bleeding are:
- proctitis – inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum. Lose the deeper layers of the rectal wall leads to bleeding rarely;
- pseudomembranous colitis is an inflammatory lesions of various departments of the colon (including the rectum), due to dysbiosis, and is manifested by the formation of a specific film on the mucosa;
- ulcerative colitis – inflammation of the colonic mucosa, accompanied by the formation of deep defects;
- Crohn’s disease – education in the colonic mucosa of specific granulomas-tubercles, occurring on the background of inflammation;
- rectal fistulas – abnormal passages between the rectal lumen and the adjacent organs or tissues, arising as a result of purulent fusion of rectal wall and pararectal tissues.
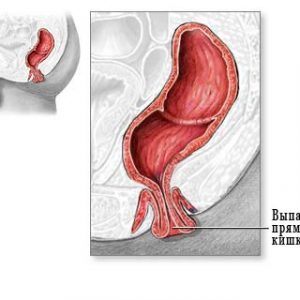
Cause rectal bleeding often become such a non-inflammatory disease of the rectum:
- rectal prolapse – presence of splayed walls of the rectum outside of the anal sphincter;
- fissure of the anus – deep linear defect of its mucosa;
- solitary ulcer of the rectum is one or more defects of the lining;
- diverticulitis – formation of saccular protrusion of the rectal wall;
- intussusception – the introduction portion of the rectum into the lumen of its adjacent plot.
Of congenital abnormalities of the rectum causing rectal bleeding, should be allocated to vascular anomalies (angiodysplasia) – abnormal development of blood vessels.
Infectious diseases lead to isolated rectal bleeding rare. Violation of the integrity of the vascular wall is observed in the majority of cases, the vascular lesions of not only the rectum, but other parts of large intestine.
It is possible with such infectious lesions:
- dysentery develops with the defeat of Shigella. While rectal bleeding manifests as bloody diarrhea;
- of the large intestine, including with involvement in the pathological process of the rectum
and so on.
The most telling example of the rectal disorders of local blood circulation, can cause bleeding are:
- hemorrhoids overflow with blood of the venous plexuses, which are located in the lower rectum;
- the weakness of the walls of the rectal vessels, which occurs as a result of lack of vitamins C and P
and so on.
As complications of diseases of other organs rectal bleeding can occur when portal hypertension – persistent increase in pressure in the portal vein (the main blood vessel in the liver). If the veins are rectal submucosal plexus expanded, against the background of portal hypertension are filled with blood, the wall can not withstand the pressure, violated its integrity – there is quite a pronounced rectal bleeding.
Trauma, which can lead to rectal bleeding, is observed as a result of:
- medical procedures;
- the impact of external traumatic factors;
- the passage of the solid particles in the rectum.
Because the rectum is supplied very well. This means that her trauma with the subsequent occurrence of bleeding can lead virtually any medical actions, namely:
- diagnostic;
- treatment.
Diagnostic manipulations that could cause rectal bleeding, is:
- finger examination of rectum;
- rectoscopy – study with a rectal mirror;
- rectoromanoscopy – study of rectum and sigmoid with sigmoidoscopy (a variety of endoscopic equipment);
- colonoscopy – examining the colon using colonoscope (a flexible probe with built-in optical system), which is introduced into the colon through the anus;
- biopsy – a tissue rectal wall for their subsequent study under a microscope.
Therapeutic measures that can cause rectal bleeding, is often:
- setting enemas with the use of traumatic adaptations (chipped bits);
- polypectomy – removal of polyps;
- hemorrhoidectomy – removal of internal hemorrhoids;
- surgery on the pelvic organs, located adjacent to the rectum
and so on.
Non-medical trauma the rectum causing bleeding, possible during:
- anal sex (especially on the background of dilated rectal venous plexus, characterized by a weak wall);
- energetic anal Masturbation with the help of improvised means, which are able to injure the rectal wall;
- the impact of external traumatic factors is chopped, sliced, torn, gunshot wounds.
Often injuries of the rectum followed by bleeding occur when trying maiming:
- with the aim of deliberate damage to its own tissues (for example, in the unwillingness to be mobilized for military service);
- mentally ill people;
- during the violent action of a person related to another person.
Severe trauma of the rectum followed by bleeding may occur as a result of the passage of solid particles in its lumen. This:
- solid faecal mass, formed as a result of persistent constipation;
- fecal stones – the solid structure formed in a toast to the intestine on the background of some rectal diseases or involutive (ageing) changes;
- a foreign body that got into the gastrointestinal tract through the mouth and out in a natural way, thus injuring the rectum. It can be accidentally or intentionally swallowed objects – close the fish bones, fragments of animal bones, fruit pits or fragments with sharp edges, knives, forks, studs, pins, badges, and so on.
Radioactive effects on the rectum are fraught with bleeding, if it is long. Such bleeding can occur when:
- radiation therapy diseases of small pelvis organs;
- contact with radioactive substances due to the nature of employment;
- unauthorized access to radioactive substances (smuggling).
The development of the pathology
Rectal bleeding is the secretion of rectal blood in any quantity – whether it’s even streaks of blood in the stool, blood smears on underwear or personal hygiene. In most cases, rectal bleeding is not pronounced. Only 10-15% of all clinical cases of rectal bleeding is accompanied by appreciable blood loss, which can lead to systemic hemodynamic (blood flow) with the development of collapse (sharp decline in blood pressure) or syncope (loss of consciousness). Therefore, rectal bleeding rarely require urgent surgical aid in the surgery.

The most pronounced may be rectal bleeding that occurred:
- as a result of injury of the rectum;
- the decay of a malignant tumor. In this case, profuse (expressed) bleeding is observed in the melting of large vessels.
Even if rectal bleeding unexpressed, but occur regularly, they can lead to the development of anemia – reducing the number of hemoglobin and erythrocytes.
In some pathologies alertness in terms of occurrence of rectal bleeding needs to occur at the early stages of development of such diseases. In particular, this:
and so on.
Symptoms rectal bleeding
The clinical picture of rectal bleeding is very diverse and depends on the underlying pathological condition that caused rectal bleeding. Bleeding from anal fissures and minor manifestoes separate bright red smears on the toilet paper. Patients complain for the expressed pain during defecation.

If rectal bleeding occurred on the background of internal hemorrhoids, the early stages of the pathology, the number of allocated blood will also be minor, such as spots on underwear or toilet paper. Pain during bowel movements do not exist – except strangulated hemorrhoid. With the progression of hemorrhoids rectal bleeding may be more intensive (selection of clusters), until the development of anemia.
The reason for the formation of the diverticulum of the rectum, and inflammation (diverticulitis) rectal bleeding develops less frequently than in other cases – but about the possibility of such a cause should be remembered. Practitioners suspect diverticulum as a precipitating factor of rectal bleeding in the last turn that leads to late diagnosis, wrong tactics and large blood loss because of bleeding on the background of the diverticulum of the rectum can be significant.
Bleeding during the formation of diverticula is capable of:
- to stop yourself;
- recur months or even years after the outbreak of the first allocation of blood.
Rectal bleeding due to rectal polyps often occurs in the absence of any clinical symptoms, speaking in such cases, the first symptom of polyps. Rarely it is diagnosed on the background:
Polyphonie bleeding is often minor, but repeated often, what develops persistent anemia. This is especially true of so-called family polyposis – when in the rectum, a large number of villous polyps, which are prone to severe bleeding.
Rectal bleeding when rectal cancer first is expressed slightly.
The blood in the stool is defined as:
- veins;
- clots.
In addition, manifestirutaya:
About the fact that the disease causing rectal bleeding, has a malignant nature, have documented the following violations:
- weakness;
- weight loss;
- poor appetite;
- aversion to meat;
- hyperthermia (increased body temperature).
If the bleeding is provoked by the malignancy, the amount of blood increases, it signals the disintegration of the tumor.
Rectal bleeding in angiodysplasia can manifest:
- anemia;
- the presence in the stool of bright red blood.
Other symptoms are lacking.
The clinical picture in polyps may also be absent. Color bleeding depends on the location of the polyp: the higher it is, the blood darker.
As a provocateur rectal bleeding can be suspected inflammatory lesions of the rectum, if the bleeding is accompanied by:
In addition to blood in the stool can also be detected:
- mucus;
- pus.
When progressive, severe form of inflammatory processes of the rectum provoke them rectal bleeding can increase, but still they are not so significant to cause significant blood loss. Distinctive clinical feature of rectal bleeding on a background of radiation injury of the rectum is that at the termination of radiation therapy such bleeding stop.
Diagnosis of rectal bleeding
The identification of rectal bleeding is not difficult. More difficult to determine the pathology which caused it. Therefore, accurate diagnosis should apply all possible methods of examination – medical history (clarification of information on the history of the disease), physical, instrumental, laboratory.
Data examination the following:
- on examination, the patient may be uninformative with minor bleeding. Only when the blood loss causing anemia, skin and visible mucous membranes are pale. In the case of serious diseases (in particular cancer) is visualized deterioration of the General condition of the patient – it is adynamic, weak;
- when digital examination of rectum – on the glove revealed blood traces. By its color it is possible to make some preliminary conclusions about how high in the rectum is the source of bleeding: the higher it is, the blood darker.
Instrumental methods used in the evaluation of rectal bleeding, the following:
- rectoscopy – examination of rectum using a rectal mirrors;
- sigmoidoscopy – examination of rectum and sigmoid with sigmoidoscopy (endoscope);
- plain radiography of the pelvic organs;
- computed tomography (CT) – evaluation of the rectal wall with the help of computer slicers.
- visceral angiography – performance of x-ray examination of blood vessels after injection into the bloodstream of a contrast agent;
- fistulografiya – perform x-ray examination of the fistula after the introduction into it of a contrast agent;
- biopsy – a tissue of the rectum with subsequent study under a microscope.

Also used methods of laboratory diagnosis – namely:
- General analysis of blood the number of erythrocytes and hemoglobin to assess the severity of blood loss;
- coprogram – cal study for the presence of blood, mucus and pus;
- fecal occult blood test – a method used for detecting blood traces;
- bacteriological analysis of feces – it can determine the causative agent, which could provoke pathology of the rectum, causing rectal bleeding;
- biochemical analysis of feces for the presence of trace elements in feces and make a conclusion about the pathology of the rectum;
- study a biopsy under a microscope.
Differential diagnosis of
Differential diagnosis of rectal bleeding should be bleeding from other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Complications
Complications rectal bleeding can be:
- anemia;
- infection blood clots in the lumen of the rectum with subsequent development purulent lesions of its walls.
Treatment of rectal bleeding
Treatment of rectal bleeding depends on:
- its intensity;
- pathology that provoked it.
The main principles of treatment in this case is:
- stop bleeding;
- restoration of circulating blood volume;
- the elimination of the pathology causing the described pathology.

Rectal bleeding is stopped by such methods as:
- hypothermia, local cooling;
- surgical diathermy – “to brew” the bleeding blood vessels using an electric current;
- laser photocoagulation the same principle, but using a laser;
- collage (sticking) hemostatic films.
In the case of ineffectiveness of these methods, surgery is performed during which:
- ligated the bleeding vessels;
- remove the bleeding focus.
Important is the restoration of circulating blood volume. With this purpose, perform intravenous administration of blood products and blood substitutes.
If rectal bleeding was observed once and it was a short appointment with the following:
- peace;
- a sparing diet of easily digestible food intake in order to avoid the formation of dense stool, can injure bleeding tissue, thereby exacerbating the bleeding.
In all cases should be treatment of the underlying disease that caused rectal bleeding.
Prevention of rectal bleeding
Prevention of rectal bleeding is a very wide range of activities. Their common point:
- prevention of occurrence of pathologies (illnesses and injuries), able to trigger the development of rectal bleeding;
- if such diseases arise – the need for their timely detection and treatment.
Forecast
The prognosis of rectal bleeding depends on the amount of blood loss, but generally favorable. Rectal bleeding often stop on their own and to any serious consequences they bring.
Prognosis worsens with profuse rectal bleeding, which are rare. Mortality in such cases reaches 4-10%.



