Fatty liver or pancreas refers to a rather dangerous pathologies can significantly undermine human health. Many attribute this phenomenon only to the excessive consumption of alcohol, which is not always true. The disease can touch any person at the combination of certain factors.
A disease such as fatty liver and pancreas, has a good prognosis for the restoration of the functions of these organs, but with early detection of disease and efficient treatment.
In advanced form, the disease can cause serious consequences, including cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis. All of this points to the importance of identifying the disease at an early stage.
What is this disease?
Fatty liver or fatty hepatitis (steatosis) of the liver is a pathology caused by the replacement of liver tissue adipose structure. Cumulative fatty liver disease (NIBP) is the reflexive reaction of the liver to the effects of certain toxins and pathogenic factors associated with the diseases and abnormal processes in the body. NIBP refers to steatosis that can cause obesity and other organs, including the pancreas. Fatty liver – fatty infiltration of the liver.
Fatty hepatitis (as well as steatosis of the pancreas) is the process of simple accumulation of fat and degeneration of normal cells of the body in fat cells due to the concentration of triglycerides in hepatocytes. This phenomenon arises from the fact that the body sends to the liver, all penetrated into the blood toxins that are out there and turn into simple fats. But when excess received of the fat do not have time to receive and concentrated in the body.
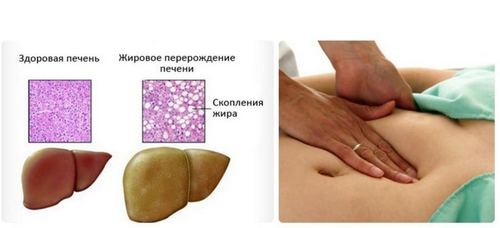
The degeneration of cells leads to functional impairment of the organ, which in turn enhances the process.
In General fatty liver (or pancreas) is a chronic, but reversible process of degeneration of the organ. However, if it is not stopped, the hepatitis fatty liver leads to the development of fibrosis and then cirrhosis.
Types and stages
Given the etiology of fatty hepatitis has two major forms: alcoholic hepatosis non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Alcoholic form of the disease caused by excessive alcohol consumption and poisoning other toxins whose effects may increase the hereditary factor. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease occurs when metabolic disorders and other abnormalities without the involvement of alcohol or other toxins.

According to the severity of the symptoms of fatty hepatitis is divided into 4 stages:
- The initial stage (stage 0): there is the appearance of small amounts of fat in certain cells of the liver (pancreas).
- Stage 1: small fatty liver noticeable fat accumulation in individual cells.
- Stage 2: obesity of most cells, but with varying degrees (from microscopic particles of fat to large concentrations).
- Stage 3: diffuse the development of obesity with large clusters and the appearance of extracellular obesity, the formation of fatty cysts.
The causes of the disease
Causes of accumulation of fat in the liver depend on the type of disease. In alcoholic steatosis lead to pathology of alcoholic toxins coming into the liver in too great quantity. A similar phenomenon is observed in other toxic poisoning, when the body can not cope with the excess toxins. Most often, alcohol increases the effects of genetic predisposition, resulting in genes abnormal sensitivity to such toxins. To other provoking factors of alcoholic origin of steatosis is defined as presence of hepatitis C virus, leading to additional inflammatory responses, excessive body weight, excess iron, poor diet.

Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may occur even in perfectly sober people and most often appears in people aged 25-40 years. The most likely cause is a metabolic process. At increased risk are people with excessive weight or patients with diabetes. Often non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is noted with a significant increase in cholesterol, and insulin resistance. The hepatitis of this type can cause oxidative stress. To provoking factors include the presence of hepatitis viruses, intake of certain medicines, liver disease of autoimmune nature, poor nutrition, malnutrition.
A special category are pregnant women. They have hepatitis fatty liver (obesity and pancreas) is quite frequent, which is likely related to hormonal changes in the body.
The symptoms of the disease
In the initial stages of fatty hepatitis can be a long time to occur completely asymptomatic, and identify it by using ultrasonography in prophylactic examinations. During the first stage of fatty liver is manifested through fluctuations in the level of enzymes Alat and ASAT. Starts sluggish inflammatory process.
At the second stage of fatty hepatitis shows more obvious symptoms: sensation of heaviness in the upper quadrant and abdominal discomfort on the right side, enlargement of the liver, seal liver tissue with increased echogenicity by ultrasound, reducing the speed of blood flow in the vessels of the liver, darkening of the skin on the neck and in the armpits.
Progressive disease the most obvious symptoms manifesting on stage 3. Typical symptoms include nausea, persistent pain under the ribs and in the abdomen to the right, feeling of fullness in right side, impaired digestive function, loss of appetite and weight loss.
Diagnosis
Treatment of steatosis starts after carrying out a comprehensive diagnosis of the disease. Primary diagnosis is based on the results of ultrasound of the liver (pancreas). In this study determined the increase of the body, diffuse increased echogenicity, and severe stages – the granularity of the parenchyma. Confirmation of the diagnosis and differentiation of disease are produced by means of computer and magnetic resonance tomography. If you need a complete picture of the condition of the liver can be performed her biopsy.
Treatment
Fatty liver hepatitis is treated in an integrated manner (with the use of drug therapy, herbal medicine, physiotherapy techniques).
An important part of healing is to optimize lifestyle: increased activity, exercise, outdoor walks, special diet, (diet number 5).
Special diet
Treatment of fatty liver is based on maintaining a diet with increased content in protein products and substances capable of dissolving liver fat (cereals, cheese), but severely restrict animal fats. Prohibited foods include whole milk, cream cheese, muffins and white bread, sweets, pasta, mayonnaise, sausage, margarine, soft drinks and sodas. Strictly forbidden alcohol. Should not eat fried foods and restrict the sugar consumption.
The emphasis in the diet should do in the vegetables with choleretic action (cabbage, carrots, pumpkin), protein foods (meat and fish stews). Very useful kefir, yogurt. You should increase fluid intake (2 l per day). Meals should be frequent, but fractional.
Drug therapy
Treatment of steatosis involves the appointment of agents, stabilizing the function of the liver and regenerating tissue. Essential drugs are phospholipids (Essliver, Essentiale Forte, Berlition), sulfaminokislotu (taurine, methionine), hepatoprotectors of plant-based (karsil, artichoke extract), antioxidant vitamins kinds (tocopherol, retinol), preparations on the basis of selenium, b vitamins.





With thanks! Valuable information!
Don’t wear seat belts lest you drown in you own urine?
Black on black in the Charg I’m creepin’ Rub me the right way, you might get a genie B.o.B, black Houdini
Black on black in the Charger I’m creepin’ Rub me the right way, you might get a genie B.o.B, black Houdini
I understand this, but I do have a question. Do you mind chatting?