Gallstone disease is a common pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Initially formed suspension in the gall bladder: what it is, few people know of people who are faced with this disease.
But it the components of bile that are included with this suspension, subsequently kristallizuetsya, forming stones.
Sludge in the gallbladder is a small grain of sand of bile, which are formed due to the disruption of the biliary system. The stagnation of bile, accompanied by the formation of suspended solids, called sludge syndrome.
This condition can develop in anyone at any age (including in children), but most of the flakes in the gall bladder appear in women older than 40 years.
What is a sludge-syndrome?
The suspension consists of crystals of cholesterol, protein and calcium salts which have different patients can be formed in various proportions relative to each other. It is possible to detect the precipitate in an ultrasound gallbladder. Education of suspended solids is considered the first stage of gallstone disease, as the appearance of the stones results in the suspended particles bonding to each other.
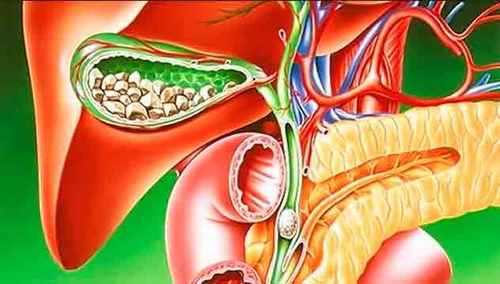
Biliary (gallbladder) sludge can be a primary, developing as an independent disease and not accompanied by a concomitant disease, and secondary, which occurs on the background of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., pancreatitis).
The nature of the composition of suspended matter in the gallbladder can vary. Thus, when the ultrasound some patients are identified clumps of bile zamoskvoreckogo character or microlithiasis, there are small inclusions that can be seen by changing the position of patient’s body. A certain proportion of patients detected by the combination of thick bile and microlithiasis.
The reasons for the development of the pathology and diagnosis of the disease

The main causes of the disease are:
- violation of cholesterol metabolism, which is caused by sedentary lifestyle and consumption of junk food (fried, greasy and salty foods, fast food);
- pregnancy, contributing to increased intra-abdominal pressure and, as a consequence, the development of bile stasis;
- oral contraceptives, affect the composition of bile.
The progression of the disease contribute to diabetes, obesity, atherosclerosis and cirrhosis of the liver.
At the initial stage of development of the disease, when the first clumps are formed in the gallbladder, the patient often feels no discomfort.
With the progression of pathological States appear symptoms such as:
- pain in the right hypochondrium (the manifestation of pain may be different, their nature is paroxysmal or permanent, which becomes more intense after a meal);
- loss of appetite;
- nausea and vomiting (sometimes bile);
- heartburn;
- violation of stool (constipation, diarrhea or alternating).
Diagnosis is made on the basis of several factors. First of all, the doctor-gastroenterologist collects medical history: the patient asks about when the first symptoms, what is their nature and where localized pain. Be sure to take into account the existing patient’s gastrointestinal pathology and the facts of medication or regular alcohol consumption.
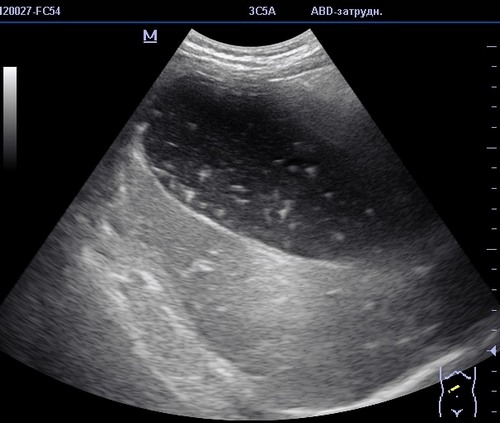
Then the doctor examines the patient and assigns the urine and blood. Laboratory tests can determine the liver enzymes, bilirubin, cholesterol and total protein in blood to estimate the speed of metabolism.
The most popular research methods include:
- Ultrasound examination of abdominal cavity to detect flakes and to quantify and assess the condition of the walls of the gallbladder;
- magnetic resonance imaging, which enables to detect various changes in the gallbladder and liver tissues;
- duodenal intubation for obtaining bile and the study of its composition.
Treatment of the disease
Depending on the condition of the biliary tract, the treatment may be carried out by one of three schemes:
- Patients with minimal disruption corrective shows diet number 5, but drug therapy involves the elimination of the causes which led to the development of pathology.
- The second (basic) group of patients, conservative treatment is indicated, which provides for receiving funds, eliminating the stagnation of bile, protects the liver and relieves pain. The patient is also assigned a diet that excludes fatty and fried foods, flour products, eggs, mayonnaise and sauces.
- If such treatment fails, the patient is assigned to surgical intervention.
If echogenic impurities in the bile are not eliminated in a timely manner, the patient may develop biliary colic, pancreatitis, cholangitis, or cholecystitis.
The fight against disease involves the normalization of body weight and elimination of diseases that contribute to development of pathologies of the gallbladder.