Renal failure called a pathological condition caused by violation of kidney function in the formation and excretion of urine. Since the result is the accumulation of toxins, changes in acid-base and electrolyte balance, the symptoms of kidney failure affect different organs and systems.
The development of renal insufficiency structures (nephrons), has many causes.
Depending on how it is expressed and how quickly changes the clinical picture distinguish acute and chronic forms of the disease. To determine how kidney damage, it is important to select the most rational treatment.
Mechanisms of formation of clinical signs in acute renal failure
Acute renal failure is 5 times more common in the elderly than in the young. Depending on the level of the lesion, to distinguish between types of failure.
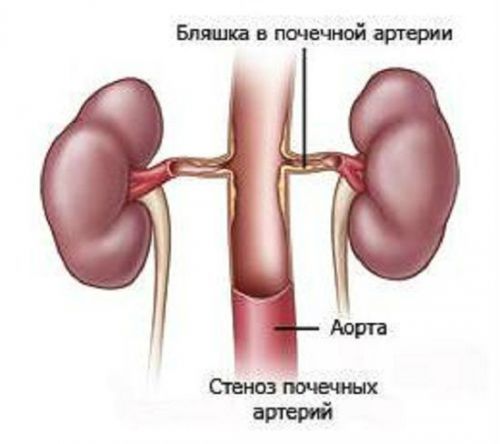
Prerenal – develops under disturbed flow of blood through the renal artery. Ischemia of the renal parenchyma occurs in the case of a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Such States are called:
- shock (pain, hemorrhagic, septic, blood transfusions, injuries);
- severe dehydration frequent vomiting, diarrhea, massive blood loss, burns.
Atherosclerosis of the renal artery creates conditions for thrombosis of a main feeding vessel and contributes to ischemia of the parenchyma
In thromboembolism there is a complete blocking of supply of the kidney with the development of necrosis of the epithelium, basement membrane, hypoxia glomeruli. Tubules become impassable, their squeeze necrotic cells, edema, protein deposition.
In response to increased renin production, decreased vasodilator action of prostaglandins, which exacerbates the violation of renal blood flow. Termination of the filter causes the condition anuria (absence of urine).
In renal failure renal type should take into account two main reasons:
- mechanism of autoimmune destruction of glomeruli and tubules complexes of antibodies on the background of existing diseases (systemic vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, collagen diseases, acute glomerulonephritis, and other);
- direct action on renal tissue received into the bloodstream and toxic substances (heavy mushroom poisoning, lead compounds, phosphorous and mercury, medications in toxic doses, intoxication in septic complications after an abortion, massive inflammation in the urinary tract).
Among nephrotoxic drugs in the first place are the aminoglycoside antibiotics group. Found that 5-20% of patients they cause moderate signs of renal failure, 2% of marked clinical manifestations.
Under the influence of nephrotoxic substances in the tubular epithelium is necrotic, delaminate from the basement membrane.
The differences between prerenal and renal types of anuria are that:
- in the first case there is a total disruption of blood flow, therefore one can expect signs of heart disease;
- second, all changes are isolated within the renal parenchyma.
Most often found in the practice of urology postrenal failure.

It is called:
- narrowing or complete obstruction (overlapping diameter) of the ureter stones, blood clot, external compression by tumor of the colon or genital organs;
- the possibility of erroneous ligation or suturing of the ureter during surgery.
The structural units of the kidney are compressed overstretched the pelvis and cups
The clinical course of this type of kidney failure you’ll be at a slower pace. Before the development of irreversible necrosis of nephrons have three or four days, during which treatment will be effective. Restoration of urinary output occurs during catheterization of the ureters, the puncture and insertion of drains in the pelvis.
Some authors emphasize burichenko (caused by lack of kidney) form congenital malformation (aplasia). It is possible for the newborn or when you delete the only working kidney. Revealing aplasia of kidneys considered a defect incompatible with life.
What changes in the body are caused by acute anuria?
Signs of kidney failure associated with the lack of production and excretion of urine, lead to increasing changes in General metabolism.
Occurs:
- the accumulation of electrolytes, increase in extracellular fluid concentrations of sodium, potassium, chlorine;
- blood quickly increases the level of nitrogenous substances (urea, creatinine), in the first 24 hours it doubles the total creatinine content, and every next day there is an increase in 0.1 mmol/l;
- shift of acid-base balance is caused by reduction of salts of bicarbonate leads to metabolic acidosis;
- inside the cells starts with the collapse of protein complexes, fats, carbohydrates with accumulation of ammonia and potassium, so disturbed heart rhythm can cause cardiac arrest;
- nitrogenous substances of the plasma reduce the ability of platelets to stick together, leading to accumulation of heparin that prevents blood clotting, promotes bleeding.
The clinical picture of acute renal failure
Symptoms for acute kidney failure is determined by the cause of disease and degree of functional disorders. Early signs may hide a common disease. The clinic is divided into 4 periods.
Initial or shock – dominated by manifestations of the underlying pathology (trauma, shock, severe pain, infection). Against this background, the patient detected a sharp decrease in the allocated amount of urine (oliguria), until the complete cessation.
Oligoanalgesia – lasts up to three weeks is considered the most dangerous.
Patients are observed:
- lethargy or General anxiety;
- swelling of the face and hands;
- blood pressure is lowered;
- nausea, vomiting;
- when starting the edema of the lung tissue increases shortness of breath;
- violation of heart rhythm associated with hyperkalemia, is usually fixed bradycardia (rate less than 60 per minute);
- often have chest pain;
- in the absence of treatment, there are signs of heart failure (swelling in the feet and legs, shortness of breath, enlarged liver);
- back pains are dull in nature, due to the hyperextension of the capsule of the kidney, the transition of the swelling into the layers of fat tissue pain subside;
- intoxication is the development of acute ulcers in the stomach and intestines;
- hemorrhagic complications such as subcutaneous hemorrhage, gastric or uterine bleeding caused by activation Universiada system.
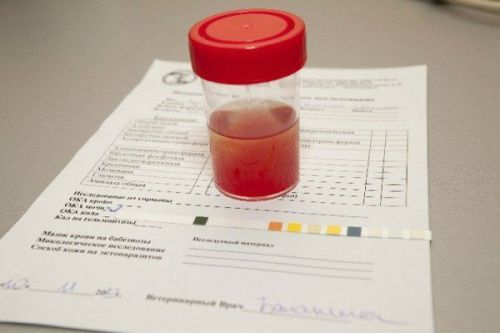
To diagnose the degree of kidney damage can be by what changes are detected in the blood and urine.
Urine has bloody character with a massive precipitate
Microscopic examination of the urine erythrocytes, occupying the entire field of view, granular cylinders (protein casts). Specific gravity low.
In the blood there are signs of uremic intoxication in the form:
- reduce the content of sodium, chlorine;
- increase in the concentration of magnesium, calcium, potassium;
- the accumulation of acidic metabolic products (sulfates, phosphates, organic acids, residual nitrogen);
- anemia always accompanies renal failure.
What are the signs differ in the recovery stage?
The early recovery is the stage of polyuria. Lasts up to two weeks, takes place in 2 periods. Initial symptom is the increase in daily diuresis up to 400-600 ml. a Sign is seen as favorable, but only conditionally, since the increase in urine output occurs on the background of growth of azotemia, severe hyperkalemia.
It is important that in this period of “relative prosperity” killed ¼ of the patients. The main reason for heart disorders. The allocated volume of urine is insufficient for the removal of accumulated toxins.
The patient is experiencing:
- mental changes;
- perhaps a comatose condition;
- a drop in blood pressure (collapse);
- arrhythmia breathing.
- cramps;
- vomiting;
- severe weakness;
- an aversion to water.
Further development of polyuria facilitates the excretion of nitrogenous substances, excess electrolytes. But the danger remains as long as the kidney will not recover the ability not only to maintain and regulate the necessary balance of nutrients, water and electrolytes.
The recovery period lasts up to a year.
Confidence in a full recovery of the patient occurs when:
- the definition in the blood of normal electrolytes, creatinine;
- sufficient urine output in accordance with the consumed fluid, and the normal daily fluctuations of the specific weight;
- the absence of pathological inclusions in urine sediment.
About the peculiarities of diagnostics of kidney failure read in this article.
Clinic of chronic renal failure
Signs of chronic renal failure detected in 1/3 of the patients in urology departments. It is most commonly associated with long-term current diseases of kidneys, especially against the background of anomalies of development, diseases, sharply breaking metabolism (gout, diabetes mellitus, amyloidosis of internal organs).
Clinical features:
- the beginning of renal tubular apparatus system;
- the presence of recurrent infections in the urinary tract of the patient;
- accompanied by impaired outflow urinary tract;
- wave-like change of the reversibility of signs;
- slow the progression of irreversible changes;
- often timely surgical intervention can cause long-term remission.
In the early stages of chronic insufficiency symptoms manifested only in the case of increasing the burden on the kidneys.
It can be caused by:
- consumption of salted or smoked meats;
- a large amount of beer or other alcohol;
- pregnancy in women that impedes the flow of urine in the third trimester.

Patients find swelling of the face in the morning, weakness and reduced ability to work. Only laboratory data indicate early failure of the kidneys.
Loss of appetite is one of the primary symptoms of kidney damage
With increasing destruction of renal tissue appear more characteristic features:
- nocturia is predominant excretion of urine at night;
- sensation of dryness in the mouth;
- insomnia;
- allocate a large amount of liquid urine (polyuria);
- increased bleeding gums, mucous in connection with the suppression of platelet function and accumulation of heparin.
Pathology goes through stages:
- latent,
- compensated
- intermittent,
- terminal.
The ability to compensate for the loss of part of the structural units of the kidney associated with a transient hyperfunction of the remaining nephrons. Decompensation begins with reduction of urine formation (oliguria). Blood accumulates ions of sodium, potassium and chlorine, nitrogenous compounds. Hypernatremia leads to significant fluid retention inside the cells and in the extracellular space. It is a cause of high blood pressure.
As affects internal organs with kidney failure?
In chronic renal failure, all the changes occur very slowly, but they are persistent and lead to the simultaneous defeat of all organs and systems of man. Hyperkalemia causes brain damage, muscle paralysis, heart on the background of severe myocardiodystrophy developing blockade of the conduction system may stop (asystole).
The combination of electrolyte disturbances, acidosis, anemia, fluid accumulation within cells leads to uremic myocarditis. Myocytes lose their ability to synthesize energy for contraction. Evolving myocardial dystrophy and subsequent heart failure. The patient has shortness of breath when walking and at rest, swelling in the feet and legs.
The swelling of the feet constant, increases after a walk in the evening
One of the manifestations of uremia is a dry pericarditis, which you can listen with a stethoscope in the shape of a pericardial RUB. Pathology is accompanied by pain behind the breastbone. ECG reveals inperceptably curve.
From the lungs may develop uremic pneumonia, tracheitis and bronchitis, edema of the lung.
Concerned:
- cough;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- hoarseness;
- possible hemoptysis;
- chest pain when breathing caused by dry pleurisy.
Auscultation listened mixed wet rales, areas with a hard breath.
Liver cells (hepatocytes) are highly sensitive to pathogenic changes. They stop the synthesis of the necessary enzymes and substances. Comes kidney and liver failure.
The symptoms are added:
- yellowish coloration of skin and sclera;
- increased dryness and sagging of the skin;
- loss of muscle tone, tremor of the fingers;
- possible bone pain, arthropathy.
Already in the early stages, patients with urological problems are often treated for chronic colitis, disorders of the chair, vague pain during bowel. This is due to the reaction of the intestinal epithelium to altered kidney function. In the advanced stages of nitrogenous substances begin to stand out through the intestines, saliva. There is the smell of urine out of the mouth, stomatitis. Ulcers in the stomach and intestines have a tendency to hemorrhage.
What are the symptoms characteristic of each stage of failure?
For chronic kidney failure 4 typical stages of the disease. In the latent stage the patient seldom makes a complaint.
Sometimes marked:
- the increased fatigability during physical work;
- fatigue and weakness to the end of the day;
- feeling of dryness in the mouth.
The urinalysis revealed protein and cylinders, in the blood of minor changes of electrolytes.
In the compensation stage – malaise increases. Patients copious urine (up to 2.5 liters per day). Laboratory data reveal the initial changes in the filtration capacity of the kidneys.
Intermittent stage is characterized by increased content of nitrogenous substances in the blood plasma.
Patients concerned about in addition to latent manifestations:
- thirst, constant dry mouth;
- loss of appetite;
- the feeling of the unpleasant taste;
- constant nausea, frequent vomiting;
- tremor of the hands;
- convulsive twitching of the muscles.
Any infections are very hard (SARS, tonsillitis, pharyngitis). The degradation is caused by errors in diet, workload, stress.
Itchy skin can wear a painful character
End-stage manifests a versatile organ.
Patient has:
- emotional instability of the psyche (there are frequent transitions from drowsiness and apathy to excitement);
- inappropriate behavior;
- severe puffy face with swelling under the eyes;
- dry cracked skin with signs of scratching due to the itching;
- visible exhaustion;
- yellowness of sclera and skin;
- dull hair;
- hoarse voice;
- the smell of urine out of his mouth, sweat;
- painful sores in the mouth;
- tongue coated grayish-brown patina, on the surface of the ulcers;
- nausea and vomiting, belching;
- frequent foul-smelling stools, possibly with blood;
- urine during the day not selected.
- hemorrhagic manifestations in the form of bruises, minor rashes, uterine or gastrointestinal bleeding.
Urgent diagnosis and treatment of patients with acute renal failure allows for recovery of most patients. In chronic kidney failure need treatment of the underlying disease, prevention of exacerbations, and timely surgery to restore patency of the outflow pathways of urine. Hope for treatment of folk remedies is not justified.
Most patients with chronic form requires the use of the apparatus “artificial kidney”, organ transplantation. Choosing a method of therapy, doctors according to the clinical manifestations judged on the stage of the disease. Proper assessment of the patient depends on the experience and capabilities of the survey.



500 new player bonus. Enjoy the most fun slots action online now