In the instructions to the drug always indicated by its effect on the various organs, side effects and need for dose adjustment depending on renal pathology. If kidneys hurt after antibiotics, this is due to existing disease that is exacerbated under the influence of drugs.
Antibiotics toxic to the kidneys
The leader in the nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides is. Gentamicin, Kanamycin, Tobramycin, Amikacin prolonged intravenous use to the maximum dose can cause damage to the glomerular tubules.
Clinically it is manifested by the appearance in the urine of albumin, traces of erythrocytes, enzymes. When kidney failure, they are administered with great care.
The kidneys can develop after treatment with polimiksinami. With normal kidney function and recommended doses side effects are rare.
Tetratziklinove a number has no direct nephrotoxic effect, but after taking the patients with renal insufficiency increase the concentration of urea in the blood. When the disease high severity is developing azotemia, acidosis and vomiting.

A group of cephalosporins are considered relatively safe for those with kidney disease. But the old representatives of Cephalothin and Cephaloridine have a nephrotoxic effect. Dangerous combination with aminoglycosides. Action on the kidneys is manifested in the development of necrosis of the renal tubules.
The kidneys can get sick after taking medicines to treat tuberculosis – Rifampicin, Benedicine, Streptomycin.
Penicillins are low toxic, their ingestion, even in large doses, not accompanied by renal damage.
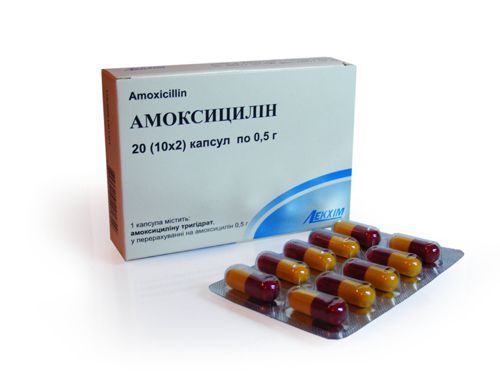
Amoxicillin belongs to the group of penicillins that are not toxic to the kidneys
The mechanism of damage
Kidney damage occurs in allergic or toxic to the path, possibly a combination of both. Reaction develops after sensitization – initial contact with allergens drugs, preobrazovanii immune complexes.
Re-introduction of antibacterial drug causes an immune response – formation of immune complexes antigen-antibody, activation of cells – macrophages, enhanced antibody synthesis. It krupnomasshtabnye protein formation, and therefore, they do not pass through the renal tubules.
Toxic effect develops in the nephrons, there is a direct tubular damage Department. The lesion may develop indirectly, through the violation of hemodynamics, homeostasis, microcirculation, and metabolism.
What leads to such pathologies?
Morphological changes in renal tissue depends on the mechanism of action of the antibiotic. Occurs swelling of the parenchyma, infiltration of eosinophils, giant cells. Violated the permeability of cell membranes, changes its lipid composition.
If dominated immune response, there is a loss of glomeruli with the development of glomerulonephritis. Tubular necrosis leads to an increase in acute renal failure.
Chronic kidney damage by antibiotics causes degenerative changes in the tubules, proliferation of connective tissue, swelling of the glomeruli and vascular injury by type of hemorrhagic vasculitis. This leads to the formation of chronic renal failure.
Clinical manifestations
In addition, kidney pain, gradually there are other symptoms:
- fever;
- skin rash;
- swelling;
- increase or decrease in blood pressure against the background of anaphylactic shock;
- increases urine protein up to 12 g/l;
- in General, the analysis appear leukocytes, erythrocytes, cylinders;
- reduced clearance of urea, renal plasmotek;
- reduced daily diuresis;
- develops azotemia,
- rarely glycosuria.
Depending on the severity of symptoms, after discontinuation of the antibiotic, the symptoms disappear, the kidneys are restored. But in severe cases, the possible transition of nephropathy in the chronic form.

Glomerulonephritis affects the glomeruli
Whether to stop taking drugs?
What should I do if started to hurt the kidneys on the background of treatment with antibiotics? Cancel the drug should not. This decision is made by the attending physician. Incomplete treatment leads to development of resistance in microorganisms to antibiotics. Therefore, for the treatment of infectious diseases course is not less than 7 days.
Correct tactics will be the best practices for taking the drug. Not necessary to change the dosage or frequency of use. If there are unpleasant side effects, you need to consult a doctor. It is possible that further study would be needed of renal function, ultrasound for dose adjustment or replacement of the drug less toxic. To quickly remove toxic products of metabolism, it is recommended to drink a large kolichestvennoi.
To recover from antibiotics dairy products, kidney tea, probiotics.
Kidney damage can have varying degrees of severity. The development of acute renal failure is often lethal, especially considering anaphylactic reactions the use of antibiotics. Other acute lesions of the pass with proper treatment after 4-6 months, but often become chronic.
To avoid unpleasant consequences, you should not self-medicate. The choice of drug should always be done by the doctor.