In the differential diagnosis of various renal pathologies is of great importance laboratory methods, including the examination of urine. This biological environment is studied by many parameters, among which is the determination of the amount of protein.
This figure is very informative and helps to timely and accurately diagnose as kidney disease, and some functional abnormalities.
But in any case the allocation of kidneys increased amount of protein complexes and detect them in the urine, or proteinuria, requires careful study as one of the signs of possible diseases.
How is the allocation of kidney protein
The formation of urine from blood is in the renal glomeruli and tubular system. Thanks to the coordinated work of these structures, the urine has a salt composition, specific gravity and acidity, it contains some cells, enzymes and other organic compounds, including proteins.
Through a complex filtration system is able to penetrate only the albumin (another name for proteins), which have a low molecular structure. Therefore, a number of protein complexes in the urine is always normal is detected in the daily amount of urine not more than 50 mg of albumin.
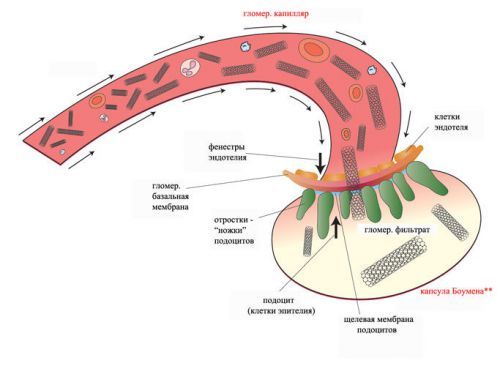
Filtering is carried out by the renal glomeruli, has three levels:
- endothelial cells, i.e. the first layer in contact with the blood plasma; these cells are connected to each other loosely, forming a rounded opening;
- the basement membrane, which is a gel layer;
- epithelial cells, which are located between their legs plexus.
The filtration system of the kidney has a complex structure
The result is a complex three-tiered mesh filtering system, which depends on many factors. Thus, the change in the velocity of blood flow increased pressure in the blood vessels, deposition of immune complexes can disrupt normal filtration and lead to the fact that urine will penetrate and high molecular weight proteins. The more, the more pronounced albuminuria (now instead of the term used in more modern “proteinuria”).
The described mechanism is not only in the formation of proteinuria. This laboratory characteristic can be pathological, that is a manifestation of many renal diseases, or physiological, that is temporary and not harmful to human body.
Types of proteinuria
The detection of protein in urine can occur for various reasons and as a result of various mechanisms, therefore there is the following classification of pathology:
- disease;
- according to the source, or the place of penetration of protein into the urine;
- the composition of protein complexes;
- for the amount of protein in urine.
Protein in the urine caused by fever, most often is a temporary phenomenon

Albuminuria develops not only in various diseases of the kidneys and other parts of the urinary system, called pathological. Very often, the protein in the urine indicates some functional States, lasting not transitory, and combined with laboratory signs such as pyuria or erythrocyturia.
The functional include the following types of proteinuria observed in patients on the background of a perfectly healthy kidney and are always characterized by a low level of albumin in the urine:
- orthostatic proteinuria is observed only in the upright position of man and disappears in the supine position, mainly among young people, the level of protein – no more than 1 g per day;
- feverishdetermined when the temperature of the body, mainly the elderly and children, the amount of protein – 1-2 g/day; but with the appearance of other laboratory symptoms of renal disease (hematuria, leukocyturia) and a high level of protein in the urine of physiological goes into the category of pathological proteinuria;
- albuminuria voltagewhich develops after prolonged or heavy physical exertion;
- in obesity or in pregnancy, which is associated with increased glomerular filtration in the background of these States.

Proteinuria in obesity is not considered a symptom of kidney disease
In violation of the mechanism of filtration and reabsorption of protein complexes that occur at a certain point in clubocka-tubular system, share prerenal, renal and postrenal proteinuria. Usually with these types of pathology occur massive loss of protein in urine, up to 20 grams per day.
Their differentiation to diagnose a serious disease. So, prerenal albuminuria is characteristic of myeloma nephropathy or intravascular hemolysis. Renal, subdivided into tubular and glomerular, detected in all glomerulonephritis, amyloidosis, glomerulosclerosis, interstitial nephritis, tubulopathy different, kanalzeva necrosis, transplanted kidney rejection, Fanconi syndrome. Postrenal albuminuria is a consequence of infectious processes in the urinary system and is due to increased filtration of protein complexes from plasma into the urine. This kind of disease is characteristic of all pyelonephritis.
In addition, the penetration of protein in urine can be random or selective. The concept of “selectivity” in this case means the choice of protein complexes, has low weight molecules, which allows them to overcome the glomerular filtration system, even when slightly expressed in kidney disease. This feature is present mainly albumin, so their detection in the urine in moderate amounts is evidence of severe renal abnormalities and is considered a prognostically favorable.
Normal structure of renal tissue is damaged in many pathologies, leading to inefficiency of the filtration system
If the destruction of the nephron reaches a considerable degree, and the filtration system is intensively damaged. Through the formed in it “holes” and “gaps” are able to penetrate into the urine are not only low molecular weight proteins, but proteins with more complex structure and a high mass: gamma globulin, lipoproteins, macro globulins. Therefore, their appearance in the urine is a sign of severe renal disease and proteinuria is called selective.
The following classification describes the symptoms of proteinuria and is carried out according to the number of protein complexes with different molecular mass was detected in the urine:
- Microalbuminuria is characterized by the level of protein in the urine from 30 to 500 mg per day, which is marginally higher than normal. However, this feature is very important in diagnosis, because it begins with damage to the kidneys as a target organ in diabetes, hypertension. In such cases, by means of General analysis of urine microalbuminuria is not detected, it is necessary a more accurate study.
- Low or moderate proteinuriais diagnosed when bacterial (tuberculosis, pyelonephritis), autoimmune (glomerulonephritis) inflammation, urolithiasis, and malignancy of the kidneys. Depending on the level of protein (at low, up to 1 g/day, with a moderate – 1-3 g/day) is the process of determining the degree of severity of the disease.
- High proteinuria nephrotic otherwise referred to, the loss of the daily protein is from 3.1 grams or more. This symptom is very dangerous in the prognostic plan and is a symptom of nephrotic syndrome, which also is a significant reduction of proteins in the blood (hypoalbuminemia) and a sharp deterioration in its clotting. Nephrotic syndrome may develop in severe forms of glomerulonephritis, renal amyloidosis, cancer.
All of these types of proteinuria occur in various pathologies of the kidneys are not in an isolated manner, but in the form of the complex. Thus, tubular, or tubular, is often low or moderate, and selective. Orthostatic tachycardia – always benign and transient, i.e. a transient and isolated and not combined with other symptoms of renal pathologies. Proteinuria is usually benign, isolated and tubular.
The appearance in urine of proteins of high molecular weight is a sign of severe renal pathology
Every disease of the renal parenchyma is characterized by a complex of several types of proteinuria. Laboratory examination of the urine and accurate characterization of protein loss, as well as features themselves are protein molecules that helps identify causes of proteinuria, that is diagnosing the type of renal pathology. In other words, using a urine test for proteinuria can be precisely and quickly differentiate the disease and assign the appropriate therapy.
What is the danger of proteinuria
Detection in the urine protein molecules becomes primarily a method of clarifying any kidney disease. But do low and high molecular weight albumins and proteins, falling in excessive quantities in the tubular neck, pyelocaliceal renal system and then in the urinary channels, are not “neutral” for of the epithelium of these structures. They have a negative, nephrotoxic effects.

Thus, increased amounts of albumin amplify the inflammatory process, destroy the epithelial cells of proximal renal tubules, contribute to their spasm. Another protein, transferrin, increases the formation of oxygen radicals, increases the severity of inflammation. The higher the level of pathological proteinuria, the more intense the negative effects on the interstitium of the kidneys. It has been proved that the high content of protein molecules in the primary urine is becoming a leading risk factor for kidney failure in most renal diseases, especially in nephropathies with chronic. In addition, the same factor, mainly microalbuminuria is a catalyst for the development of complications of the heart and blood vessels.
The excess protein in a common urine test to judge the possibility of kidney disease
Differential diagnosis of States involving the presence of protein in the urine
In General, the urinalysis, which examines a single (morning) dose of urine, to determine the daily protein impossible. But this study found in the urinary sediment hyaline casts, composed of protein molecules. To Refine the appearance of proteinuria and its level, on the basis of results of urinalysis is further determination of the daily protein, the protein of Bens-Jones, the level of albumin in the blood.
Through these laboratory methods to diagnose the various patient functional status and renal pathology: congenital and acquired, infectious and somatic.
In General, the course and the stages of diagnosis can be represented as follows:
- The detection of protein in the General analysis of urine: the patient investigated the complaints and anamnesis, external examination is performed. At this stage, functional proteinuria differentialsa with pathological. If the functional protein in the urine is excluded, then follows the second stage.
- Analysis of circadian protein and the protein of Bens-Jones, an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder and prostate indicated. At this stage excluded proteinuria voltage, leaving only the pathological types of renal diseases.
- Is the whole complex of additional laboratory and instrumental methods, it is then possible to diagnose the patient’s primary or secondary renal pathology, and adversely affect the condition of the renal parenchyma (hemolysis, lymphoma, myeloma).
All these stages is feasible at the level of the ordinary clinic or hospital in a serious but difficult to diagnose cases, the patient should be sent to the regional or provincial centers. Depending on what the diagnosis is determined, treatment will be carried out in outpatient or inpatient.
Treatments
The appearance of protein in the urine with the pathological characteristics (resistant, massive, selective or non-selective proteinuria) is a sign of any kidney disease. Therefore, the main therapy remains the causal direction, which in this case is to eliminate or reduce the intensity of symptoms of the underlying pathology.

Assigned pathogenetic and treatment, affecting the mechanisms of development of proteinuria, and also aimed at reducing the toxic effects of protein molecules on the tubular system. Therefore among all medicines through which the treatment of proteinuria include medications renal protection effect: statins, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, receptor blockers angiotensin.
Between courses of drug therapy folk ways, including decoction of kernels of corn
Therapy conduct courses for a long time. In many cases, in agreement with the doctor between courses allowed the use of herbal remedies. So, to reduce the level of protein in the urine will help the infusion of parsley seeds or birch buds, cranberry or bearberry leaf, a decoction of oats or corn.
The effectiveness of therapy depends on many factors. Fast positive dynamics, that is, decrease of protein in urine, considered prognostically very favorable for disease and the health of the patient. In all cases, the detection of proteins in urine must be further examined, which often helps not to miss serious pathology of the kidneys.



I must show my admiration for your kindness giving support to individuals that should have help with your question. Your very own dedication to passing the message throughout had become especially effective and has usually permitted workers just like me to arrive at their desired goals. Your own interesting instruction implies a whole lot to me and far more to my peers. Warm regards; from everyone of us.
I blog frequently and I truly thank you for your content. This article has really peaked my interest. I will take a note of your blog and keep checking for new information about once a week. I subscribed to your RSS feed too.