The composition and concentration of dissolved substances in urine the reflect the progress of all types of metabolism. Waste products of metabolism are excreted in the urine, if the size of the molecules allows them to pass through the renal filter. The rest are sent to the intestine.
Bile pigments in the urine are present in very small quantities. They color the urine a yellowish color. Conventional laboratory methods to detect this minimum is not possible, nor considered necessary.
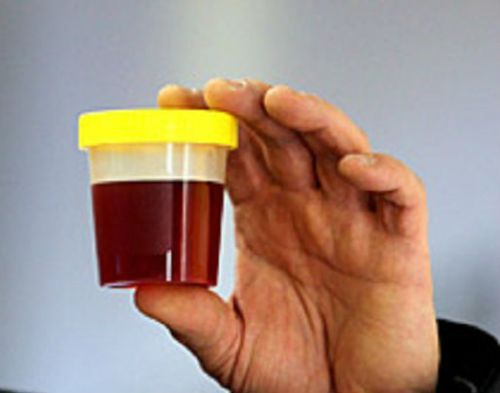
In the case of the darkening of urine color to “color of beer” there is a suspicion of increased concentration of bile pigments due to their high content in the blood. Analysis of urine with qualitative and quantitative reactions allows correct diagnosis.
What are the bile-pigments fall into the urine
In the urine detected 2 types of bile pigments:
- bilirubin;
- the urobilinogen.

Accordingly, such state may be referred to as bilirubinuria and urobilinuria.
What is the bilirubin?
The breakdown of red blood cells causes an increased release of hemoglobin. It is from the liver produces bilirubin.
The substance may be present in the blood in two conditions:
- free bilirubin (an unconjugated) through the renal barrier membrane does not pass, then in the urine it is not normally the case, despite the increased level;
- bound (conjugated) – reacts with glucuronic acid, becomes soluble compound and is excreted in urine, bile, and hence into the intestine.
Transformations take place in the liver cells. Bilirubinuria is due to the increased content of bilirubin in the blood.
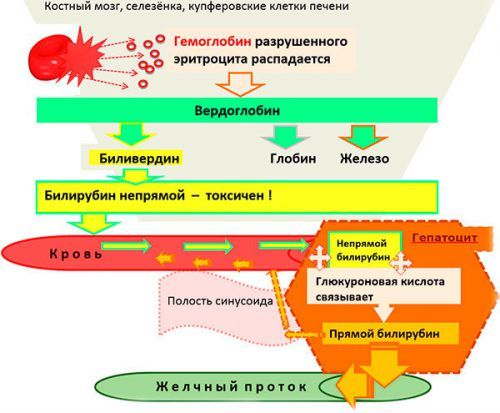
The formation of bilirubin is related to the process of the breakdown of red blood cells
How is urobilinogen formed?
The urobilinogen is a product of further processing of bilirubin in the intestine forces:
- enzymes mucosa;
- bacteria.
More modern evidence urobilinogen bodies, which include derivatives of:
- mesoveliidae,
- i-urobilinogen,
- the urobilinogen IX a,
- d-urobilinogen,
- third urobilinogen.
The last two types and stercobilinogen synthesized in sufficiently small quantities, the values for diagnosis have not.
The formation of urobilinogen from bilirubin occurs in the upper part of the small and beginning of the colon. Some researchers believe that it is synthesized by cellular enzymes dehydrogenase in the gallbladder with the participation of bacteria.
A small part of urobilinogen through the intestinal wall and absorbed into the portal vein and returns to the liver, where it undergoes complete fission. The other is processed in stercobilinogen.
Further, through the hemorrhoidal veins, these substances can get into the bloodstream, the kidneys are allocated in urine. The majority of stercobilinogen in the lower intestine transformirovalsya in sterkobilina and excreted in the feces. It is the main pigment that provides the color of the stool.
Normal level in urine is considered to be no more than 17 µmol/L. If the urine is not long in contact with the air, urobilinogen is subjected to oxidation with oxygen and is transformed into urobilin.
This can be identified by color:
- the urobilinogen is a colorless substance, fresh urine has a straw-yellow hue;
- after some time, due to the formation of urobilin it darkens.
Jaundiced newborns is associated with increased breakdown of red blood cells and transition to your own blood
What “they say” the pigments in the urine?
Given the biochemical and transforming properties of the bile pigments, their definition can be considered a reliable sign of liver damage, inability to cope with the disposal of breakdown products of erythrocytes.
In identifying bilirubinuria assume 2 variants of the pathology:
- malfunction of liver cells (inflammation, loss of quantity due to the replacement of scar tissue, compression of edema, dilated and congested bile ducts), this process is confirmed by checking the blood levels of aspartic and alanine transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, total protein;
- the accumulation in the blood of the high content of hemoglobin from the destroyed red blood cell cells, for clarification will require study of hematopoiesis, the analysis of the bone marrow.
When disturbed, the content of bilirubin in the urine?
An unconjugated bilirubin appears in the blood in diseases of the liver:
- viral hepatitis;
- toxic hepatitis in cases of poisoning by toxic substances (drugs);
- the dire consequences of allergies;
- cirrhosis;
- oxygen hypoxia of liver tissue in heart failure;
- metastatic lesion of cancer cells from other organs.
But in the urine it is not transferred due to the inability of filtration. Only in the case of renal-hepatic insufficiency with destruction of the membrane of the nephron can be detected in urine.
These diseases are accompanied by accumulation of conjugated bilirubin. According to his blood levels judged on the degree of destruction of liver tissue. “Renal threshold” for bilirubin is considered to be a level of 0.01-0.02 g/L.
If liver function is not broken, but difficult the flow of bile into the intestine, the blood receives a significant amount of bilirubin and correspondingly increases its urinary excretion.

This option pathology develops when:
- gallstones;
- compression of bile duct tumor of the pancreatic head or swelling in acute pancreatitis.
Violation of the outflow of bile leads to large numbers of bilirubin in urine
Bilirubinuria is a result of slow flow of bile into interlobular ducts (cholestasis), the bile seeps into the blood vessels. The patient is expressed in the jaundice of the skin and sclera. The ratio in the blood and urine of free – bilirubin determine the type of jaundice (mechanical or parenchymatous, obstructive or hepatic).
An important feature of hemolytic States is the absence of bilirubinuria.
What you judge on the content of urobilinogen?
The diagnosis has the value as high and low levels of pigment in the urine.
The growth of the upper normal level is possible due to:
- Lesions of the liver parenchyma, but preservation of income of the main mass of bile into the intestine. Returned by the portal vein part of the pigment is not metabolized by the cells of the hepatocytes due to their functional disability. So the urobilinogen is excreted in the urine.
- Activation of hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) in the intestine is enhanced synthesis urobilinogen bodies and sterkobilina. While returning part of the split working urobilinogen by the liver to the final product (pettipant), and the sterkobilina takes the hemorrhoidal veins into the General circulation, kidney and excreted in the urine.
- The intestinal diseases which are accompanied by increased reverse suction of stercobilinogen through the affected wall (long-term constipation, enterocolitis, chronic intestinal obstruction, cholangitis).
The mechanism of hemolysis is characteristic of diseases such as:
- malaria;
- anemia of Addison-Barmera;
- lobar pneumonia;
- infectious mononucleosis;
- the disease idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura;
- some types of hemorrhagic diathesis;
- sepsis.
Massive hemolysis is called:
- a complication of massive internal bleeding;
- transfusion of incompatible blood group;
- resorption of large hematomas.
Parenchymal failure, sometimes a secondary disorders of blood circulation after myocardial infarction, development of heart failure. Treatment of liver cirrhosis by applying the shunt to eliminate portal hypertension may be complicated by thrombosis of the renal vein.
The decrease in the concentration of urobilinogen indicates:
- blockage of bile ducts due to stone or crush the tumor;
- the inhibition of the formation of bile until the complete cessation in severe hepatitis, toxic liver damage.
Methods of qualitative and quantitative determination of pigments in the urine
Qualitative tests reveal the substance, but does not indicate its mass. Samples for bilirubin is based on the ability of the oxidation with iodine or nitric acid to form a compound of the green color (biliverdin). In a tube with 5 ml of urine is poured in layers iodine solution (Lugol’s solution, potassium iodide, alcoholate).
For bilirubinuria indicates education on the boundary of the green ring

For the detection of urobilin from the urine and remove the bilirubin, which prevents reaction of calcium chloride and ammonia, is then carried out various tests:
- with copper sulfate – the urine is combined with copper sulphate, then with a solution of chloroform, after shaking appears intense pink color;
- using the spectroscope, which remains the blue-green part of the spectrum.
Depending on the intensity of the color in conclusion I can put the crosses:
- (+) – weak positive reaction;
- (++++) – iscopalian.
Detailed determination of the quantity of bile pigments in the urine is carried out using biochemical reagents in special clinics. The fact that the study of bile pigments is more indicative of the results of the blood tests, not urine.
When to test urine for bile pigments?
Qualitative tests for bile pigments included in the mandatory list of the standard urine test.
Therefore, when the patient reports:
- dyspepsia;
- vague pain in the right upper quadrant;
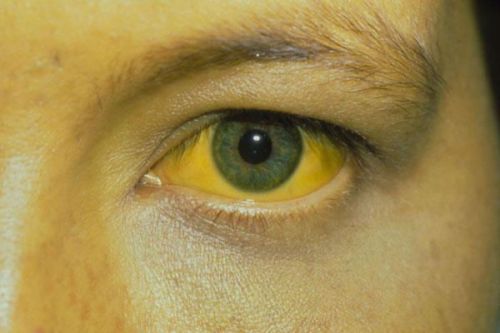
- jaundiced sclera, skin;
- dark urine and pale feces;
- it is necessary to exclude diseases of the liver, the gallbladder.
When choosing a method of treatment of the patient, the doctor must not damage the organs and systems of the person, so the analysis is necessary to exclude the toxic effect of the drug on the liver.
The appearance of jaundice requires examination of bile pigments
Poisoning by various toxic substances are accompanied by a lesion of the kidney and liver. To identify bile pigments roughly one can assume a degree of frustration.
In severe diseases of the myocardium-positive analysis indicates the involvement of liver tissue in the formation of General hypoxia.
Are there features collection of urine for analysis?
When the urine collection should be performed General requirements:
- mandatory hygiene of the external genitalia;
- for the study used only the average portion of morning urine;
- the container with the urine should not be stored for more than two hours, do not leave the transparent jar exposed to the light;
- for the investigation of 50 ml.
Bile pigments in urine are involved in the metabolism of important organs and systems blood. Their determination in the urine plays a significant role in diagnosis.


There are some interesting points in time in this article but I don?t know if I see all of them center to heart. There is some validity but I will take hold opinion until I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we want more! Added to FeedBurner as well
I have wanted to write about something like this on my webpage and you gave me an idea. Cheers.
I understand the reasoning in this article, although I hope to see more writing in this vein from you in the future.
This is quite informative. Would it be ok to volunteer a few questions?
Hello ,what is better ? ASP.Net or Php? thank you
So this post abslutely made me think! Thank You-I hadn’t considered things from your p.o.v otherwise.